Rhodium
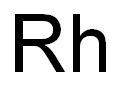
- CAS No.
- 7440-16-6
- Chemical Name:
- Rhodium
- Synonyms
- Rh;RHODIUM ON ALUMINA;RHODIUM ON CARBON;Rhodium powder;5% Rhodium on carbon;rhodium atom;RHODIUM SPONGE;Rhodium, 5 % on alumina;rh-945;Rhodiu
- CBNumber:
- CB9365715
- Molecular Formula:
- Rh
- Molecular Weight:
- 102.91
- MOL File:
- 7440-16-6.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/5/29 10:47:01
| Melting point | 1966 °C (lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 3727 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 12.41 g/cm3 (lit.) |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Room Temperature |
| solubility | insoluble in acid solutions, slightly soluble in aqua regia |
| form | wire |
| Specific Gravity | 12.41 |
| color | Red |
| Resistivity | 4.33 μΩ-cm, 20°C |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble |
| Merck | 14,8186 |
| Exposure limits |
ACGIH: Ceiling 2 ppm OSHA: Ceiling 5 ppm(7 mg/m3) NIOSH: IDLH 50 ppm; Ceiling 5 ppm(7 mg/m3) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7440-16-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Rhodium(7440-16-6) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Rhodium (7440-16-6) |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 359 GPa |
|---|---|
| Hardness, Vickers | 800 |
| Hardness, Brinell | 722, Converted from Vickers for 3000 kg load/10 mm ball Brinell test. |
| Hardness, Rockwell A | 83, Converted from Vickers. |
| Hardness, Rockwell B | 51, Converted from Vickers. |
| Hardness, Rockwell C | 63, Converted from Vickers. |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS07,GHS08,GHS02 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H315-H319-H228-H413-H332-H335-H373 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P210-P240-P241-P280-P370+P378a-P261-P305+P351+P338-P405-P501a-P260-P314-P304+P340-P312a-P403+P233 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | C,Xi,F | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 36/38-11-36/37/38-36-34-23 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 26-24/25-16-22-36-17-45-36/37/39 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 3089 4.1/PG 2 | |||||||||
| OEB | D | |||||||||
| OEL | TWA: 0.1 mg/m3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | VI9069000 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 4.1 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| HS Code | 7110390000 | |||||||||
| IDLA | 100 mg Rh/m3 | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Rhodium price More Price(63)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 680710 | Rhodium on carbon Evonik NOBLYST? P3053 5% Rh | 7440-16-6 | 1G | ₹6354.28 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 680710 | Rhodium on carbon Evonik NOBLYST? P3053 5% Rh | 7440-16-6 | 5G | ₹18932.93 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 212857 | Rhodium on alumina extent of labeling: 5?wt. % loading, matrix alumina support, powder | 7440-16-6 | 1G | ₹19333.45 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 679488 | Rhodium nanoparticles entrapped in aluminum hydroxide matrix preparation 5 wt. % loading | 7440-16-6 | 1G | ₹5347.55 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 212857 | Rhodium on alumina extent of labeling: 5?wt. % loading, matrix alumina support, powder | 7440-16-6 | 5G | ₹54698.73 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Rhodium Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Rhodium is one of the platinum group elements, and is found at very low concentrations in the Earths crust. Rhodium was discovered by William Hyde Wollaston (England) in 1804. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word rhodon, meaning rose. The plated solid is very corrosion resistant and exceptionally hard. While inert in air and acids, it can produce a violent reaction to chlorine, bromine pentafluoride, bromine trifluoride, and fluorine monoxide.
Chemical Properties
Rhodium, together with platinum, palladium, iridium, ruthenium, and osmium, is one of the platinum-group metals in Group VIII of the Periodic Table. Rhodium metal is a white, hard, ductile, malleable solid with a bluish-gray luster. soluble in ether, alcohol, and water. The alloys of rhodium can also be used in high temperature conditions (i.e., thermocouples and crucibles). It also can be used in electroplating glass products due to its reflective properties.

Physical properties
Rhodium is a hard shiny-white metal that resists corrosion from oxygen, moisture, andacids at room temperatures. As a member of group 8 (VIII), 45Rh shares many chemical andphysical properties with cobalt (27Co) just above it and iridium (77Ir) below it in the verticalgroup. Therefore, it is considered one of the elements that are transitory between metals andnonmetals. It is rare and only found in combination with platinum ores.
Rhodium’s melting point is 1,966°C, its boiling point is 3,727°C, and its density is 12.41g/cm3.
