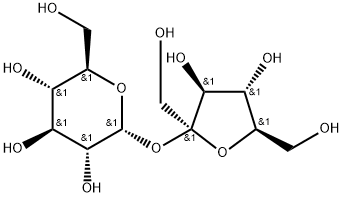
Sucrose
- CAS No.
- 57-50-1
- Chemical Name:
- Sucrose
- Synonyms
- SUGAR;SACCHAROSE;CANE SUGAR;Granulated sugar;White sugar;(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-(((2S,3S,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-2,5-bis(hydroxyMethyl)tetrahydrofuran-2-yl)oxy)-6-(hydroxyMethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triol;SACCHARUM;BEET SUGAR;Sucrose BP;Table sugar
- CBNumber:
- CB4337508
- Molecular Formula:
- C12H22O11
- Molecular Weight:
- 342.3
- MOL File:
- 57-50-1.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/7/22 15:18:42
| Melting point | 185-187 °C (lit.) |
|---|---|
| alpha | 67 º (c=26, in water 25 ºC) |
| Boiling point | 397.76°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.5805 |
| refractive index | 66.5 ° (C=26, H2O) |
| Flash point | 93.3°C |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Room Temperature |
| solubility | H2O: 500 mg/mL |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | 12.7(at 25℃) |
| color | White |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH Range | 5.5 - 7 at 342 g/l at 25 °C |
| PH | 5.0-7.0 (25℃, 1M in H2O) |
| optical activity | [α]25/D +66.3 to +66.8°(lit.) |
| Water Solubility | 1970 g/L (15 ºC) |
| λmax |
λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.11 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.08 |
| Merck | 14,8881 |
| BRN | 90825 |
| Dielectric constant | 3.3(Ambient) |
| Exposure limits |
ACGIH: TWA 10 mg/m3 OSHA: TWA 15 mg/m3; TWA 5 mg/m3 NIOSH: TWA 10 mg/m3; TWA 5 mg/m3 |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. Hydrolyzed by dilute acids and by invertase. |
| InChIKey | CZMRCDWAGMRECN-UGDNZRGBSA-N |
| LogP | -4.492 (est) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 57-50-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Sucrose(57-50-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Sucrose (57-50-1) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS07 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Warning | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H315-H319-H335 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P261-P271-P280 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xi | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 36/37/38 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 24/25-37/39-26 | |||||||||
| OEB | B | |||||||||
| OEL | TWA: 10 mg/m3 (total) | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 2 | |||||||||
| RTECS | WN6500000 | |||||||||
| F | 3 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HS Code | 17019910 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in Rabbit: 29700 mg/kg | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Sucrose price More Price(73)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | S9378 | Sucrose ≥99.5% (GC) | 57-50-1 | 10MG | ₹4494 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | S9378 | Sucrose ≥99.5% (GC) | 57-50-1 | 500G | ₹6310 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | S9378 | Sucrose ≥99.5% (GC) | 57-50-1 | 1KG | ₹8480 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | S9378 | Sucrose ≥99.5% (GC) | 57-50-1 | 5KG | ₹24100 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | S9378 | Sucrose ≥99.5% (GC) | 57-50-1 | 10KG | ₹63827 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Sucrose Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
Sucrose is a sugar obtained from sugar cane (Saccharum officinarum Linne' (Fam. Gramineae)), sugar beet (Beta vulgaris Linne' (Fam. Chenopodiaceae)), and other sources. It contains no added substances. Sucrose occurs as colorless crystals, as crystalline masses or blocks, or as a white crystalline powder; it is odorless and has a sweet taste.
Uses
sucrose (table sugar) is an emollient, mild emulsifier, and humectant. It can be used in place of glycerin.
Production Methods
Sucrose is obtained from the sugar cane plant, which contains 15–20% sucrose, and sugar beet, which contains 10–17% sucrose. Juice from these sources is heated to coagulate water-soluble proteins, which are removed by skimming. The resultant solution is then decolorized with an ion-exchange resin or charcoal and concentrated. Upon cooling, sucrose crystallizes out. The remaining solution is concentrated again and yields more sucrose, brown sugar, and molasses.
Definition
ChEBI: Sucrose is a disaccharide formed by glucose and fructose units joined by an acetal oxygen bridge from hemiacetal of glucose to the hemiketal of the fructose.
General Description
White odorless crystalline or powdery solid. Denser than water.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble. Sugar dust explosion is possibility.
Reactivity Profile
D(+)-Sucrose is a reducing agent. Can react explosively with oxidizing agents such as chlorates and perchlorates. Is hydrolyzed by dilute acids and by invertase (a yeast enzyme) . Chars rapidly and exothermically when mixed with concentrated sulfuric acid.
Hazard
Dental erosion. Questionable carcinogen.
Health Hazard
None
Agricultural Uses
is obtained from sugar beet, sugar cane and sweet
sorghum. Table sugar is the most common form of
sucrose. It comprises a glucose unit joined to a fructose
unit. Honey consists of sucrose and its hydrolysis
products.
Sucrose, glucose and fructose all exhibit optical
activity. When sucrose is hydrolyzed, the rotation
changes from right to left. This is called inversion, and an
equimolar mixture of glucose and fructose is called invert
sugar. The enzyme invertase hydrolyzes sucrose to
glucose and fructose.
Sugar occurs universally throughout the plant
kingdom in fruits, seeds, flowers and roots.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Sucrose is widely used in oral pharmaceutical formulations.
Sucrose syrup, containing 50–67% w/w sucrose, is used in
tableting as a binding agent for wet granulation. In the powdered
form, sucrose serves as a dry binder (2–20% w/w) or as a bulking
agent and sweetener in chewable tablets and lozenges. Tablets
that contain large amounts of sucrose may harden to give poor
disintegration.
