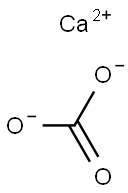
Calcium carbonate
- CAS No.
- 471-34-1
- Chemical Name:
- Calcium carbonate
- Synonyms
- pz;LIMESTONE;precipitated calcium carbonate;CALCITE;light calcium carbonate;CHALK;akadama;ARAGONITE;CALCII CARBONAS;nz
- CBNumber:
- CB2154602
- Molecular Formula:
- CCaO3
- Molecular Weight:
- 100.0869
- MOL File:
- 471-34-1.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2024/8/4 16:55:17
| Melting point | 825 °C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 800 °C |
| Density | 2.93 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| refractive index | 1.6583 |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | 5 M HCl: 0.1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | random crystals |
| Specific Gravity | 2.93 |
| color | White-beige to slightly beige-gray |
| PH | 9.91(1 mM solution);9.91(10 mM solution);9.91(100 mM solution); |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH Range | 8 |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble |
| λmax |
λ: 260 nm Amax: ≤0.09 λ: 280 nm Amax: ≤0.06 |
| Merck | 14,1657 |
| BRN | 8008338 |
| Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) | pKsp: 8.54 |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH: TWA 10 mg/m3; TWA 5 mg/m3 |
| Dielectric constant | 6.1(Ambient) |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with acids, fluorine, ammonium salts, alum. |
| InChIKey | VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 471-34-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Calcium carbonate (471-34-1) |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 10.0 - 80.0 GPa |
|---|---|
| Hardness, Vickers | 105 - 136 |
| Hardness, Mohs | 2.0 - 5.0 |
| Hardness, Knoop | 75 - 120 |
| Hardness, Shore H | 10 - 60 |
| Drilling Hardness | 50 |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS07 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Warning | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H315-H319-H335 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P261-P280-P271 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xi | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 37/38-41-36/38-36 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 26-36/37/39-37/39-37 | |||||||||
| OEB | B | |||||||||
| OEL | TWA: 10 mg/m3 (total) | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | - | |||||||||
| RTECS | FF9335000 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HS Code | 28365000 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in Rabbit: 6450 mg/kg LD50 dermal Rat > 2000 mg/kg | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Calcium carbonate price More Price(98)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | PHR1326 | Calcium carbonate Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material | 471-34-1 | 5G | ₹4470.73 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | C5929 | Calcium carbonate BioReagent, suitable for insect cell culture, ≥99.0% | 471-34-1 | 100G | ₹4135.15 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | C6763 | Calcium carbonate ReagentPlus? | 471-34-1 | 500G | ₹11842.55 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | C5929 | Calcium carbonate BioReagent, suitable for insect cell culture, ≥99.0% | 471-34-1 | 500G | ₹9590.95 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | C4830 | Calcium carbonate BioXtra, ≥99.0% | 471-34-1 | 100G | ₹5690 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Calcium carbonate Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Calcium carbonate occurs in nature as limestone in various forms, such as marble, chalk, and coral. It is probably the most widely-used raw material in the chemical industry. It has numerous applications, primarily to produce cement, mortars, plasters, refractories, and glass as building materials. It also is used to produce quicklime, hydrated lime and a number of calcium compounds. It is produced either as powdered or precipitated calcium carbonate. The latter consists of finer particles of greater purity and more uniform size. They also have many important commercial applications. Various grades of precipitated calcium carbonate are used in several products, such as textiles, papers, paints, plastics, adhesives, sealants, and cosmetics.

calcium carbonate block
Chemical Properties
Calcium carbonate occurs in two forms—hexagonal crystal known as calcite, and orthorhombic form, aragonite. Calcite decomposes on heating at 825°C, aragonite melts at 1,339°C (at 102.5 atm). Density 2.71 g/cm3 (calcite), 2.83 g/cm3 (aragonite); insoluble in water (15mg/L at 25°C); Ksp 4.8x10–9 ; soluble in dilute mineral acids.
Physical properties
Calcium carbonate is a naturally occurring compound found in organisms and throughout the earth’s crust. After quartz, calcium carbonate, primarily in the form of calcite, is the most common mineral found in the crust. Geologically, calcium carbonate exists in several mineral forms: calcite, aragonite, and vaterite. Calcite is the most common calcium carbonate mineral, whereas vaterite is a very rare form. The different mineral forms of calcium carbonate are based on their crystalline structure. The form of calcium carbonate depends on the conditions at its formation such as temperature and pressure.
Occurrence
Calcium carbonate occurs in nature as limestone in various forms, such as marble, chalk, and coral. It is probably the most widely-used raw material in the chemical industry. It has numerous applications, primarily to produce cement, mortars, plasters, refractories, and glass as building materials. It also is used to produce quicklime, hydrated lime and a number of calcium compounds. It is produced either as powdered or precipitated calcium carbonate. The latter consists of finer particles of greater purity and more uniform size. They also have many important commercial applications. Various grades of precipitated calcium carbonate are used in several products, such as textiles, papers, paints, plastics, adhesives, sealants, and cosmetics.
