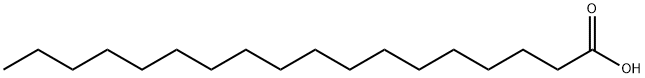
Stearic acid
- CAS No.
- 57-11-4
- Chemical Name:
- Stearic acid
- Synonyms
- OCTADECANE;Octadecanoic acid;C18;OCTADECANEDIOIC ACID;C18:0;Stearic;Steric acid;TRIPLE PRESSED STEARIC ACID;1800;Stearil Acid
- CBNumber:
- CB4853859
- Molecular Formula:
- C18H36O2
- Molecular Weight:
- 284.48
- MOL File:
- 57-11-4.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/8/15 16:24:08
| Melting point | 67-72 °C (lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 361 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 0.845 g/cm3 |
| vapor pressure | 1 mm Hg ( 173.7 °C) |
| FEMA | 3035 | STEARIC ACID |
| refractive index | 1.4299 |
| Flash point | >230 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, soluble in ethanol (96 per cent) and in light petroleum (bp: 50-70 °C). |
| form | powder |
| pka | pKa 5.75±0.00(H2O t = 35) (Uncertain) |
| Specific Gravity | 0.84 (80℃) |
| color | White |
| Odor | odorless mild fatty |
| Odor Type | odorless |
| Water Solubility | 0.1-1 g/100 mL at 23 ºC |
| JECFA Number | 116 |
| Merck | 14,8804 |
| BRN | 608585 |
| Dielectric constant | 2.3(22℃) |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 10 mg/m3; TWA 3 mg/m3 |
| InChIKey | QIQXTHQIDYTFRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | 8.22 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 57-11-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Octadecanoic acid(57-11-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Stearic acid (57-11-4) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS07 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Warning | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H315-H319-H335 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P261-P280a-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P405-P501a | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xi,F | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 38-36/37/38-11 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 37/39-26-16 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | WI2800000 | |||||||||
| Autoignition Temperature | 395 °C | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HS Code | 38231100 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 i.v. in mice, rats: 23±0.7, 21.5±1.8 mg/kg, L. Or, A. Wretlind, Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 18, 141 (1961) | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Stearic acid price More Price(35)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | W303518 | Stearic acid ≥95%, FCC, FG | 57-11-4 | 1SAMPLE-K | ₹5141.88 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | W303518 | Stearic acid ≥95%, FCC, FG | 57-11-4 | 1KG | ₹7588.33 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | W303518 | Stearic acid ≥95%, FCC, FG | 57-11-4 | 8KG | ₹19961.3 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | W303518 | Stearic acid ≥95%, FCC, FG | 57-11-4 | 25KG | ₹35614.25 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | S4751 | Stearic acid Grade I, ≥98.5% (capillary GC) | 57-11-4 | 1G | ₹3983.6 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Stearic acid Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Stearic acid (STAIR-ik or STEER-ik) is the saturated fatty acid with an 18 carbon chain and has the IUPAC name octadecanoic acid. It is a waxy solid, and its chemical formula is CH3(CH2)16CO2H. Its name comes from the Greek word στ?αρ "stéar", which means tallow. The salts and esters of stearic acid are called stearates. Stearic acid is one of the most common saturated fatty acids found in nature following palmitic acid.
Chemical Properties
Stearic acid, CH3(CH2)16COOH, is a white or colorless, waxlike solid with a melting point of 70°C (158 OF), and a boiling point of 232°C (450 OF) at 2 kPa. It is soluble in alcohol, ether, and chloroform,and is insolublein water. Stearic acid, nature's most common fatty acid, is derived from natural animal and vegetable fats. Also known as n-octadecanoic acid, stearic acid is used in the preparation of metallic stearates, as a lubricant, and in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, candles, and food packaging.
Occurrence
Stearic acid is naturally present in the glycerides of animal fats and most vegetable oils. Reported found in fresh apple, banana, Vitis vinifera L., melon, tomato, ginger, blue cheeses, cheddar cheese, Swiss cheese, feta cheese, buttermilk, raw fatty fish, raw lean fish, raw shrimp, grapefruit juice, guava, papaya, cucumber, saffron, pork and lamb liver, pork fat, hop oil, beer, cognac, rum, whiskies, sherry, tea, peanut oil, soybean, roast coconut, coconut milk, avocado, passion fruit, rose apple, mushroom, starfruit, fenugreek, mango, cardamom, cooked rice, prickly pear, dill seed, buckwheat, malt, wort, cassava, loquat, shrimp, crab, cape gooseberry and Chinese quince.
