Phosphoric acid
- CAS No.
- 7664-38-2
- Chemical Name:
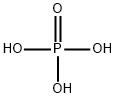
- Phosphoric acid
- Synonyms
- H3PO4;ORTHOPHOSPHORIC ACID;linsuan;Phosphoric;O-PHOSPHORIC ACID;hydrogenphosphate;Acide phosphorique;phosphoricacidsolutions;phosophoric Acid;Phosphoric Acid Powder
- CBNumber:
- CB3854273
- Molecular Formula:
- H3O4P
- Molecular Weight:
- 98
- MOL File:
- 7664-38-2.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/8/2 10:49:27
| Melting point | ~40 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 158 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.685 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 3.4 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 2.2 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index |
n |
| FEMA | 2900 | PHOSPHORIC ACID |
| storage temp. | no restrictions. |
| solubility | H2O: soluble |
| pka | 2.1-7.2-12.3(at 25℃) |
| form | Solid or Viscous Liquid |
| Specific Gravity | 1.7 |
| color | ≤10(APHA) |
| PH | 3.06(1 mM solution);2.26(10 mM solution);1.63(100 mM solution); |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH Range | 1.5 |
| Water Solubility | MISCIBLE |
| λmax |
λ: 260 nm Amax: ≤0.05 λ: 280 nm Amax: ≤0.04 |
| Merck | 14,7344 |
| BRN | 1921286 |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 1 mg/m3 (ACGIH, MSHA, and OSHA); TLV-STEL 3 mg/m3 (ACGIH). |
| Dielectric constant | 61.0 |
| InChIKey | NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | -2.15 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7664-38-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Phosphoric acid(7664-38-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Phosphoric acid (7664-38-2) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS05,GHS07 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H290-H302-H314 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P234-P270-P280-P301+P312-P303+P361+P353-P305+P351+P338 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | C,Xn,T,F | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 34-35-22-39/23/24/25-36/38-23/24/25-11 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 7-16-26-36/37-45-36/37/39-1/2-24/25 | |||||||||
| OEB | C | |||||||||
| OEL | TWA: 1 mg/m3, STEL: 3 mg/m3 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 3453 8/PG 3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | TB6300000 | |||||||||
| F | 3-10 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HS Code | 2809 20 00 | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 8 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| Toxicity | ADI 0 to 70 mg / kg (total phosphate content in terms of phosphorus, FAO / WHO, 2001). GRAS (FDA, § 182.1073, 2000). LD501530mg / kg (rat, oral). In case of daily intake of 2 ~ 4 g, it can cause mild diarrhea. The amount of sour agent used as a cola drink is 0.02% to 0.06%. |
|||||||||
| IDLA | 1,000 mg/m3 | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Phosphoric acid price More Price(60)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | W290017 | Phosphoric acid solution 85?wt. % in H2O, FCC, FG | 7664-38-2 | 1SAMPLE-K | ₹5141.88 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | W290017 | Phosphoric acid solution 85?wt. % in H2O, FCC, FG | 7664-38-2 | 1KG | ₹6971.3 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | P5811 | Phosphoric acid BioReagent, suitable for insect cell culture, 85% | 7664-38-2 | 100G | ₹5661.48 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | P5811 | Phosphoric acid BioReagent, suitable for insect cell culture, 85% | 7664-38-2 | 500G | ₹7057.9 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 79622 | Phosphoric acid puriss. p.a., crystallized, ≥99.0% (T) | 7664-38-2 | 100G | ₹3334.1 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Phosphoric acid Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Phosphoric acid was prepared first by Robert Boyle in 1694 by dissolving phosphorus pentoxide in water. Phosphoric acid is probably the most important compound of phosphorus. It is the second largest inorganic chemical by volume, after sulfuric acid, marketed in the United States.
The single most important application of Phosphoric acid is manufacturing phosphate salts for fertilizers. Such fertilizer phosphates include sodium, calcium, ammonium, and potassium phosphates. Other applications are in metal pickling and surface treatment for removal of metal oxides from metal surfaces; electropolishing of aluminum; as a bonding agent in various refractory products such as alumina and magnesia; as a catalyst in making nylon and gasoline; as a dehydrating agent; in fireproofing wood and fabrics; in lithographic engraving; in textile dyeing; in dental cement; in coagulating rubber latex; in purifying hydrogen peroxide; and as a laboratory reagent. Dilute solutions of phosphoric acid are used as additives to carbonated beverages for a pleasing sour taste. Also, dilute acid is used in refining sugar; as a nutrient; and as a buffering agent in preparing jam, jelly, and antibiotics. The commercial phosphoric acid is 85% (w/w) in strength.
Chemical Properties
Phosphoric acid is a colorless, odorless, crystalline solid or a thick syrupy liquid. Physical state is strength and temperature dependent.
