Sodium Phosphate Monobasic Monohydrate
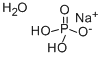
- CAS No.
- 10049-21-5
- Chemical Name:
- Sodium Phosphate Monobasic Monohydrate
- Synonyms
- PHOSPHATE BUFFER;Sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate;POTASSIUM PHOSPHATE BUFFER;Phosphate buffered;RIA BUFFER;PH 7 BUFFER;BUFFER FOR BOD;BUFFER MDB 9.50;Dilution bottle;diltuion bottles
- CBNumber:
- CB5158267
- Molecular Formula:
- H4NaO5P
- Molecular Weight:
- 137.992291
- MOL File:
- 10049-21-5.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2023/9/20 18:48:35
| Melting point | 100°C -H₂O |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 399 °C |
| Density | 2,04 g/cm3 |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: 1 M, clear, colorless |
| form | Solid |
| color | White semi-transparentor |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH Range | 4.1 - 4.5 at 50 g/l at 25 °C |
| PH | 4.1-4.5 (25℃, 50mg/mL in H2O) |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water; insoluble in ethanol, ether and chloroform. |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| λmax |
λ: 260 nm Amax: ≤0.03 λ: 280 nm Amax: ≤0.02 |
| Merck | 14,8660 |
| InChIKey | BBMHARZCALWXSL-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
| LogP | -2.148 (est) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 10049-21-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Monosodium phosphate monohydrate (10049-21-5) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS07 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Warning | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H315-H319-H335 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P261-P280a-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P405-P501a | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xi | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 36/37/38-36 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 26-36/37/39-36-39-24/25 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 1 | |||||||||
| RTECS | WA1900000 | |||||||||
| F | 3 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HS Code | 2835 22 00 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in Rabbit: > 2000 mg/kg LD50 dermal Rabbit > 7940 mg/kg | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Sodium Phosphate Monobasic Monohydrate price More Price(31)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | S9638 | Sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate ACS reagent, ≥98% | 10049-21-5 | 25G | ₹4200.1 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | S9638 | Sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate ACS reagent, ≥98% | 10049-21-5 | 250G | ₹7240 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | S9638 | Sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate ACS reagent, ≥98% | 10049-21-5 | 500G | ₹12670 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | S9638 | Sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate ACS reagent, ≥98% | 10049-21-5 | 1KG | ₹21170 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | S9638 | Sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate ACS reagent, ≥98% | 10049-21-5 | 3KG | ₹61442.7 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Sodium Phosphate Monobasic Monohydrate Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Sodium Phosphate Monobasic Monohydrate is a reagent with very high buffering capacity widely used in molecular biology, biochemistry and chromatography. it can be used as a buffer to adjust pH. In medicine, it is sometimes used as a stimulant laxative before certain operations and medical procedures. Sodium Phosphate Monobasic Monohydrate is often used in foods and in water treatment. It is used as sequestrant, emulsifier, mordant in dyeing, reagent and buffer in foods and analytical chemistry. It is applied as a fireproofing agent and for weighting silk in tanning. It is employed in manufacturing of enamels, ceramics, detergents, boiler compounds, in soldering and brazing instead of borax.
Monobasic sodium phosphate is used in baking powders, acid cleansers, electroplating, as a dry acidulant, and in treating boiler water.
Chemical Properties
Anhydrous salt: white crystalline powder; slightly hygroscopic; forms sodium acid pyrophosphate, Na2H2P2O7 on heating above 225°C and sodium metaphosphate (NaPO3)n at about 350 to 400°C; very soluble in water, aqueous solution acidic.
Monohydrate: white orthorhombic crystals or granules; density 2.04 g/cm3 ; loses its water of crystallization at 100°C; very soluble in water, pH of 1% solution 4.5; insoluble in alcohol.
Dihydrate: large transparent crystals; orthorhombic bisphenoidal structure; density 1.915 g/cm 3 ; decomposes at 60°C; very soluble in water; insoluble in alcohol.
Uses
Sodium Phosphate Monobasic Monohydrate is often used in foods and in water treatment. it can be used as a buffer to adjust pH. In medicine, it is sometimes used as a stimulant laxative before certain operations and medical procedures.
Production Methods
Monobasic sodium phosphate is prepared by adding phosphoric acid to a hot, concentrated solution of disodium phosphate until the liquid ceases to form a precipitate with barium chloride. This solution is then concentrated and the monobasic sodium phosphate is crystallized.
