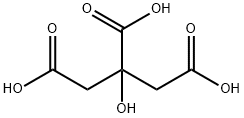
Citric acid
- CAS No.
- 77-92-9
- Chemical Name:
- Citric acid
- Synonyms
- Citric acid anhydrous;Anhydrous citric acid;BETZ 6251;acid citric;citric acid solution;Citric acid Anhydrate;Citro;CheMfill;Citric acid anhydrou;BUFFER CONCENTRATE, PH 4.00
- CBNumber:
- CB9854361
- Molecular Formula:
- C6H8O7
- Molecular Weight:
- 192.12
- MOL File:
- 77-92-9.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/7/14 20:44:35
| Melting point | 153-159 °C (lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 248.08°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.67 g/cm3 at 20 °C |
| vapor density | 7.26 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | <0.1 hPa (20 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.493~1.509 |
| FEMA | 2306 | CITRIC ACID |
| Flash point | 100 °C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Citric acid also dissolves in absolute (anhydrous) ethanol (76 parts of citric acid per 100 parts of ethanol) at 15 °C. |
| form | grit |
| pka | 3.14(at 20℃) |
| color | White |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH | 3.24(1 mM solution);2.62(10 mM solution);2.08(100 mM solution); |
| Odor Type | odorless |
| explosive limit | 8%, 65°F |
| Water Solubility | soluble in Water (1174g/L at 10°C, 1809g/L at 30°C, 3825g/L at 80°C). |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| λmax |
λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.20 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.10 |
| Merck | 14,2326 |
| JECFA Number | 218 |
| BRN | 782061 |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with bases, strong oxidizing agents, reducing agents, metal nitrates. |
| InChIKey | KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | -1.64 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 77-92-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 1,2,3-Propanetricarboxylic acid, 2-hydroxy-(77-92-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Citric acid (77-92-9) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS07 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Warning | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H319-H335 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P261-P264-P271-P280-P304+P340+P312-P305+P351+P338 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xi,C,T | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 41-36/37/38-36/38-37/38-34-36-35-61-60 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 26-39-37/39-24/25-36/37/39-45-36-53 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 1789 8/PG 3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 1 | |||||||||
| RTECS | GE7350000 | |||||||||
| F | 9 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HS Code | 2918 14 00 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 in mice, rats (mmol/kg): 5.0, 4.6 i.p. (Gruber, Halbeisen) | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Citric acid price More Price(57)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | W230618 | Citric acid ≥99.5%, FCC, FG | 77-92-9 | 1SAMPLE-K | ₹5141.88 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | W230618 | Citric acid ≥99.5%, FCC, FG | 77-92-9 | 1KG | ₹6624.9 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | W230618 | Citric acid ≥99.5%, FCC, FG | 77-92-9 | 10KG | ₹21671.65 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | W230618 | Citric acid ≥99.5%, FCC, FG | 77-92-9 | 25KG | ₹29195.03 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | PHR1071 | Citric acid, Anhydrous Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material | 77-92-9 | 1G | ₹8530.1 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Citric acid Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Citric acid is a white, crystalline, weak organic acid present in most plants and many animals as an intermediate in cellular respiration. Citric acid contains three carboxyl groups making it a carboxylic, more specifically a tricarboxylic, acid.the name citrus originates from the Greek kedromelon meaning apple of melon for the fruit citron. Greek works mention kitron, kitrion, or kitreos for citron fruit, which is an oblong fruit several inches long from the scrublike tree Citrus medica. Lemons and limes have high citric acid content, which may account for up to 8% of the fruit's dry weight.
Citric acid is a weak acid and loses hydrogen ions from its three carboxyl groups (COOH) in solution.the loss of a hydrogen ion from each group in the molecule results in the citrate ion,C3H5O(COO)33. A citric acid molecule also forms intermediate ions when one or two hydrogen atoms in the carboxyl groups ionize.the citrate ion combines with metals to form salts, the most common of which is calcium citrate. Citric acid forms esters to produce various citrates, for example trimethyl citrate and triethyl citrate.