Concentrated phosphoric acid occurs as a colorless, odorless, syrupy liquid. It has a pleasing acid taste when suitably diluted.
Pure phosphoric acid, also called orthophosphoric acid, is a clear, colorless, mineral acid with moderate strength. It is normally marketed as an aqueous solution of 75–85% in which it exists as a clear, viscous liquid.
Food-grade phosphoric acid is used to acidify foods and beverages. It provides a tangy or sour taste and, being a mass-produced chemical, is available cheaply and in large quantities. Phosphoric acid, used in many soft drinks, has been linked to lower bone density in epidemiological studies. In brief, phosphoric acid is a strong acid and common industrial chemical used in the manufacture of a wide number of products, notably porcelain and metal cleaners, detergents, and fertilisers. It is also used as a food additive and is a major constituent of many soft drinks. Low phosphate concentrations are found in drinking water to which it is added in some areas in order to reduce lead solubility.
Physical properties
Chemists refer to orthophosphoric acid as phosphoric acid, which is the IUPAC name for this compound. The prefix “ortho” is used to distinguish the acid from other phosphoric acids, which are generally called polyphosphoric acids. Orthophosphoric acid is a nontoxic, rather weak triprotic acid. When pure, it is a solid at STP. Orthophosphoric acid is a very polar molecule which makes it highly soluble in water. The valence state of phosphorous in orthophosphoric acid and other phosphoric acids is +5. Triprotic means that the orthophosphoric acid molecule can dissociate up to three times, producing a hydrogen cation, H+, each time.
Occurrence
Phosphoric acid is a natural constituent of many fruits and their juices.
History
Phosphoric acid was produced but not identified by alchemists in ancient times. It derives its name from the element phosphorus, which was discovered in 1669 by Henning Brand (1630 1710).Scheele subsequently isolated phosphorus from bone ash and produced phosphoric acid by reacting phosphorus and nitric acid. Scheele's method replaced bone as the main source of phosphorus rather than urine.
John Bennett Lawes (1814 1900) patented a process in 1841 of making superphosphate from bones and later extended his process to phosphates obtained from rock. Superphosphates are made by treating Ca3(PO4)2 with sulfuric acid to make more soluble calcium hydrogen phosphates: Ca3(PO4)2 + 2H2SO4 Ca(H2PO4)2 + 2CaSO4. In this reaction Ca(H2PO4)2 is monobasic calcium phosphate, which is also called superphosphate. Calcium hydrogen phosphates (superphosphates) are more water soluble and therefore more readily available to plants.
Uses
Phosphoric Acid is an acidulant that is an inorganic acid produced by burning phosphorus in an excess of air, producing phosphorus pentoxide which is dissolved in water to form orthophosphoric acid of varying concentrations. it is a strong acid which is soluble in water. the acid salts are termed phosphates. it is used as a flavoring acid in cola and root beer beverages to provide desirable acidity and sourness. it is used as a synergistic antioxidant in vegetable shorten- ings. in yeast manufacture, it is used to maintain the acidic ph and provide a source for phosphorus. it also functions as an acidulant in cheese. it is also termed orthophosphoric acid.
Production Methods
The majority of phosphoric acid is made by digesting phosphate rock (essentially tricalcium phosphate) with sulfuric acid; the phosphoric acid is then separated by slurry filtration. Purification is achieved via chemical precipitation, solvent extraction, crystallization, or ion exchange.
Definition
ChEBI: Phosphoric acid is a phosphorus oxoacid that consists of one oxo and three hydroxy groups joined covalently to a central phosphorus atom. It has a role as a solvent, a human metabolite, an algal metabolite and a fertilizer. It is a conjugate acid of a dihydrogenphosphate and a phosphate ion.
Preparation
Low-purity technical grade phosphoric acid for use in fertilizers is produced from phosphate rocks by digestion with concentrated sulfuric acid. The apatite types, primarily consisting of calcium phosphate phosphate rocks, are used: Ca3(PO4)2 + 3H2SO4 + 6H2O → 2H3PO4 + 3(CaSO4•2H2O)
The insoluble calcium sulfate slurry is filtered out. Acid from this wet process is impure but can be purified by various methods. Purification steps involve precipitation, solvent extraction, crystallization, and ion exchange techniques.
