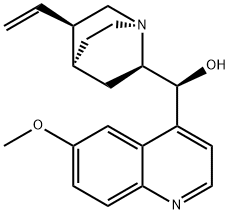
Quinidine
- CAS No.
- 56-54-2
- Chemical Name:
- Quinidine
- Synonyms
- QUNIDINE;QUINDINE;Cin-quin;Quinidex;Quinaglute;6-METHOXY-A-(5-VINYL-2-QUINUCLIDINYL)-4-QUINOLINE-METHANOL;(1S)-(6-Methoxyquinolin-4-yl)((2R,4S,5R)-5-vinylquinuclidin-2-yl)Methanol;(S)-(6-methoxyquinolin-4-yl)((1S,2R,4S,5R)-5-vinylquinuclidin-2-yl)methanol;(S)-[(2R,4S,5R)-5-ethenyl-1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-2-yl](6-methoxyquinolin-4-yl)methanol;Kinidin
- CBNumber:
- CB9208047
- Molecular Formula:
- C20H24N2O2
- Molecular Weight:
- 324.42
- MOL File:
- 56-54-2.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2024/3/19 15:37:50
| Melting point | 168-172 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| alpha | 256 º (c=1, EtOH) |
| Boiling point | 462.75°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.1294 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5700 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | insoluble in H2O; ≥10.32 mg/mL in EtOH with ultrasonic; ≥11.95 mg/mL in DMSO |
| form | Powder |
| pka | 5.4, 10.0(at 20℃) |
| color | White to off-white |
| optical activity | [α]20/D +265±5°, c = 0.8% in ethanol (dry matter) |
| Water Solubility | 0.05 g/100 mL (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Light Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,8060 |
| BRN | 91866 |
| BCS Class | 1 |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| LogP | 3.440 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 56-54-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Quinine(56-54-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Quinidine (56-54-2) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS06 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H301-H317 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P261-P264-P270-P280-P301+P310-P302+P352 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xn | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 22-20/21/22 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 36-22 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | VA4725000 | |||||||||
| F | 8 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 6.1(b) | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29392000 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 in rats (mg/kg): 30 i.v., 263 orally (Dietmann) | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Quinidine price More Price(6)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | Q3625 | Quinidine anhydrous | 56-54-2 | 5G | ₹4373.3 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | Q3625 | Quinidine anhydrous | 56-54-2 | 25G | ₹16573.08 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 22600 | Quinidine crystallized, ≥98.0% (dried material, NT) | 56-54-2 | 10G | ₹8703.3 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 22600 | Quinidine crystallized, ≥98.0% (dried material, NT) | 56-54-2 | 50G | ₹26997.55 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| TCI Chemicals (India) | Q0006 | Quinidine | 56-54-2 | 5G | ₹3900 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
Quinidine Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Quinidine is a commonly used class I antiarrhythmic drug. It is a stereoisomer of quinine, originally derived from the bark of the cinchona tree. It exerts its antiarrhythmic effects on the heart by interacting with the electrophysiology mechanisms that cause arrhythmias to modify the abnormalities in impulse initiation and conduction. Quinidine depresses normal automaticity in cardiac fibers that may act as ectopic pacemakers causing arrhythmias. Quinidine also blocks the slowly inactivating, tetrodotoxin-sensitive Na current, the slow inward calcium current (ICa), the rapid (IKr) and slow (IKs) components of the delayed potassium rectifier current, the inward potassium rectifier current (IKI), the ATP-sensitive potassium channel (IKATP) and Ito.
Chemical Properties
white to light yellow crystal powde
Physical properties
Appearance: Quinidine is commonly used in its sulfate form with white needle-like crystal and bitter smell. It changes color easily when exposed to light. Solubility: It was soluble in ethanol and chloroform. Its water solubility is 0.05?g/100?mL (20?°C). Specific optical rotation: 256° (c?=?1, EtOH). Melting point: 168–172?°C.
History
In 1820, the French chemists Pierre Pelletier and Joseph Caventou extracted some alkaloids from the cinchona bark, including quinine and quinidine. Subsequently, quinine was demonstrated to play a very important role in the treatment of malaria after a number of scientific researches. Quinidine is the dextroisomer of quinine and has the similar pharmacological properties as quinine, but quinidine’s effects are five to ten times stronger on the heart than quinine.