Chemical Properties
Citric acid is soluble 66 % in water, 33% in alcohol,
3% in ether. Soluble about 20% in Propylene
glycol. Virtually odorless. The aqueous solution
has a clean acid taste, pleasant in the concentration of 0.02 to 0.08%. Citric acid is a weak organic acid with the formula C6H8O7. It is a natural preservative / conservative and is also used to add an acidic, or sour, taste to foods and soft drinks. In biochemistry, the conjugate base of citric acid, citrate, is important as an intermediate in the citric acid cycle, which occurs in the metabolism of all aerobic organisms.
Citric acid is a commodity chemical, and more than a million tonnes are produced every year by fermentation. It is used mainly as an acidifier, as a flavoring, and as a chelating agent.
Physical properties
CITRIC ACID, white crystalline solid, decomposes at higher temperatures, sp gr 1.542. Citric acid is soluble in H2O or alcohol and slightly soluble in ether. The compound is a tribasic acid, forming mono-, di-, and tri- series of salts and esters.It occurs in large amounts is citrus fruits, and is used widely in industry as an acidifier, as a flavoring and chelating agent. pKa values are 5.21, 4.28 and 2.92 at 25 °C (extrapolated to zero ionic strength).
Citric acid is a good buffering agent for solutions between about pH 2 and pH 8. It is popular in many buffers in many techniques, electrophoresis (SSC Buffer #), to stop reactions, for biopurifications, crystallography... In biological systems around pH 7, the two species present are the citrate ion and mono-hydrogen citrate ion. the pH of a 1 mM solution of citric acid will be about 3.2.
Occurrence
Citric acid exists in greater than trace amounts in a variety of fruits and vegetables, most notably citrus fruits. Lemons and limes have particularly high concentrations of the acid; it can constitute as much as 8 % of the dry weight of these fruits (about 47 g/L in the juices ) . The concentrations of citric acid in citrus fruits range from 0.005 mol/L for oranges and grapefruits to 0.30 mol/L in lemons and limes. Within species, these values vary depending on the cultivar and the circumstances in which the fruit was grown.
History
The discovery of citric acid is credited to Jabir ibn Hayyan (Latin name Geber, 721–815).
Citric acid was first isolated in 1784 by the Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele (1742–1786), who crystallized it from lemon juice.
The crystalline structure of anhydrous citric acid, obtained by cooling hot concentrated solution of the monohydrate form, was first elucidated by Yuill and Bennett in 1934 by X-ray diffraction.
In 1960 Nordman and co-workers further suggested that in the anhydrous form two molecules of the acid are linked through hydrogen bonds between two –COOH groups of each monomer.
Uses
Citric Acid is an acidulant and antioxidant produced by mold fermentation of sugar solutions and by extraction from lemon juice, lime juice, and pineapple canning residue. it is the predominant acid in oranges, lemons, and limes. it exists in anhydrous and monohydrate forms. the anhydrous form is crystallized in hot solutions and the monohydrate form is crystallized from cold (below 36.5°c) solutions. anhydrous citric acid has a solubility of 146 g and monohydrate citric acid has a solubility of 175 g/100 ml of distilled water at 20°c. a 1% solution has a ph of 2.3 at 25°c. it is a hygroscopic, strong acid of tart flavor. it is used as an acidulant in fruit drinks and carbonated beverages at 0.25-0.40%, in cheese at 3-4%, and in jellies. it is used as an antioxidant in instant potatoes, wheat chips, and potato sticks, where it prevents spoilage by trapping the metal ions. it is used in combination with antioxidants in the processing of fresh frozen fruits to prevent discoloration.
Preparation
By mycological fermentation using molasses and strains of Aspergillus niger; from citrus juices and pineapple wastes
Definition
ChEBI: Citric acid is a tricarboxylic acid that is propane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid bearing a hydroxy substituent at position 2. It is an important metabolite in the pathway of all aerobic organisms. It has a role as a food acidity regulator, a chelator, an antimicrobial agent and a fundamental metabolite. It is a conjugate acid of a citrate(1-) and a citrate anion.
