Benzidine
- CAS No.
- 92-87-5
- Chemical Name:
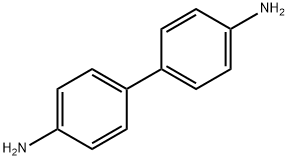
- Benzidine
- Synonyms
- BENZIDINE-D8;Benzidin;Benzidina;benzidine solution;BENZIDINE-RINGS-D8;biphenyl-4,4’-diamine;4,4’-biphenylenediamine;BENZIDINE-D8 (RINGS-D8);ai3-00140;Benzydyna
- CBNumber:
- CB5152058
- Molecular Formula:
- C12H12N2
- Molecular Weight:
- 184.24
- MOL File:
- 92-87-5.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2025/1/27 9:38:02
| Melting point | 127-128 °C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 402°C |
| Density | 1.25 |
| vapor pressure | Based on the specific vapor density value of 6.36 (Sims et al., 1988), the vapor pressure wascalculated to be 0.83 at 20 °C. |
| refractive index | 1.6266 (estimate) |
| Flash point | 11 °C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Soluble in ethanol (U.S. EPA, 1985) and ether (1 g/50 mL) (Windholz et al., 1983) |
| pka | 4.66(at 30℃) |
| color | Grayish-yellow, crystalline powder; white or sltlyreddish crystals, powder |
| Water Solubility | Sparingly soluble. <0.1 g/100 mL at 22 ºC |
| Merck | 13,1077 |
| BRN | 742770 |
| Henry's Law Constant | (x 10-11 atm?m3/mol): 3.88 at 25 °C (estimated, Howard, 1989) |
| Exposure limits |
Because it is a carcinogen and readily
absorbed through skin, no TLV has been
assigned. Exposure should be at an absolute
minimum. Recognized Human Carcinogen (ACGIH); Human Carcinogen (MSHA); Carcinogen (OSHA); Human Sufficient Evidence, Animal Sufficient Evidence (IARC). |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| InChIKey | HFACYLZERDEVSX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 92-87-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 1 (Vol. 29, Sup 7, 99, 100F) 2012 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Benzidine(92-87-5) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Benzidine (92-87-5) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS07,GHS08,GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H302-H350-H410 |
| Precautionary statements | P201-P202-P264-P273-P301+P312-P308+P313 |
| Hazard Codes | T,N,F,Xn |
| Risk Statements | 45-22-50/53-52/53-39/23/24/25-23/24/25-11-36/37/38-20/21/22-51/53-67 |
| Safety Statements | 53-45-60-61-36/37-16-7-36-26 |
| RIDADR | UN 1885 6.1/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | DC9625000 |
| F | 8 |
| HazardClass | 6.1(a) |
| PackingGroup | II |
| HS Code | 29215900 |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 92-87-5(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| Toxicity | Acute oral LD50 for mice 214 mg/kg, rats 309 mg/kg (quoted, RTECS, 1985). |
Benzidine price More Price(12)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | B3503 | Benzidine ≥98.0% (N) | 92-87-5 | 10G | ₹44339.2 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 40005 | Benzidine solution certified reference material, 5000?μg/mL in methanol | 92-87-5 | 1ML | ₹5705.7 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 31614 | Benzidine analytical standard | 92-87-5 | 100MG | ₹5390.85 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 12115 | Benzidine purum p.a., ≥98.0% (N) | 92-87-5 | 10G | ₹37151.4 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 12115 | Benzidine purum p.a., ≥98.0% (N) | 92-87-5 | 100G | ₹154808.33 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Benzidine Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Benzidine is a white, greyish-yellow, or slightly reddish crystalline solid or powder. The major use for benzidine is in the production of dyes, especially azo dyes in the leather, textile, and paper industries and as a synthetic precursor in the preparation and manufacture of dyestuffs. It is also used in the manufacture of rubber, as a reagent, and as a stain in microscopy. It is slightly soluble and slowly changes from a solid to a gas.