Isotopes
There are 52 isotopes of rhodium, ranging from Rh-89 to Rh-122. All are producedartificially with relatively short half-lives except one stable isotope, Rh-103, whichconstitutes 100% of the element’s existence in the Earth’s crust.
Origin of Name
Named after the Greek word rhodon, which means “rose,” because of the reddish color of its salt compounds.
Occurrence
Rhodium is rare, but not as rare as ruthenium. It makes up only 1 part in 20 million of theelements found in the Earth’s crust. Even so, it is considered the 79th most abundant elementand is found mixed with platinum ore, and to a lesser extent, it is found with copper andnickel ores. It is found in Siberia, South Africa, and Ontario, Canada.
Rhodium is recovered from platinum and other ores by refining and purification processesthat start by dissolving the other platinum group metals and related impurities with strongacids that do not affect the rhodium itself. Any remaining platinum group elements areremoved by oxidation and bathing the mixture in chlorine and ammonia.
Rhodium is usually produced as a powder and can be formed by either casting or powdermetallurgy.
Characteristics
Rhodium is one of the six platinum transition elements that include Ru, Rh, Pd, Os, Ir, andPt. Of these metals, rhodium has the highest electrical and thermal conductivity. Although arelatively scarce metal, rhodium makes an excellent electroplated surface that is hard, wearswell, and is permanently bright—ideal for plating the reflectors in automobile headlights.
History
Wollaston discovered rhodium in 1803-4 in crude platinum ore he presumably obtained from South America. Rhodium occurs native with other platinum metals in river sands of the Urals and in North and South America. It is also found with other platinum metals in the copper-nickel sulfide ores of the Sudbury, Ontario region. Although the quantity occurring here is very small, the large tonnages of nickel processed make the recovery commercially feasible. The annual world production of rhodium in 1999 was only about 9000 kg. The metal is silvery white and at red heat slowly changes in air to the sesquioxide. At higher temperatures it converts back to the element. Rhodium has a higher melting point and lower density than platinum. Its major use is as an alloying agent to harden platinum and palladium. Such alloys are used for furnace windings, thermocouple elements, bushings for glass fiber production, electrodes for aircraft spark plugs, and laboratory crucibles. It is useful as an electrical contact material as it has a low electrical resistance, a low and stable contact resistance, and is highly resistant to corrosion. Plated rhodium, produced by electroplating or evaporation, is exceptionally hard and is used for optical instruments. It has a high reflectance and is hard and durable. Rhodium is also used for jewelry, for decoration, and as a catalyst. Fifty-two and isomers are now known. Rhodium metal (powder) costs about $180/g (99.9%).isotopes
Uses
Rhodium is a transition metal catalyst used in a multitude of inorganic synthesis.
Production Methods
Pure rhodium is prepared by the reduction of its ammonium salt (dichloropentaaminorhodium).
Definition
A rare silvery hard transition metal. It is difficult to work and highly resistant to corrosion. Rhodium occurs native but most is obtained from copper and nickel ores. It is used in protective finishes, alloys, and as a catalyst. Symbol: Rh; m.p. 1966°C; b.p. 3730°C; r.d. 12.41 (20°C); p.n. 45; r.a.m. 102.90550.
General Description
This product has been enhanced for energy efficiency.
Hazard
The powder and dust of rhodium metal are flammable in air. Some of the compounds maycause skin irritations. It is best to use approved laboratory procedures when handling any ofthe six elements in the platinum family of metals.
Health Hazard
There are no data demonstrating acute or chronic rhodium-related diseases; irritation and sensitization have occasionally been reported in humans from exposure to the salts of rhodium. Solutions of insoluble salts splashed in the eye may cause mild irritation.
Industrial uses
Metallic rhodium is the whitest of the platinum metals and does not tarnish under atmospheric conditions. It is insoluble in most acids, including aqua regia, but is attacked by chlorine at elevated temperatures and by hot fuming sulfuric acid. Liquid rhodium dissolves oxygen, and ingots are made by argon-arc melting. At temperatures above 1200 C, rhodium reacts with oxygen to form rhodium oxide, Rh2O3. Rhodium is used to make the nibs of writing pens, to make resistance windings in high-temperature furnaces, for high-temperature thermocouples, as a catalyst, and for laboratory dishes. It is the hardest of the platinum-group metals; the annealed metal has a Brinell hardness of 135. Rhodium is also valued for electroplating jewelry, electric contacts, hospital and surgical instruments, and especially reflectors.