Uses
Quinidine occurs in cinchona bark to about0.25–0.3% and also in cuprea bark. It is present in quinine sulfate mother liquor. Itis formed by isomerization of quinine. Itis used in the prevention of certain cardiacarrhythmias.
Indications
Quinidine acts as a class I antiarrhythmic agent (Ia) in the heart. It was clinically applicable to the treatment of recurrent, documented, life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias .
Definition
ChEBI: A cinchona alkaloid consisting of cinchonine with the hydrogen at the 6-position of the quinoline ring substituted by methoxy.
Biological Functions
Quinidine is an alkaloid obtained from various species of Cinchona or its hybrids, from Remijia pedunculata, or from quinine. Quinidine is the dextrorotatory isomer of quinine.Quinidine (Quinidex) was one of the first clinically used antiarrhythmic agents. Because of the high incidence of ventricular proarrhythmia associated with its use and numerous other equally efficacious agents, quinidine is now used sparingly. Quinidine shares all of the pharmacological properties of quinine, including antimalarial, antipyretic, oxytocic, and skeletal muscle relaxant actions.
General Description
Crystals or white powder.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Hazard
Poison.
Health Hazard
Quinidine is more potent than quinine in itsaction on the cardiovascular system. Overdosesmay cause lowering of blood pressure.Gastric effects are lower than quinine. Toxicityis lower relative to quinine; subcutaneouslethal dose in mice is 400 mg/kg against200 mg/kg for quinine.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Quinidine are not available. Quinidine is probably combustible.
Pharmacology
Quinidine exhibits all of the pharmacological properties of quinine, including antimalarial, fever-reducing, and other properties. Quinidine is used in various forms of arrhythmia for preventing tachycardia and atrial fibrillation, and particularly for preventing ciliary fibrillation, paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia, extrasystole, and ventricular tachycardia. However, it is a toxic drug and is used relatively rarely. It is also prescribed under the name cardioquin, duraquin, quinidex, and others.
Clinical Use
Primary indications for the use of quinidine include (1) abolition of premature complexes that have an atrial, A-V junctional, or ventricular origin; (2) restoration of normal sinus rhythm in atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation after controlling the ventricular rate with digitalis; (3) maintenance of normal sinus rhythm after electrical conversion of atrial arrhythmias; (4) prophylaxis against arrhythmias associated with electrical countershock; (5) termination of ventricular tachycardia; and (6) suppression of repetitive tachycardia associated with Wolff- Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome.
Although quinidine often is successful in producing normal sinus rhythm, its administration in the presence of a rapid atrial rate (flutter and possibly atrial fibrillation) can lead to a further and dangerous increase in the ventricular rate secondary to inhibition of basal vagal tone upon the A-V node. For this reason, digitalis should be used before quinidine when one is attempting to convert atrial flutter or atrial fibrillation to normal sinus rhythm.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, subcutaneous, intravenous, intramuscular, and intraperitoneal routes. A skin irritant. Implicated in aplastic anemia. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Drug interactions
Quinidine can increase the plasma concentrations of
digoxin, which may in turn lead to signs and symptoms of
digitalis toxicity. Gastrointestinal, central nervous system
(CNS), or cardiac toxicity associated with elevated
digoxin concentrations may occur.Quinidine and digoxin
can be administered concurrently; however, a downward
adjustment in the digoxin dose may be required.
Drugs that have been associated with elevations in
quinidine concentrations include acetazolamide, the
antacids magnesium hydroxide and calcium carbonate,
and the H2-receptor antagonist cimetidine. Cimetidine
inhibits the hepatic metabolism of quinidine. Phenytoin,
rifampin, and barbiturates increase the hepatic metabolism
of quinidine and reduce its plasma concentrations.