Application
Citric acid is a weak organic acid that is known as a commodity chemical, as more than a million tonnes are produced every year by mycological fermentation on an industrial scale using crude sugar sol utions, such as molasses and strains of Aspergillus niger. Citric acid is widely distributed in plants and in animal tissues and fluids and exist in greater than grace amounts in variety of fruits and vegetables, most notably in citrus fruits such as lemon and limes. Citric acid is mainly used as an acidifier, flavoring agent and chelating agent. It was also used as a chemical restrainer particularly in developers for the collodion process and in silver nitrate solutions used for sensitizing salted and albumen papers.
General Description
Citric acid appears as colorless, odorless crystals with an acid taste. Denser than water. (USCG, 1999)
Air & Water Reactions
The pure material is moisture sensitive (undergoes slow hydrolysis) Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Citric acid reacts with oxidizing agents, bases, reducing agents and metal nitrates . Reactions with metal nitrates are potentially explosive. Heating to the point of decomposition causes emission of acrid smoke and fumes [Lewis].
Health Hazard
Inhalation of dust irritates nose and throat. Contact with eyes causes irritation.
Biotechnological Applications
Citric acid cycle
Citrate, the conjugate base of citric acid is one of a series of compounds involved in the physiological oxidation of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates to carbon dioxide and water.
This series of chemical reactions is central to nearly all metabolic reactions, and is the source of two-thirds of the foodderived energy in higher organisms. Hans Adolf Krebs received the 1953 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for the discovery. The series of reactions is known by various names, including the "citric acid cycle", the "Krebs cycle" or "Szent-Gy?rgyi — Krebs cycle", and the "tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle".
Other biological roles
Citrate is a critical component of bone, helping to regulate the size of calcium crystals.
Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous route. Moderately toxic by subcutaneous and intraperitoneal routes. Mildly toxic byingestion. A severe eye and moderate skin irritant. An irritating organic acid, some allergenic properties. Combustible liquid. Potentially explosive reaction with metal nitrates. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and fumes.
Citric acid Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of2
chevron_rightPreparation Products
1of8
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANJI BIOSCIENCES | +91-9000100077 +91-9000100077 | Hyderabad, India | 430 | 58 | Inquiry |
| LABDHI CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES | +91-9322229293 +91-9322229293 | Mumbai, India | 21 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Vardhaman P Golechha | 9704422000 | Telangana, India | 294 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Indiana ChemPort | +91-91-2652638667 +91-7574886711 | Gujarat, India | 85 | 58 | Inquiry |
| ADVENT CHEMBIO PRIVATE LIMITED | +91-9821524116 +91-9821524116 | Mumbai, India | 353 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Gangotri Inorganic Private Limited | +91-9725738888 +91-9898237777 | Gujarat, India | 33 | 58 | Inquiry |
| SYNOVA CHEMICALS | +91-9920741772 +91-9920741772 | Mumbai, India | 428 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Nyne Organics Pvt Ltd | +91-9920180386 +91-9920180386 | Mumbai, India | 53 | 58 | Inquiry |
| PERFECT CHEMICAL | +91-9820465461 +91-9820465461 | Mumbai, India | 391 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Evans Fine Chem | +91-9821340302 +91-9821340302 | Maharashtra, India | 286 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| ANJI BIOSCIENCES | 58 |
| LABDHI CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES | 58 |
| Vardhaman P Golechha | 58 |
| Indiana ChemPort | 58 |
| ADVENT CHEMBIO PRIVATE LIMITED | 58 |
| Gangotri Inorganic Private Limited | 58 |
| SYNOVA CHEMICALS | 58 |
| Nyne Organics Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| PERFECT CHEMICAL | 58 |
| Evans Fine Chem | 58 |
Related articles
- The health benefits of Citric acid
- Citric acid is a tricarboxylic acid, which is widely used in various industrial fields such as pharmaceuticals, food, chemical....
- Apr 16,2024
- Citric acid:General description,Application,and Production
- Citric acid (CA) is the most valuable weak organic acid, widely used on the market for many applications. It is a tricarboxyli....
- Apr 24,2023
- How do you make citric acid?
- Citric acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula HOC(CO2H)(CH2CO2H)2. Usually encountered as a white solid, it is ....
- Aug 18,2021
77-92-9(Citric acid)Related Search:
1of5
chevron_right




