Microcrystalline cellulose
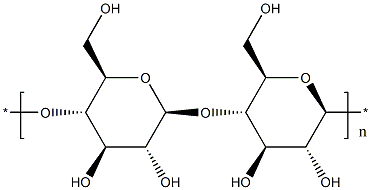
- CAS No.
- 9004-34-6
- Chemical Name:
- Microcrystalline cellulose
- Synonyms
- CELLULOSE;avicel;SOLKA-FLOC;CELLULOSE MICROCRYSTALLINE;Α-Cellulose;cepo;CELLULOSE POWDER;microcrystalline;Microcrystalline Cellulose 101;arbocel
- CBNumber:
- CB4217972
- Molecular Formula:
- (C12H20O10)n
- Molecular Weight:
- 324.28
- MOL File:
- 9004-34-6.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/7/4 21:45:01
| Melting point | 76-78 °C(Solv: acetone (67-64-1); chloroform (67-66-3)) |
|---|---|
| Density | 1.5 g/cm3 (20℃) |
| refractive index | n20/D 1.504 |
| Flash point | 164 °C |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, in acetone, in anhydrous ethanol, in toluene, in dilute acids and in a 50 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide |
| form | powder |
| color | White or almost white |
| PH | 5-7.5 (100g/l, H2O, 20℃)(slurry) |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
| Merck | 14,1965 |
| Exposure limits |
ACGIH: TWA 10 mg/m3 OSHA: TWA 15 mg/m3; TWA 5 mg/m3 NIOSH: TWA 10 mg/m3; TWA 5 mg/m3; TWA 1 mg/m3 |
| Dielectric constant | 3.2(Ambient) |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| InChIKey | UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cellulose (9004-34-6) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS07 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard statements | H335 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P261-P304+P340-P312a-P403+P233-P405-P501a | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xi | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 37 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 24/25 | |||||||||
| OEB | B | |||||||||
| OEL | TWA: 10 mg/m3 (total) | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | FJ5950200 | |||||||||
| F | 3 | |||||||||
| Autoignition Temperature | 232 °C | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HS Code | 39129090 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in Rabbit: > 5000 mg/kg LD50 dermal Rabbit > 2000 mg/kg | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Microcrystalline cellulose price More Price(40)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | S6790 | Sigmacell Cellulose Type 101, Highly purified, fibers | 9004-34-6 | 100G | ₹4221.75 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | S6790 | Sigmacell Cellulose Type 101, Highly purified, fibers | 9004-34-6 | 500G | ₹12784.33 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | S5504 | Sigmacell Cellulose Type 50, 50?μm | 9004-34-6 | 500G | ₹8302.78 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | S5504 | Sigmacell Cellulose Type 50, 50?μm | 9004-34-6 | 1KG | ₹10478.6 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | S3504 | Sigmacell Cellulose Type 20, 20?μm | 9004-34-6 | 500G | ₹7772.35 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Microcrystalline cellulose Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
Microcrystalline cellulose and carboxymethylcellulose sodium
occurs as a white or off-white odorless and tasteless hygroscopic
powder containing 5–22% sodium carboxymethylcellulose. It is a
water-dispersible organic hydrocolloid.
Occurrence
The fiber in typical paper can be called “cellulosic”, meaning that cellulose is its most prominent component. Cellulose is present not only in wood, but also in various non-woody plants, such as straw, sugarcane (bagasse), reeds, and hemp.
Uses
Microcrystalline Cellulose is a gum that is the nonfibrous form of cellulose, an alpha-cellulose. It is dispersible in water but not soluble, requiring considerable energy to disperse and hydrate. In this form it is used in dry applications such as tableting, capsules, and shredded cheese where it functions as a non-nutritive filler, binder, flow aid, and anticaking agent. By the addition of carboxymethylcellulose to the alpha-cellulose prior to drying, improved functional properties of hydration and dispersion are obtained. This product is designed for use in water dispersions, being insoluble in water but dispersing in water to form colloidal sols below 1% and white opaque gels above the 1% usage level. It is used as a heat shock stabilizer and bodying agent in frozen desserts, as an opacifier in low-fat dressings, as a foam stabilizer in whipped toppings, and as an emulsifier in dressings. Also termed cellulose gel.