Metabolism
Quinidine's bioavailability appears to depend on a combination of metabolism and P-gp efflux. The bioavailabilities of quinidine sulfate and gluconate are 80 to 85% and 70 to 75%, respectively. Once absorbed, quinidine is subject to hepatic first-pass metabolism and is approximately 85% plasma protein bound, with an elimination half-life of approximately 6 hours. Quinidine is metabolized mainly in the liver, and renal excretion of unchanged drug also is significant (~10–50%). The metabolites are hydroxylated derivatives at either the quinoline ring through first-pass O-demethylation or at the quinuclidine ring through oxidation of the vinyl group. These metabolites possess only about one-third the activity of quinidine. Their contribution to overall therapeutic effect of quinidine is unclear. Recently, the clinical significance of the well-documented digoxin–quinidine interaction was described previously under digoxin–drug interactions. Apparently, quinidine (a P-gp substrate) inhibits the renal tubular secretion of digoxin via the P-gp efflux pump, resulting in increased plasma concentration for digoxin.
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from *C6H6 or dry CHCl3/pet ether (b 40-60o), discarding the initial, oily crop of crystals. Dry it under vacuum at 100o over P2O5. It has been used as a chiral catalyst [Wynberg & Staring J Am Chem Soc 104 166 1982, J Org Chem 50 1977 1985]. [Beilstein 23 H 506, 23 I 164, 23 II 414, 23 III/IV 3261, 23/13 V 395.]
Precautions
One of the few absolute contraindications for quinidine
is complete A-V block with an A-V pacemaker or idioventricular
pacemaker; this may be suppressed by
quinidine, leading to cardiac arrest.
Persons with congenital QT prolongation may develop
torsades de pointes tachyarrhythmia and should
not be exposed to quinidine.
Owing to the negative inotropic action of quinidine,
it is contraindicated in congestive heart failure and hypotension.
Digitalis intoxication and hyperkalemia can accentuate
the depression of conduction caused by quinidine.
Myasthenia gravis can be aggravated severely by
quinidine’s actions at the neuromuscular junction.
The use of quinidine and quinine should be avoided
in patients who previously showed evidence of quinidine-
induced thrombocytopenia.
References
Wit, Andrew L. "The Effects of Quinidine on the Cellular Electrophysiology of the Heart: A Brief Review." Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology 3.5(2010):316-322.
Alloway, J. A., and M. P. Salata. "Quinidine-induced rheumatic syndromes. " Seminars in Arthritis & Rheumatism 24.5(1995):315-322.
Nakano, J, and M. C. R. Jr. "Effect of quinidine on cardiovascular dynamics." Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 168.2(1967):400-416.
Quinidine Preparation Products And Raw materials
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prism Industries Ltd | +91-9825050731 +91-9227406992 | Gujarat, India | 28 | 58 | Inquiry |
| VIVAN Life Sciences Pvt Ltd | +91-2225870080 +91-9987465183 | Maharashtra, India | 49 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Prism Industries Ltd. | 91-8037401956 | Gujarat, India | 17 | 58 | Inquiry |
| OCEAN TRADING CORPORATION | +91(22) 24921669 | New Delhi, India | 6211 | 58 | Inquiry |
| CHEMSWORTH | +91-261-2397244 | New Delhi, India | 6707 | 30 | Inquiry |
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | +91-22-45045900 | Hyderabad, India | 6351 | 58 | Inquiry |
| A.J Chemicals | 91-9810153283 | New Delhi, India | 6124 | 58 | Inquiry |
| TCI Chemicals (India) Pvt. Ltd. | 1800 425 7889 | New Delhi, India | 6778 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Alfa Aesar | 1 800 209 7001 | Maharashtra, India | 6913 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Pharmaffiliates Analytics and Synthetics P. Ltd | +91-172-5066494 | Haryana, India | 6773 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Prism Industries Ltd | 58 |
| VIVAN Life Sciences Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| Prism Industries Ltd. | 58 |
| OCEAN TRADING CORPORATION | 58 |
| CHEMSWORTH | 30 |
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | 58 |
| A.J Chemicals | 58 |
| TCI Chemicals (India) Pvt. Ltd. | 58 |
| Alfa Aesar | 58 |
| Pharmaffiliates Analytics and Synthetics P. Ltd | 58 |
56-54-2(Quinidine)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