Uses
Calcium Carbonate is the calcium salt of carbonic acid which is used as an anticaking agent and dough strengthener. it is available in varying particle sizes ranging from coarse to fine powder. it is practically insoluble in water and alcohol, but the presence of any ammonium salt or carbon dioxide increases its solubility while the presence of any alkali hydroxide reduces its solubility. it has a ph of 9–9.5. it is the primary source of lime (calcium oxide) which is made by heating limestone in a furnace. calcium carbonate is used as a filler in baking powder, for calcium enrichment, as a mild buffering agent in doughs, as a source of calcium ions in dry mix desserts, and as a neutralizer in antacids. it is also termed limestone.
Preparation
Calcium carbonate may also be produced by mixing solutions of calcium chloride and sodium carbonate. In some cases, the presence of sodium is objectionable so that the ammonium carbonate salt is preferable.
Definition
calcium carbonate: A white solid,CaCO3, which is only sparingly solublein water. Calcium carbonatedecomposes on heating to give calciumoxide (quicklime) and carbondioxide. It occurs naturally as theminerals calcite (rhombohedral; r.d.2.71) and aragonite (rhombic; r.d.2.93). Rocks containing calcium carbonatedissolve slowly in acidifiedrainwater (containing dissolved CO2)to cause temporary hardness. In thelaboratory, calcium carbonate is precipitatedfrom limewater by carbondioxide. Calcium carbonate is used inmaking lime (calcium oxide) and isthe main raw material for theSolvay process.
Application
Calcium carbonate is used as a very mild abrasive for hand polishing nickel, gold, silver, or plated ware, buttons, and similar materials.
Production Methods
Calcium carbonate is obtained from natural limestone deposits. The purified compound, known as precipitated calcium carbonate, is synthesized from limestone. Limestone is calcined to calcium oxide and carbon dioxide in a kiln. The products are recombined after purification. Calcium oxide is hydrated with water to give a slurry called milk of lime, which is then carbonated by bubbling CO2 through it. The reactions involved in the process are as follows:
CaCO3 CaO + CO2
CaO + H2O Ca(OH)2
Ca(OH)2+ CO2→CaCO3+ H2O
The crystal sizes required for various commercial applications may be controlled by temperature, pH, concentrations, and mixing rate.
Calcium carbonate also may be precipitated by mixing solutions of calcium chloride and sodium carbonate.
Reactions
Calcium carbonate decomposes to calcium oxide and CO2 on heating. Treatment with dilute mineral acids produces corresponding calcium salts with liberation of CO2:
CaCO3+ 2HCl →CaCl2+ H2O + CO2
In the presence of CO2 it dissolves in water with the formation of bicarbonate:
CaCO3+ H2O + CO2→Ca2++ 2HCO3 ¯
It is reduced to calcium carbide when heated with coke or anthracite in an electric furnace:
2CaCO3+ 5C→(high temperature)→2CaC2+ 3CO2
General Description
Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3) is a naturally found material in chalk, limestone, and marble. It is composed of three elements which include carbon, oxygen, and calcium. It is formed by reacting carbon dioxide with slaked or burnt lime. It can be used for a variety of applications ranging from industrial, food to agriculture.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) can be found in clinical applications such as antacids, but not that an excessive intake can be hazardous.
A variety of calcium salts are used for clinical application, including calcium carbonate, calcium chloride,
calcium phosphate, calcium lactate, calcium aspartate and calcium gluconate. Calcium carbonate is the most
common and least expensive calcium supplement. It can be difficult to digest and may cause gas in some
people because of the reaction of stomach HCl with the carbonate and the subsequent production of CO2.
Calcium carbonate is recommended to be taken with food, and the absorption rate in the intestine depends
on the pH levels. Taking magnesium salts with it can help prevent constipation. Calcium carbonate consists
of 40% Ca2+, which means that 1000 mg of the salt contains around 400 mg of Ca2+. Often, labels will only
indicate the amount of Ca2+ present in each tablet and not the amount of calcium carbonate.
Agricultural Uses
Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) is a naturally occurring
white solid that is sparingly soluble in water. It is most
commonly used to neutralize soil acidity to the required
level in a process called liming.
The major sources of calcium carbonate are calcitic
limestone, dolomitic limestone, marl, chalk and marble.
Calcium carbonate is made by passing carbon dioxide
(CO2) into limewater. Pure calcium carbonate is assumed
to have a 100% neutralizing value. The values of other
liming materials are measured against the neutralizing
value of pure calcium carbonate. Calcium carbonate, on
heating, decomposes to give calcium oxide (quick lime)
and carbon dioxide.