Production Methods
Microcrystalline cellulose and carboxymethylcellulose sodium is a spray- or bulk-dried blend of microcrystalline cellulose and sodium carboxymethylcellulose. It is prepared by the chemical depolymerization of highly purified wood pulp. The original crystalline areas of the pulp fibers are combined with sodium carboxymethylcellulose, which serves as a protective colloid and also facilitates dispersion of the product; it is then either spray- or bulk-dried.
Definition
A natural carbohydrate high polymer (polysaccha- ride) consisting of anhydroglucose units joined by an oxygen linkage to form long molecular chains that are essentially linear. It can be hydrolyzed to glucose. The degree of polymerization is from 1000 for wood pulp to 3500 for cotton fiber, giving a molecular weight from 160,000 to 560,000. Cellulose is a colorless solid, d approximately 1.50, insoluble in water and organic solvents. It will swell in sodium hydroxide solution and is soluble in Schweitzer’s reagent. It is the fundamental con- stituent of all vegetable tissues (wood, grass, cotton, etc.) and the most abundant organic material in the world. Cotton fibers are almost pure cellulose; wood contains approximately 50%. The physical structure of cellulose is unusual in that it is not a single crystal but consists of crystalline areas embedded in amorphous areas. Chemical reagents penetrate the latter more easily than the former. Cel- lulose is virtually odorless and tasteless and is com- bustible, with an ignition point of approximately 450F. In some forms, it is flammable. For example, railroad shipping regulations require a flammable label on such items as burnt fiber, burnt cotton, wet waste paper, and wet textiles. Fires have been known to occur in warehouses in which telephone books were stored. These were undoubtedly due to heat buildup in the paper caused by microbial activity and self-sustaining oxidation.
General Description
Odorless, white powdery fibers. Density 1.5 g cm-3. The biopolymer composing the cell wall of vegetable tissues. Prepared by treating cotton with an organic solvent to de-wax Cellulose microcrystalline and removing pectic acids by extration with a solution of sodium hydroxide. The principal fiber composing the cell wall of vegetable tissues (wood, cotton, flax, grass, etc.). Technical uses depend on the strength and flexibility of its fibers. Insoluble in water. Soluble with chemical degradation in sulfuric aicd, and in concentrated solutions of zinc chloride. Soluble in aqueous solutions of cupric ammonium hydroxide (Cu(NH3)4(OH)2).
Reactivity Profile
Cellulose microcrystalline is combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents including bromine pentafluoride, sodium nitrate, fluorine, perchlorates, perchloric acid, sodium chlorate, magnesium perchlorate, F2, zinc permanganate, sodium nitrite, sodium nitrate, sodium peroxide. Nitration with a mixture of nitric and sulfuric acids produces Cellulose microcrystalline nitrates (celluloid pyroxylin, soluble pyroxyline, guncotton) which are flammable or explosive.
Health Hazard
Cellulose is inert and is classified
as a nuisance dust.
It has little, if any, adverse effect on the
lung, and there are no reports of organic
disease or toxic effect. The health effects
attributed to wood, cotton, flax, jute, and hemp
are not attributable to their cellulose content
but rather to the presence of other substances.
Cellulose fibers were found in the blood
and urine of human volunteers fed dyed cellulose;
there were no ill effects.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Microcrystalline cellulose and carboxymethylcellulose sodium is
used to produce thixotropic gels suitable as suspending vehicles in
pharmaceutical and cosmetic formulations. The sodium carboxymethylcellulose
aids dispersion and serves as a protective colloid.
Concentrations of less than 1% solids produce fluid dispersions,
while concentrations of more than 1.2% solids produce thixotropic
gels. When properly dispersed, it imparts emulsion stability, opacity
and suspension in a variety of products, and is used in nasal sprays,
topical sprays and lotions, oral suspensions, emulsions, creams
and gels.
Industrial uses
Cellulose is the main constituent of the structureof plants (natural polymer) that, whenextracted, is employed for making paper,plastics, and in many combinations. Celluloseis made up of long-chain molecules inwhich the complex unit C6H10O5 is repeatedas many as 2000 times. It consists of glucose molecules with three hydroxyl groups foreach glucose unit.
