Vinyl ether
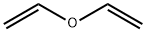
- CAS No.
- 109-93-3
- Chemical Name:
- Vinyl ether
- Synonyms
- Vinydan;Vinethene;Vinyl ether;Vinesthesin;divinyl oxide;Divinyl ether;ethenyloxyethene;(vinyloxy)ethene;vinyloxyethylene;1,1'-oxybisethene
- CBNumber:
- CB4851587
- Molecular Formula:
- C4H6O
- Molecular Weight:
- 70.09
- MOL File:
- 109-93-3.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/3/19 15:37:51
| Melting point | -101.1°C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | bp 28.4° |
| Density | d2020 0.774; d420 0.773 |
| refractive index | nD20 1.3989 |
| Water Solubility | 5.25g/L(37 ºC) |
| Dielectric constant | 3.9(20℃) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ethene, 1,1'-oxybis- (109-93-3) |
Vinyl ether Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
Clear, colorless liquid with a characteristicodor; boils at 28.5°C (83°F); density 0.774[at 20°C (68°F)]; soluble in most organicsolvents, slightly soluble in water [0.53 g/dLat 37°C (98°F)].
Uses
Vinyl ether is used as an anesthetic and inorganic synthesis.
General Description
A clear colorless liquid with a characteristic odor. Flash point below -22°F. Less dense than water. Autoignition temperature 680°F. Slightly soluble in water; miscible with alcohol, acetone, chloroform, and ether. Must be protected from light.Vapors heavier than air. Toxic by inhalation.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Slightly soluble in water. Oxidizes readily in air to form unstable peroxides that may explode spontaneously [Bretherick, 1979 p.151-154, 164].
Reactivity Profile
Ethers, such as DIVINYL ETHER, can act as bases. They form salts with strong acids and addition complexes with Lewis acids. The complex between diethyl ether and boron trifluoride is an example. Ethers may react violently with strong oxidizing agents. In other reactions, which typically involve the breaking of the carbon-oxygen bond, ethers are relatively inert. Vinyl ether is miscible with alcohol, acetone, chloroform and ether and must be protected from light [Hawley].
Health Hazard
Vinyl ether exhibits low inhalation toxicity.Like ethyl ether, inhalation of its vapors pro duces an anesthetic effect. At concentrationsabove 5% (by volume in air), it can causeunconsciousness in humans. Exposure to a5.1% concentration of its vapor (in air) waslethal to mice.
Divinyl ether exhibited mutagenicity inmicrosomal assay and microbial mutationtests. There is no report on its carcinogenicityin animals or humans.
Fire Hazard
Highly flammable; flash point (closed cup) <
-30°C (<-22°F); vapor density 2.4 (air =
1); the vapor is heavier than air and can travel
a considerable distance to a source of igni tion and flash back; autoignition temperature
360°C (680°F); can be ignited by lightning
or static electricity; fire-extinguishing agent:
dry chemical, foam, or CO2; use a water
spray to keep fire-exposed containers cool
and to disperse the vapors
Vinyl ether forms explosive mixtures with
air, with LEL and UEL values of 1.7%
and 27% by volume of air, respectively. It
forms unstable peroxides on long standing or
in the presence of oxygen. These peroxides
can explode spontaneously or when heated.
It decomposes to acetaldehyde (toxic and
highly flammable) when exposed to light.
Safety Profile
Mildly toxic by inhalation. Mutation data reported. Prolonged exposure causes liver injury. A very dangerous fire hazard when exposed to heat or flame; can react vigorously with oxidizing materials. A severe explosion hazard in the form of vapor when exposed to heat or flame. Forms peroxides when exposed to air or oxygen. Hypergolic reaction with concentrated nitric acid. To fight fire, use CO2, dry chemical. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes. Used as an inhalation anesthetic. See also ETHERS.
storage
Vinyl ether is stored in a flammable-liquidsstorage room or cabinet separated from oxidizing and combustible materials. It shouldbe protected from physical damage andfrom static electricity or lightning. It isshipped in amber glass bottles or metaldrums.
Waste Disposal
Vinyl ether is mixed with an excess ofhigher-boiling solvent and burned in a chem ical incinerator equipped with an afterburnerand scrubber. Small amounts, free of peroxides, can be evaporated in a fume hood awayfrom a source of ignition.
Vinyl ether Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of2
chevron_rightPreparation Products
1of2
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jay Chem Marketing | 08048964412 | Mumbai, India | 231 | 58 | Inquiry |
| career henan chemical co | +86-0371-86658258 +8613203830695 | China | 29826 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Shaanxi Didu New Materials Co. Ltd | +86-89586680 +86-13289823923 | China | 9003 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Shaanxi Dideu Medichem Co. Ltd | 029-81124267 15229202216 | China | 10011 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Laohekou Xinjing Technology Co., Ltd. | 0710-8221823 | CHINA | 12 | 58 | Inquiry |
| CHEMICAL LAND21 | 82- 2 -783 - 8063 | South Korea | 6315 | 74 | Inquiry |
| Connect Chemicals GmbH | +49 2102 2077 0 | The Netherlands | 132 | 60 | Inquiry |
| Lanospharma Laboratories Co.,Ltd | 13440048448 | China | 6343 | 56 | Inquiry |
| Hubei xinjing new material co. LTD | 027-83496456 15629169208 | China | 2 | 58 | Inquiry |
109-93-3(Vinyl ether)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