Phosphoric acid also can be made by many different methods. Dissolution of phosphorus pentoxide in water and boiling yields phosphoric acid. Pure phosphoric acid can be obtained by burning phosphorus in a mixture of air and steam:
P4 (l) + 5O2 (g) →P4O10 (s)
P4O10 (s) + H2O (g) → 4H3PO4 (l)
The acid also may be prepared by heating violet phosphorus with 33% nitric acid:
4P + 10HNO3 + H2O → 4H3PO4 + 5NO ↑ + 5NO2 ↑
or by heating red phosphorus with nitric acid (1:1). The overall equation is:
P + 3HNO3 → H3PO4 + NO + 2NO2
General Description
A clear colorless liquid or transparent crystalline solid. The pure solid melts at 42.35°C and has a density of 1.834 g / cm3. Liquid is usually an 85% aqueous solution. Shipped as both a solid and liquid. Corrosive to metals and tissue. Used in making fertilizers and detergents and in food processing.
Air & Water Reactions
Soluble in water with small release of heat.
Reactivity Profile
Phosphorous acid reacts exothermically with bases. May react with active metals, including such structural metals as aluminum and iron, to release hydrogen, a flammable gas. Can initiate the polymerization of certain classes of organic compounds. Reacts with cyanide compounds to release gaseous hydrogen cyanide. May generate flammable and/or toxic gases in contact with dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, nitriles, sulfides, and strong reducing agents. Forms explosive mixture with nitromethane. Reacts violently with sodium tetrahydroborate. In the presence of chlorides can corrode stainless steel to form explosive hydrogen gas. Emits toxic and irritating fumes of oxides of phosphorus when heated to decomposition [Lewis, 3rd ed., 1993, p. 1029].
Hazard
Phosphoric acid is water soluble and absorbs oxygen readily, and the specific gravity is 1.89, which is heavier than water. It is toxic by ingestion and inhalation and an irritant to the skin and eyes, with a TLV of 1 mg/m3 of air. The four-digit UN identification number is 1805. The NFPA 704 designation is health 3, flammability 0, and reactivity 0. The primary use of phosphoric acid is in chemical analysis and as a reducing agent.
Health Hazard
Phosphoric acid is less corrosive and hazardous than is concentrated sulfuric or nitricacid. Its concentrated solutions are irritantsto the skin and mucous membranes. Thevapors (P2O5 fumes) can cause irritation tothe throat and coughing but could be tolerated at <10 mg/m3.The acute oral toxicity in rats is reported tobe low, the LD50 value being 1530 mg/kg(NIOSH 1986).
Fire Hazard
Non-combustible, substance itself does not burn but may decompose upon heating to produce corrosive and/or toxic fumes. Some are oxidizers and may ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Phosphoric acid is widely used as an acidifying agent in a variety of
pharmaceutical formulations. It is used in pharmaceutical products
as part of a buffer system when combined with a phosphate salt
such as sodium phosphate, monobasic or dibasic. It is also widely
used in food preparations as an acidulant, flavor, and synergistic
antioxidant (0.001–0.005%) and sequestrant.
Therapeutically, dilute phosphoric acid has been used welldiluted
in preparations used in the treatment of nausea and
vomiting. Phosphoric acid 35% gel has also been used to etch
tooth enamel and to enhance delivery of drugs through the nail.
)
Nanosized hydroxyapatite powder was made by combining
phosphoric acid with egg shells.
Agricultural Uses
Phosphoric acid (H3PO4), also known as orthophosphoric
acid, is the most significant source of
phosphate fertilizers. Phosphoric acid based fertilizers
mainly include ammonium phosphate, diammonium
phosphate and monoammonium phosphate.
Phosphoric acid is deliquescent and commercially the
most important derivative of phosphorus, accounting for
over 90% of the phosphate rock mined. The white
rhombic solid is highly soluble in water and ethanol, and
the concentrated aqueous solution is generally available
for use.
Phosphoric acid is used in several industries other
than the fertilizer industry. Most elemental phosphorus is
converted into phosphoric acid for non-fertilizer use.
There are two basic processes for the production of
phosphoric acid.
Metaphosphoric acid is obtained by heating
phosphoric acid until dense white fumes begin to appear.
The product is highly deliquescent and glassy in
appearance. Its salts are known as metaphosphates.
Orthophosphoric acid is the most common and is used
as an important phosphate ingredient in commercial
fertilizers.
Industrial uses
As a cleanser for metals, phosphoric acid produces a light etch on steel, aluminum, or zinc, which aids paint adhesion. Deoxidine is a phosphoric acid cleanser for metals. Nielite D is phosphoric acid with a rust inhibitor, used as a nonfuming pickling acid for steel. Albrite is available in 75, 80, and 85% concentrations in food and electronic grades, both high-purity specifications. DAB and Phosbrite are called Bright Dip grades, for cleaning applications. Phosphoric anhydride, or phosphorus pentoxide, P2O5, is a white, water-soluble powder used as a dehydrating agent and also as an opalizer for glass. It is also used as a catalyst in asphalt coatings to prevent softening at elevated temperatures and brittleness at low temperatures.