Uses
stearic acid is an emulsifier and thickening agent found in many vegetable fats. Stearic acid is the main ingredient used in making bar soaps and lubricants. It occurs naturally in butter acids, tallow, cascarilla bark, and in other animal fats and oils. Stearic acid may cause allergic reactions in people with sensitive skin and is considered somewhat comedogenic.
Preparation
Commercially it is produced by the hydrogenation of the unsaturated 18-carbon fatty acids of soybean, cottonseed or other vegetable oils. When obtained from animal fats by hydrolysis and fractional crystallization, commercial stearic acid is a mixture of solid organic acids, chiefly palmitic and stearic acids. Commercial products containing about 90% stearic acid are produced by hydrolysis and crystallization of a completely hydrogenated vegetable oil or by fractional distillation of fatty acid mixtures obtained from tallow
Production Methods
Stearic acid is manufactured by hydrolysis of fat by continuous
exposure to a countercurrent stream of high-temperature water and
fat in a high-pressure chamber. The resultant mixture is purified by
vacuum steam distillation and the distillates are then separated
using selective solvents.
Stearic acid may also be manufactured by the hydrogenation of
cottonseed and other vegetable oils; by the hydrogenation and
subsequent saponification of olein followed by recrystallization
from alcohol; and from edible fats and oils by boiling with sodium
hydroxide, separating any glycerin, and decomposing the resulting
soap with sulfuric or hydrochloric acid. The stearic acid is then
subsequently separated from any oleic acid by cold expression.
Stearic acid is derived from edible fat sources unless it is intended
for external use, in which case nonedible fat sources may be used.
The USP32–NF27 states that stearic acid labeled solely for external
use is exempt from the requirement that it be prepared from edible
sources. Stearic acid may contain a suitable antioxidant such as
0.005% w/w butylated hydroxytoluene.
Definition
ChEBI: A C18 straight-chain saturated fatty acid component of many animal and vegetable lipids. As well as in the diet, it is used in hardening soaps, softening plastics and in making cosmetics, candles and plastics.
General Description
White solid with a mild odor. Floats on water.
Air & Water Reactions
Slightly soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Stearic acid is incompatible with strong oxidizers and strong bases. Stearic acid is also incompatible with reducing agents.
Health Hazard
Compound is generally considered nontoxic. Inhalation of dust irritates nose and throat. Dust causes mild irritation of eyes.
Fire Hazard
Stearic acid is combustible. Stearic acid can heat spontaneously.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Stearic acid is widely used in oral and topical pharmaceutical
formulations. It is mainly used in oral formulations as a tablet and
capsule lubricant, although it may also be used as a
binder or in combination with shellac as a tablet coating. It has
also been suggested that stearic acid may be used in enteric tablet
coatings and as a sustained-release drug carrier.
In topical formulations, stearic acid is used as an emulsifying and
solubilizing agent. When partially neutralized with alkalis or
triethanolamine, stearic acid is used in the preparation of
creams. The partially neutralized stearic acid forms a creamy
base when mixed with 5–15 times its own weight of aqueous liquid,
the appearance and plasticity of the cream being determined by the
proportion of alkali used.
Stearic acid is used as the hardening agent in glycerin
suppositories.
Stearic acid is also widely used in cosmetics and food products.
Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous route. A human sktn irritant. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data by implantation route. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame. Heats spontaneously. To fight fire, use CO2, dry chemical. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Safety
Stearic acid is widely used in oral and topical pharmaceutical
formulations; it is also used in cosmetics and food products. Stearic
acid is generally regarded as a nontoxic and nonirritant material.
However, consumption of excessive amounts may be harmful.
LD50 (mouse, IV): 23 mg/kg
LD50 (rat, IV): 21.5 mg/kg
Carcinogenicity
Stearic acid was administered subcutaneously to several groups of Swiss–Webster mice at doses of 0.05 or 0.5mg once weekly for 25 weeks (total dose of 1.3–130 mg), 1.0 mg thrice a week for a total of 10 injections or 1.0 mg twice weekly for a total of 82 injections. No neoplasms were reported in these studies . In 3 groups of 10–15 BALB/c mice administered 0.05 mg or 0.5 mg stearic acid (twice weekly for 52 or 57 weeks), one pulmonary neoplasm was detected in each group after 19–21 months.Afewsubcutaneous sarcomas and one adrenal carcinoma were also reported.No injection site sarcomas or other carcinogenic effects were reported by the same authors in a later study of mice injected with 0.05–0.5 mg weekly for 26 weeks. Rats given subcutaneous injections of 0.05 or 0.5 mg stearic acid weekly for 26 weeks did not develop sarcomas at the site of injection. When rat fibroblast cells were transfected with an activated human c-H-ras oncogene and the cells subsequently grown in a medium supplemented with stearic acid (20–80 mM), there was a marked increase in the number of transformed foci. Stearic acid inhibited the colony-forming ability of four out of five rat and two human tumor continuous cell lines in vitro. Using rats pretreated with nitrosomethyl urea as a model for mammary carcinoma, Habib et al. demonstrated that subcutaneous injection of stearic acid at weekly intervals prevented tumor development. Increasing levels of stearate in the diet resulted in decreased mammary tumor incidence and increased time to tumor in mice.