Sucrose syrups are used as tablet-coating agents at concentrations
between 50% and 67% w/w. With higher concentrations,
partial inversion of sucrose occurs, which makes sugar coating
difficult.
Sucrose syrups are also widely used as vehicles in oral liquiddosage
forms to enhance palatability or to increase viscosity.(4,5)
Sucrose has been used as a diluent in freeze-dried protein
products.
Sucrose is also widely used in foods and confectionery, and
therapeutically in sugar pastes that are used to promote wound
healing.
Safety Profile
Mildly toxic by ingestion. An experimental teratogen. Mutation data reported. Vigorous reaction with nitric acid or sulfuric acid (forms carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide). When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Safety
Sucrose is hydrolyzed in the small intestine by the enzyme sucrase to
yield dextrose and fructose, which are then absorbed. When
administered intravenously, sucrose is excreted unchanged in the
urine.
Although sucrose is very widely used in foods and pharmaceutical
formulations, sucrose consumption is a cause of concern and
should be monitored in patients with diabetes mellitus or other
metabolic sugar intolerance.
Sucrose is also considered to be more cariogenic than other
carbohydrates since it is more easily converted to dental plaque. For
this reason, its use in oral pharmaceutical formulations is declining.
Although sucrose has been associated with obesity, renal
damage, and a number of other diseases, conclusive evidence
linking sucrose intake with some diseases could not be established.(
13,14) It was, however, recommended that sucrose intake in
the diet should be reduced.
LD50 (mouse, IP): 14 g/kg
LD50 (rat, oral): 29.7 g/kg
storage
Sucrose has good stability at room temperature and at moderate
relative humidity. It absorbs up to 1% moisture, which is released
upon heating at 90°C. Sucrose caramelizes when heated to
temperatures above 160°C. Dilute sucrose solutions are liable to
fermentation by microorganisms but resist decomposition at higher
concentrations, e.g. above 60% w/w concentration. Aqueous
solutions may be sterilized by autoclaving or filtration.
When sucrose is used as a base for medicated confectionery, the
cooking process, at temperatures rising from 110 to 145℃, causes
some inversion to form dextrose and fructose (invert sugar). The
fructose imparts stickiness to confectionery but prevents cloudiness
due to graining. Inversion is accelerated particularly at temperatures
above 130°C and by the presence of acids.
Purification Methods
Crystallise D(+)-sucrose from water (solubility: 1g in 0.5mL H2O at 20o, 1g in 0.2mL in boiling H2O). It is soluble in EtOH (0.6%) and MeOH (1%). Sucrose diacetate hexaisobutyrate is purified by melting and, while molten, treated with NaHCO3 and charcoal, then filtered. [Beilstein 17/8 V 399.]
Incompatibilities
Powdered sucrose may be contaminated with traces of heavy metals, which can lead to incompatibility with active ingredients, e.g. ascorbic acid. Sucrose may also be contaminated with sulfite from the refining process. With high sulfite content, color changes can occur in sugar-coated tablets; for certain colors used in sugarcoating the maximum limit for sulfite content, calculated as sulfur, is 1 ppm. In the presence of dilute or concentrated acids, sucrose is hydrolyzed or inverted to dextrose and fructose (invert sugar). Sucrose may attack aluminum closures.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (injections; oral capsules, solutions, syrups, and tablets; topical preparations). Included in nonparenteral and parenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Sucrose Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
1of8
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JSK Chemicals | +919879767970 | Gujarat, India | 3756 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Macleods Pharmaceuticals Limited | +91-2266762800 +91-2266762800 | Maharashtra, India | 116 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Balrampur Chini Mills Ltd | +91-3322874749 +91-3322874749 | West Bengal, India | 2 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Prakash Chemicals Agencies | +91-8511140657 | Gujarat, India | 106 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Mb Sugars And Pharmaceuticals Ltd | +91-9326192190 +91-9822651942 | Maharashtra, India | 4 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Merck Ltd | +91-2262109800 +91-2262109000 | Maharashtra, India | 272 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Arihant Innochem Pvt Ltd | +91-2267674895 +91-2267674895 | Mumbai, India | 37 | 58 | Inquiry |
| RYZE CHEMIE | +91-9702966440 +91-9702966440 | Maharashtra, India | 335 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Hexon Laboratories Pvt., Ltd. | 91-9767042000 | Maharashtra, India | 85 | 58 | Inquiry |
| ASM Organics | 91-9866122393 | Andhra Pradesh, India | 1188 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| JSK Chemicals | 58 |
| Macleods Pharmaceuticals Limited | 58 |
| Balrampur Chini Mills Ltd | 58 |
| Prakash Chemicals Agencies | 58 |
| Mb Sugars And Pharmaceuticals Ltd | 58 |
| Merck Ltd | 58 |
| Arihant Innochem Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| RYZE CHEMIE | 58 |
| Hexon Laboratories Pvt., Ltd. | 58 |
| ASM Organics | 58 |
Related articles
- Which's the reactions of Sucrose(C12H22O11)?
- Sucrose (α-d-glucopyranosyl-β-d-fructofuranoside) is a disaccharide with the general molecular formula C12H22O11. In solution,....
- Jul 22,2024
- is sugar a pure substance?
- Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food.
- Mar 5,2024
- Sugar: A Compound in Nature
- Sugar, a ubiquitous ingredient found in our everyday lives, plays a significant role in both culinary delights and biochemical....
- Feb 27,2024
57-50-1(Sucrose)Related Search:
1of5
chevron_right