Safety Profile
Human poison by ingestion. Moderately toxic by skin contact. A corrosive irritant to eyes, skin, and mucous membranes, and a systemic irritant by inhalation. A common air contaminant. A strong acid. Mixtures with nitromethane are explosive. Reacts with chlorides + stainless steel to form explosive hydrogen gas. Potentially violent reaction with solum tetrahydroborate. Dangerous; when heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of POx
Safety
In the concentrated form, phosphoric acid is an extremely corrosive
and harmful acid. However, when used in pharmaceutical formulations it is usually very diluted and is generally regarded as
an essentially nontoxic and nonirritant material.
The lowest lethal oral dose of concentrated phosphoric acid in
humans is reported to be 1286 mL/kg.
(rabbit, skin): 2.74 g/kg
(rat, oral): 1.53 g/kg
Potential Exposure
Phosphoric acid is used in the manufacture of fertilizers, phosphate salts; polyphosphates, detergents, activated carbon; animal feed; ceramics, dental cement; pharmaceuticals, soft drinks; gelatin, rust inhibitors; wax, and rubber latex. Exposure may also occur during electropolishing, engraving, photoengraving, lithographing, metal cleaning; sugar refining; and water-treating.
Carcinogenicity
Phosphoric acid was not mutagenic in bacterial assays.
storage
When stored at a low temperature, phosphoric acid may solidify, forming a mass of colorless crystals, comprising the hemihydrate, which melts at 28°C. Phosphoric acid should be stored in an airtight container in a cool, dry place. Stainless steel containers may be used.
Shipping
UN1805 Phosphoric acid solution, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material. UN3543 Phosphoric acid solid, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material.
Incompatibilities
Phosphoric acid is a strong acid and reacts with alkaline substances. Mixtures with nitromethane are explosive.
Waste Disposal
Add slowly to solution of soda ash and slaked lime with stirring, then flush to sewer with large volumes of water.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Accepted as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (infusions, injections, oral solutions, topical creams, lotions, ointments and solutions, and vaginal preparations). Included in nonparenteral and parenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Phosphoric acid Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of3
chevron_rightPreparation Products
1of8
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Otto Chemie Pvt. Ltd. | +91 9820041841 | Mumbai, India | 32 | 58 | Inquiry |
| ANJI BIOSCIENCES | +91-9000100077 +91-9000100077 | Hyderabad, India | 430 | 58 | Inquiry |
| SUKHA CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES | +91-9638875444 +91-9638875444 | Gujarat, India | 26 | 58 | Inquiry |
| SHIVAM INDUSTRIES | +91-9820823043 +91-9820823043 | Mumbai, India | 30 | 58 | Inquiry |
| oswal chemicals | +91-9173644055 +91-9173644055 | Gujarat, India | 66 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Nyne Organics Pvt Ltd | +91-9920180386 +91-9920180386 | Mumbai, India | 53 | 58 | Inquiry |
| UNILOSA INTERNATINAL PRIVATE LIMITED | +91-9999069917 +91-9999069917 | New Delhi, India | 152 | 58 | Inquiry |
| VITRAG CHEMICALS PVT LTD | +91-7490053194 +91-7490053194 | Gujarat, India | 47 | 58 | Inquiry |
| JSK Chemicals | +919879767970 | Gujarat, India | 3756 | 58 | Inquiry |
| PUNJAB CHEMICALS AND CROP PROTECTION LTD | +91-7508355205 +91-7508355205 | Punjab, India | 69 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Otto Chemie Pvt. Ltd. | 58 |
| ANJI BIOSCIENCES | 58 |
| SUKHA CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES | 58 |
| SHIVAM INDUSTRIES | 58 |
| oswal chemicals | 58 |
| Nyne Organics Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| UNILOSA INTERNATINAL PRIVATE LIMITED | 58 |
| VITRAG CHEMICALS PVT LTD | 58 |
| JSK Chemicals | 58 |
| PUNJAB CHEMICALS AND CROP PROTECTION LTD | 58 |
Related articles
- What is the pH value of phosphoric acid?
- Phosphoric acid, also known as orthophosphoric acid or phosphoric(V) acid, is a mineral (inorganic) acid having the chemical f....
- Mar 15,2024
- Health hazard of phosphoric acid
- Pure phosphoric acid is normally in the form of a white crystalline solid.It has a melting point of 42.4°C.
- Jul 25,2022
- Introduction of Phosphoric acid
- Phosphoric acid, also known as orthophosphoric acid (molecular structure formula H3PO4), is a colorless, transparent, viscous ....
- Nov 22,2021
Related Qustion
- Q:Why is Phosphoric acid used in food?
- A:?Phosphoric acid is an inorganic compound acid derived from the mineral phosphorus. It is a crystalline solid, but in its less....
- Aug 2,2024
7664-38-2(Phosphoric acid)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