Chemical Properties
Benzidine is a white, grayish-yellow, or slightly reddish crystalline solid or powder. The major use for benzidine is in the production of dyes, especially azo dyes in the leather, textile, and paper industries, as a synthetic precursor in the preparation and manufacture of dyestuffs. It is also used in the manufacture of dyes and rubber, as a reagent, and as a stain in microscopy. It is slightly soluble and slowly changes from a solid to a gas.
Physical properties
Grayish-yellow to pale reddish powder or crystals. Darkens on exposure to air or light. Odorless.
Uses
Benzidine was used extensively in the manu facture of dyes. Because of its cancer-causingeffects in humans, its application in dyes hasbeen curtailed. Other uses of this compoundare in chemical analysis: as a reagent for thedetermination of hydrogen peroxide in milkand in the analysis of nicotine. Its hydrochlo ride is used as a reagent to analyze metalsand sulfate.
Preparation
1-Nitrobenzene restore 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine?turn with acid rearrangement.
Production Methods
Benzidine production is now exclusively for captive consumption and must be carried out in closed systems under stringent workplace controls. Benzidine is used in the synthesisofdyesanddyeintermediates,asahardenerforrubber, and as a laboratory reagent. The ?rst successful synthetic direct dye was Congo Red, a diazo derivative prepared from benzidinebyBoettigerin1884.Nearlyalldirectdyesareazo products. Congo Red is used in humans intravenously for the medical diagnosis of amyloidosis. The basis for its use is an unexplained af?nity for amyloid, which rapidly removes the dye from the blood. It is used medically for the management of profuse capillary hemorrhage such as the one occurring in septicemias and in the terminal phases of leukemia.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of biphenyls that is 1,1'-biphenyl in which the hydrogen at the para-position of each phenyl group has been replaced by an amino group.
General Description
A grayish-yellow to grayish-red, crystalline solid. Toxic by ingestion, inhalation, and skin absorption. Combustion produces toxic oxides of nitrogen. Used to make other chemicals and in chemical and biological analysis.
Air & Water Reactions
Darkens on exposure to air and light. Soluble in hot water.
Reactivity Profile
Benzidine forms insoluble salts with sulfuric acid. Can be diazotized, acetylated and alkylated. Is hypergolic with red fuming nitric acid . Neutralizes acids in exothermic reactions to form salts plus water. May be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen may be generated in combination with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides.
Hazard
Highly toxic by ingestion, inhalation, and skin absorption. Confirmed carcinogen.
Health Hazard
Exposure to benzidine causes irritation to the eyes. Laboratory animals exposed to benzidine at as low as 0.01% to 0.08% in food showed adverse health effects, such as organ weight decrease in the liver, kidney, and body weight, and an increase in spleen weight, swelling of the liver, and blood in the urine. Exposure may cause an increase in urination, blood in the urine, and urinary tract tumors. Benzidine is considered acutely toxic to humans by ingestion, with an estimated oral lethal dose of between 50 and 500 mg/kg. The symptoms of acute ingestion exposure include cyanosis, headache, mental confusion, nausea, and vertigo. Dermal exposure may cause skin rashes and irritation. Prolonged exposure to benzidine causes bladder injury in humans
Safety Profile
Confirmed human carcinogen producing bladder tumors. Experimental carcinogenic and tumorigenic data. Poison by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Human mutation data reported. Can cause damage to blood, including hemolysis and bone marrow depression. On ingestion causes nausea and vomiting, which may be followed by liver and kidney damage. Any exposure is considered extremely hazardous. When heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of NOx. See also AROMATIC AMINES.
Carcinogenicity
Benzidine is known to be a human carcinogen based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in humans.
Environmental Fate
Biological. In activated sludge, <0.1% mineralized to carbon dioxide after 5 d (Freitag et al.,
1985). Kincannon and Lin (1985) reported a half-life of 76 d when benzidine in sludge was
applied to a sandy loam soil.