Preparation
Monobasic sodium phosphate can be prepared by partial neutralization of phosphoric acid with sodium hydroxide in equimolar amounts:
H3PO4+ NaOH →NaH2PO4+ H2O
It also can be made by treating disodium hydrogen phosphate with phosphoric acid in proper stoichiometric amount:
Na2HPO4+ H3PO4→2NaH2PO4
General Description
Useful in conjuction with sodium phosphate, dibasic (Cat. No. 567550) in the preparation of biological buffers(absorbance: ≤0.01 at 260 nm and 280 nm).
Pharmaceutical Applications
Monobasic sodium phosphate is used in a wide variety of
pharmaceutical formulations as a buffering agent and as a
sequestering agent. Therapeutically, monobasic sodium phosphate
is used as a mild saline laxative and in the treatment of hypophosphatemia.
Monobasic sodium phosphate is also used in food products, for
example, in baking powders, and as a dry acidulant and
sequestrant.
Safety
Monobasic sodium phosphate is widely used as an excipient in
parenteral, oral, and topical pharmaceutical formulations.
Phosphate occurs extensively in the body and is involved in
many physiological processes since it is the principal anion of
intracellular fluid. Most foods contain adequate amounts of
phosphate, making hypophosphatemia virtually unknown except
in certain disease states or in patients receiving total parenteral
nutrition. Treatment is usually by the oral administration of up to
100 mmol of phosphate daily.
Approximately two-thirds of ingested phosphate is absorbed
from the gastrointestinal tract, virtually all of it being excreted in the
urine, and the remainder is excreted in the feces.
Excessive administration of phosphate, particularly intravenously,
rectally, or in patients with renal failure, can cause
hyperphosphatemia that may lead to hypocalcemia or other severe
electrolyte imbalances. Adverse effects occur less frequently
following oral consumption, although phosphates act as mild saline
laxatives when administered orally or rectally (2–4 g of monobasic
sodium phosphate in an aqueous solution is used as a laxative).
Consequently, gastrointestinal disturbances including diarrhea,
nausea, and vomiting may occur following the use of monobasic
sodium phosphate as an excipient in oral formulations. However,
the level of monobasic sodium phosphate used as an excipient in a pharmaceutical formulation is not usually associated with adverse
effects.
LD50 (rat, IM): 0.25 g/kg(10)
LD50 (rat, oral): 8.29 g/kg
storage
Monobasic sodium phosphate is chemically stable, although it is
slightly deliquescent. On heating at 100°C, the dihydrate loses all of
its water of crystallization. On further heating, it melts with
decomposition at 205℃, forming sodium hydrogen pyrophosphate,
Na2H2P2O7. At 250℃ it leaves a final residue of sodium
metaphosphate, NaPO3.
Aqueous solutions are stable and may be sterilized by autoclaving.
Monobasic sodium phosphate should be stored in an airtight
container in a cool, dry place.
Incompatibilities
Monobasic sodium phosphate is an acid salt and is therefore
generally incompatible with alkaline materials and carbonates;
aqueous solutions of monobasic sodium phosphate are acidic and
will cause carbonates to effervesce.
Monobasic sodium phosphate should not be administered
concomitantly with aluminum, calcium, or magnesium salts since
they bind phosphate and could impair its absorption from the
gastrointestinal tract. Interaction between calcium and phosphate,
leading to the formation of insoluble calcium phosphate precipitates,
is possible in parenteral admixtures.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (injections; infusions; ophthalmic, oral, topical, and vaginal preparations). Included in nonparenteral and parenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Sodium Phosphate Monobasic Monohydrate Preparation Products And Raw materials
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indiana ChemPort | +91-91-2652638667 +91-7574886711 | Gujarat, India | 85 | 58 | Inquiry |
| JSK Chemicals | +919879767970 | Gujarat, India | 3756 | 58 | Inquiry |
| SOLFYN INTERNATIONAL LLP | +91-9321772608 +91-9321772608 | Mumbai, India | 105 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Kronox Lab Sciences Pvt Ltd | +91-9313231074 +91-9313231074 | Gujarat, India | 240 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Annexe Chem Pvt Ltd | +91-9724624061 +91-9898722162 | Gujarat, India | 57 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Nithyasri Chemicals (APURVA CHEMICALS) | +91-2512692130 +91-9323652199 | Maharashtra, India | 75 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Skc Chemie Pvt Ltd | +91-9820057869 +91-7400447421 | Maharashtra, India | 13 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Nandu Chemical Industries | +91-8362330469 +91-8362330469 | Karnataka, India | 84 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Imperial Chem Incorporation (part of Imperial Group) | +91-9723609393 +91-9723609393 | Gujarat, India | 34 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Shalibhadra Group Of Industries | +91-9898031214 +91-9825506646 | Gujarat, India | 22 | 58 | Inquiry |
10049-21-5(Sodium Phosphate Monobasic Monohydrate)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