Limestone, which consists mainly of calcium
carbonate, is called calcitic limestone or high calcium
limestone. Limestone containing more than 10%
magnesium carbonate is called dolomitic limestone or
dolomite. These forms contain about 12% magnesium.
Agricultural dolomitic limestone is a fine, grey to white
powder of a double carbonate of calcium and magnesium
with 12.8% magnesium and 17% calcium. The double
carbonate is much less soluble in water than the
individual carbonates.
Safety
Calcium carbonate is mainly used in oral pharmaceutical formulations
and is generally regarded as a nontoxic material. However,
calcium carbonate administered orally may cause constipation and
flatulence. Consumption of large quantities (4–60 g daily) may also
result in hypercalcemia or renal impairment. Therapeutically, oral
doses of up to about 1.5 g are employed as an antacid. In the
treatment of hyperphosphatemia in patients with chronic renal
failure, oral daily doses of 2.5–17 g have been used. Calcium
carbonate may interfere with the absorption of other drugs from the
gastrointestinal tract if administered concomitantly.
LD50 (rat, oral): 6.45 g/kg
storage
Calcium carbonate is stable and should be stored in a well-closed container in a cool, dry place.
Structure and conformation
The space lattice of CaCO3 belongs to the triagonal system, and the sodium nitric acid structure has a space group of D63d. It isarhombohedron crystal, with a basis comprising two molecules, and it has a lattice constant of a=0.636 nm, a=46°6'. Ca1 positions (1/4, 1/4, 1/4), Ca2 (3/4, 3/4, 3/4), C3 (0, 0, 0) and C4 (1/2, 1/2, 1/2), andCtakes the middle of Ca–Ca. The O atom positions the corner of the triangle, the plane of which is perpendicular to the optical axis, Ca–C–Ca–. This includes C and O3, as C4 shift position by 60° with the O3 of C3. The behavior of CO 2K 3 is different for light oscillating perpendicularly to the optical axis (O-ray) and light oscillating parallel to the axis (E-ray), which is the origin of the uniaxial negative crystal.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with acids and ammonium salts.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (buccal chewing gum, oral capsules and tablets; otic solutions; respiratory inhalation solutions). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Calcium carbonate Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of7
chevron_rightPreparation Products
1of8
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLR Innovations | +91 9891111994 | New Delhi, India | 4542 | 58 | Inquiry |
| ADVENT CHEMBIO PRIVATE LIMITED | +91-9821524116 +91-9821524116 | Mumbai, India | 353 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Gangotri Inorganic Private Limited | +91-9725738888 +91-9898237777 | Gujarat, India | 33 | 58 | Inquiry |
| oswal chemicals | +91-9173644055 +91-9173644055 | Gujarat, India | 66 | 58 | Inquiry |
| VAYUNANDAN IMPEX | +919836761502 | Rajasthan, India | 28 | 58 | Inquiry |
| JSK Chemicals | +919879767970 | Gujarat, India | 3756 | 58 | Inquiry |
| TIRUMALA INORGANICS | +91-9877240311 +91-9877240311 | Punjab, India | 6 | 58 | Inquiry |
| UNILOSA INTERNATINAL PRIVATE LIMITED | +91-9999069917 +91-9999069917 | New Delhi, India | 152 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Choice Chemicals | +91-9895031268 +91-9895031268 | Kerela, India | 118 | 58 | Inquiry |
| VITRAG CHEMICALS PVT LTD | +91-7490053194 +91-7490053194 | Gujarat, India | 47 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| GLR Innovations | 58 |
| ADVENT CHEMBIO PRIVATE LIMITED | 58 |
| Gangotri Inorganic Private Limited | 58 |
| oswal chemicals | 58 |
| VAYUNANDAN IMPEX | 58 |
| JSK Chemicals | 58 |
| TIRUMALA INORGANICS | 58 |
| UNILOSA INTERNATINAL PRIVATE LIMITED | 58 |
| Choice Chemicals | 58 |
| VITRAG CHEMICALS PVT LTD | 58 |
Related articles
- Is calcium carbonate easily soluble in water? What are its applications?
- Calcium carbonate is a common substance on Earth, found in minerals like aragonite, calcite, chalk, and travertine, as well as....
- Mar 21,2024
- Charge and uses of calcium carbonate
- Calcium carbonate is the active ingredient in agricultural lime and is produced when calcium ions in hard water react with car....
- Feb 5,2024
- Applications of precipitated calcium carbonate
- Precipitated calcium carbonate (PCC) is an innovative product derived from lime, which has many industrial applications. PCC ....
- Jan 12,2022
Related Qustion
- Q:What Happens When Calcium Carbonate Reacts with Acid?
- A:If you put calcium carbonate in hydrochloric acid, the solid will be quickly dissolved with bubbles emerge.
- Mar 13,2024
471-34-1(Calcium carbonate)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