Soil. Benzidine was added to different soils and incubated in the dark at 23 °C under a carbon
dioxide-free atmosphere. After 1 yr, 8.3 to 11.6% of the added benzidine degraded to carbon
dioxide primarily by microbial metabolism and partially by hydrolysis (Graveel et al., 1986).
Tentatively identified biooxidation compounds using GC/MS include hydroxybenzidine, 3-
hydroxybenzidine, 4-amino-4′-nitrobiphenyl, N,N′-dihydroxybenzidine, 3,3′-dihydroxybenzidine
and 4,4′-dinitrobiphenyl (Baird et al., 1977). Under aerobic conditions, the half-life was estimated
to be 2 to 8 d (Lu et al., 1977).
Chemical/Physical. Benzidine is not subject to hydrolysis (Kollig, 1993). Reacts with HCl
forming a salt (C12H12N2?2HCl) that is very soluble in water (61.7 mg/L at 25 °C) (Bowman et al.,
1976).
storage
Benzidine should be kept stored in a cool, well-ventilated area, in closed, sealed containers and out of sunlight and away from heat.
Shipping
UN1885 Benzidine, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1—Poisonous materials. PGII.
Purification Methods
Its solution in *benzene is decolorized by percolating through two 2-cm columns of activated alumina, then concentrated until benzidine crystallises on cooling. Recrystallise alternately from EtOH and *benzene to constant absorption spectrum [Carlin et al. J Am Chem Soc 73 1002 1951]. It has also been crystallised from hot water (charcoal) and from diethyl ether. Dry it under vacuum in an Abderhalden pistol. Store it in the dark in a stoppered container. CARCINOGENIC. [Beilstein 13 IV 364.]
Incompatibilities
Dust may form explosive mixture with air. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. On contact with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides may form flammable gases. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Contact with red fuming nitric acid may cause fire. Oxidizes in air. Neutralizes acids in exothermic reactions to form salts plus water. May be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides.
Waste Disposal
Incineration; oxides of nitrogen are removed from the effluent gas by scrubber, catalytic or thermal device. Package spill residues and sorbent media in 17 hour epoxy-lined drums and move to an EPA-approved disposal site. Treatment may include destruction by potassium permanganate oxidation, hightemperature incineration, or microwave plasma methods. 398 Benzidine Encapsulation by organic polyester resin or silicate fixation. These disposal procedures should be confirmed with responsible environmental engineering and regulatory officials.
Precautions
At high temperatures, benzidine breaks down and releases highly poisonous fumes. During use and handling, workers should wear butyl rubber gloves, goggles, and full body plastic coveralls and ensure that no skin is exposed.
Benzidine Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
1of5
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dhruvtara Chemicals Pvt. Ltd. | 91 40 27154607 | New Delhi, India | 180 | 56 | Inquiry |
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | +91-22-45045900 | Hyderabad, India | 6257 | 58 | Inquiry |
| A.J Chemicals | 91-9810153283 | New Delhi, India | 6100 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Central Drug House(P) Ltd. | 91-11-49404040 | New Delhi, India | 6157 | 58 | Inquiry |
| SynZeal Research Pvt Ltd | +1 226-802-2078 | Gujarat, India | 6514 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Otto Chemie Pvt. Ltd. | +91 9820041841 | Mumbai, India | 5870 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 | China | 21628 | 55 | Inquiry |
| ATK CHEMICAL COMPANY LIMITED | +undefined-21-51877795 | China | 33024 | 60 | Inquiry |
| career henan chemical co | +86-0371-86658258 +8613203830695 | China | 29859 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Chongqing Chemdad Co., Ltd | +86-023-6139-8061 +86-86-13650506873 | China | 39894 | 58 | Inquiry |
Related articles
- Uses of Benzidinen
- Benzidine is a biphenyl amine that exists at room temperature as a crystalline grayish-yellow, white, or reddish-gray power. I....
- Nov 19,2021
92-87-5(Benzidine)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