One of the simplest forms of cellulose usedindustrially is regenerated cellulose, in whichthe chemical composition of the finished productis similar to that of the original cellulose. Itis made from wood or cotton pulp digested ina caustic solution. Cellophane is a regeneratedcellulose in thin sheets for wrapping and otherspecial uses include windings on wire andcable.
Safety Profile
A nuisance dust. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Safety
Microcrystalline cellulose is widely used in oral pharmaceutical
formulations and food products and is generally regarded as a
relatively nontoxic and nonirritant material.
Microcrystalline cellulose is not absorbed systemically following
oral administration and thus has little toxic potential. Consumption
of large quantities of cellulose may have a laxative effect, although
this is unlikely to be a problem when cellulose is used as an excipient
in pharmaceutical formulations.
Deliberate abuse of formulations containing cellulose, either by
inhalation or by injection, has resulted in the formation of cellulose
granulomas.
storage
Microcrystalline cellulose and carboxymethylcellulose sodium is hygroscopic and should not be exposed to moisture. It is stable over a pH range of 3.5–11. Store in a cool, dry place. Avoid exposure to excessive heat.
Incompatibilities
Microcrystalline cellulose is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents.
Regulatory Status
Microcrystalline cellulose and carboxymethylcellulose sodium is a mixture of two materials both of which are generally regarded as nontoxic:
Microcrystalline cellulose GRAS listed. Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (inhalations; oral capsules, powders, suspensions, syrups, and tablets; topical and vaginal preparations). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Carboxymethylcellulose sodium GRAS listed. Accepted as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (dental preparations; intra-articular, intrabursal, intradermal, intralesional, and intrasynovial injections; oral drops, solutions, suspensions, syrups and tablets; topical preparations). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Nonmedicinal Ingredients.
Microcrystalline cellulose Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
1of3
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atul Intermediates | +91-7940399111 +91-9825071644 | Gujarat, India | 24 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Kamman Group | +91-9619902204 +91-9619902204 | Mumbai, India | 33 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Ankit Pulps and Boards Pvt. Ltd. APB | +91-9970057671 +91-7666900215 | Maharashtra, India | 10 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Rivashaa Agrotech Biopharma Pvt. Ltd. | +91-26463395 +91-7926462688 | Gujarat, India | 1615 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Keval Exports | +91-9824411251 +91-9737845678 | Gujarat, India | 4 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Varahi International | +91-7922844991 +91-7922844991 | Gujarat, India | 24 | 58 | Inquiry |
| NB Entrepreneurs | +91-9970018645 +91-9970057654 | Maharashtra, India | 7 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Patel Industries | +91-9879997220 +91-9879997220 | Gujarat, India | 7 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Nitika Pharmaceutical Specialities Pvt Ltd | +91-7122641001 +91-8956932443 | Maharashtra, India | 36 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Rubexco Pvt Ltd | +91-9825231936 +91-9909917613 | Gujarat, India | 36 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Atul Intermediates | 58 |
| Kamman Group | 58 |
| Ankit Pulps and Boards Pvt. Ltd. APB | 58 |
| Rivashaa Agrotech Biopharma Pvt. Ltd. | 58 |
| Keval Exports | 58 |
| Varahi International | 58 |
| NB Entrepreneurs | 58 |
| Patel Industries | 58 |
| Nitika Pharmaceutical Specialities Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| Rubexco Pvt Ltd | 58 |
Related articles
- Discover Multifunctional Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose (HPMC)
- Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) is a remarkable compound, manifesting in a white or off-white powder form.
- Mar 7,2024
- What Can Modified Cellulose Be Used For?
- The term "modified cellulose" pertains to chemical modifications primarily aimed at the hydroxyl groups within the cellulose b....
- Feb 29,2024
- Application of Microcrystalline cellulose
- Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) is mainly composed of β- 1,4-glucoside bonded linear polysaccharide [1] is a white, odorless ....
- Mar 7,2022
9004-34-6(Microcrystalline cellulose)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