Metabolism
An isotope labeling study in humans concluded that the fraction of dietary stearic acid oxidatively desaturated to oleic acid was 2.4 times higher than the fraction of palmitic acid analogously converted to palmitoleic acid. Also, stearic acid was less likely to be incorporated into cholesterol esters. In epidemiologic and clinical studies stearic acid was associated with lowered LDL cholesterol in comparison with other saturated fatty acids. These findings may indicate that stearic acid is healthier than other saturated fatty acids.
storage
Stearic acid is a stable material; an antioxidant may also be added to it. The bulk material should be stored in a wellclosed container in a cool, dry place.
Purification Methods
Crystallise stearic acid from acetone, acetonitrile, EtOH (5 times), aqueous MeOH, ethyl methyl ketone or pet ether (b 60-90o), or by fractional precipitation by dissolving in hot 95% EtOH and pouring into distilled water, with stirring. The precipitate, after washing with distilled water, is dried under vacuum over P2O5. It has also been purified by zone melting and partial freezing. [Tamai et al. J Phys Chem 91 541 1987, Beilstein 2 IV 1206.]
Incompatibilities
Stearic acid is incompatible with most metal hydroxides and may be
incompatible with bases, reducing agents, and oxidizing agents.
Ointment bases made with stearic acid may show evidence of
drying out or lumpiness due to such a reaction when compounded
with zinc or calcium salts.
A number of differential scanning calorimetry studies have
investigated the compatibility of stearic acid with drugs. Although
such laboratory studies have suggested incompatibilities, e.g. with
naproxen, they may not necessarily be applicable to formulated
products.
Stearic acid has been reported to cause pitting in the film coating
of tablets applied using an aqueous film-coating technique; the
pitting was found to be a function of the melting point of the stearic
acid.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Accepted as a food additive in Europe (fatty acids). Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (sublingual tablets; oral capsules, solutions, suspensions, and tablets; topical and vaginal preparations). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Stearic acid Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of4
chevron_rightPreparation Products
1of8
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ULTIMA CHEMICALS | +91 7208029458 | Mumbai, India | 95 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Gangotri Inorganic Private Limited | +91-9725738888 +91-9898237777 | Gujarat, India | 33 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Maher Chemical Industries | +91-9879575478 +91-9879575478 | Gujarat, India | 5 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Nyne Organics Pvt Ltd | +91-9920180386 +91-9920180386 | Mumbai, India | 53 | 58 | Inquiry |
| JSK Chemicals | +919879767970 | Gujarat, India | 3756 | 58 | Inquiry |
| MLA Industries | +919336432992 | Uttar Pradesh, India | 20 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Venus Ethoxyethers Pvt Ltd | +91-8322383333 +91-8669968881 | GOA, India | 19 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Sree Rayalaseema HI Strength Hypo Ltd | +91-9848867692 +91-9848867692 | Andhra Pradesh, India | 19 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Unisynth Chemicals | +91-9820430673 +91-9820430673 | Maharashtra, India | 32 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Vats International | +91-9810131850 +91-9810984000 | New Delhi, India | 19 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| ULTIMA CHEMICALS | 58 |
| Gangotri Inorganic Private Limited | 58 |
| Maher Chemical Industries | 58 |
| Nyne Organics Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| JSK Chemicals | 58 |
| MLA Industries | 58 |
| Venus Ethoxyethers Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| Sree Rayalaseema HI Strength Hypo Ltd | 58 |
| Unisynth Chemicals | 58 |
| Vats International | 58 |
Related articles
- Exploring the mysteries of stearic acid: An amazing journey from chemical molecules to widespread applications
- In this paper, the knowledge of stearic acid is popularized, and its chemical structure, production, physical properties and a....
- Jul 3,2024