The most important alloys of rhodium are rhodium platinum. They form solid solutions in any proportion, but alloys of more than 40% rhodium are rare. Rhodium is not a potent hardener of platinum but increases its high-temperature strength. It is easily workable and does not tarnish or oxidize at high temperatures. These alloys are used for thermocouples and in the glass industry.
Safety Profile
Handle carefully. It may be a sensitizer but not to the same extent as platinum. Most rholum compounds have only moderate toxicity by ingestion. Flammable when exposed to heat or flame. Violent reaction with chlorine, bromine pentafluoride, bromine trifluoride, and OF2. A catalytic metal
Potential Exposure
Rhodium has few applications by itself, as in rhodium plating of white gold jewelry or plat- ing of electrical parts, such as commutator slip rings, but, mainly, rhodium is used as a component of platinum alloys. Rhodium-containing catalysts have been proposed for use in automotive catalytic converters for exhaust gas cleanup.
Carcinogenicity
Chick embryos exposed to rhodium on the eighth day of incubation were stunted; mild reduction of limb size and feather growth inhibition were also observed. A number of rhodium compounds have tested positive in bacterial assays for genetic altering capability.
Environmental Fate
The most common route by which rhodium enters the environment
is as a component of automobile exhaust resulting
from use of catalytic converters. Rhodium is insoluble in water
and all acids, with the exception that very finely separated
material may be dissolved in concentrated sulfuric acid and
aqua regia.
Being largely inert, rhodium can undergo long-range
transport, and particulate phase matter generally leaves the
atmosphere by wet or dry deposition. In an aqueous environment,
rhodium can form complexes with halide and
nitrogen donor ligands, which may be water soluble, but
reactions can be dictated by pH, redox potential, and what
material is available for creating ligands. Reactions in soil can
depend on these same factors, as well as chloride concentrations, and rhodium is seen to be mobile only in
highly acidic soils.
Rhodium has been seen to bioaccumulate in both fresh and
salt water species, and has the potential to biomagnify.
Shipping
Flammable powder, Hazard Class: 4.1; Labels: 4.1-Flammable solid.
Incompatibilities
Flammable as a dust, fume, or powder may form explosive mixture with air. Incompatible with strong oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanga- nates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); con- tact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides, bromine pentafluoride, and bromine trifluoride; chlorine trifluoride; oxygen difluoride.
Waste Disposal
Recovery in view of the high economic value. Recovery techniques for recycling of rhodium in plating wastes and spent catalysts have been described in the literature.
Rhodium Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JIVICHEM SYNTHESIS PVT LTD | +91-7028392790 +91-7028392790 | Maharashtra, India | 337 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Evans Fine Chem | +91-9821340302 +91-9821340302 | Maharashtra, India | 286 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Arora Matthey Limited | +91-9830058614 +91-9830058614 | West Bengal, India | 24 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Dhara Industries | +91-9322395199 +91-9322395199 | Mumbai, India | 190 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Metal Chem India | +91-8999856889 +91-9011882000 | Maharashtra, India | 46 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Photon Chemicals | +91-9427132074 +91-7700911144 | Maharashtra, India | 26 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Dhara Industries (Formerly known as Karolinska Industries) | 91-9322395199 | Maharashtra, India | 97 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Evonik Catalysts India Pvt Ltd. | 91-251-2471716 | Maharashtra, India | 9 | 58 | Inquiry |
| CHEMSWORTH | +91-261-2397244 | New Delhi, India | 6707 | 30 | Inquiry |
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | +91-22-45045900 | Hyderabad, India | 6351 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| JIVICHEM SYNTHESIS PVT LTD | 58 |
| Evans Fine Chem | 58 |
| Arora Matthey Limited | 58 |
| Dhara Industries | 58 |
| Metal Chem India | 58 |
| Photon Chemicals | 58 |
| Dhara Industries (Formerly known as Karolinska Industries) | 58 |
| Evonik Catalysts India Pvt Ltd. | 58 |
| CHEMSWORTH | 30 |
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | 58 |
Related articles
- Rhodium: Major Minerals, Chemistry properties and Major Uses
- Rhodium is a rare, silvery-white, hard transition metal.
- May 29,2024
- Rhodium: Versatile Metal with Applications in Biology, Industry, and Safety Considerations
- Rhodium finds versatile applications in industries due to its corrosion resistance and biological attributes. Safety precautio....
- Dec 27,2023
- Rhodium complexes: activities and toxicity
- Rhodium complexes inhibit Aβ aggregation, JAK2 activity, and PPIs. More research needed for efficacy and safety. Cytotoxicity ....
- Aug 11,2023





