Carbon
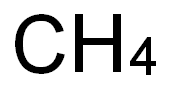
- CAS No.
- 7440-44-0
- Chemical Name:
- Carbon
- Synonyms
- CHARCOAL;TOC;PIGMENT BLACK 7;ACETYLENE BLACK;Darco;CARBON NANOTUBES;Active carbon;CHARCOAL ACTIVATED;DARCO G60;Reduced Graphene Oxide
- CBNumber:
- CB9767902
- Molecular Formula:
- C
- Molecular Weight:
- 12.011
- MOL File:
- 7440-44-0.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/6/15 22:11:33
| Melting point | 3550 °C (lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 500-600 °C(lit.) |
| Density | ~1.7 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor pressure | <0.1 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| Flash point | >230 °F |
| storage temp. | no restrictions. |
| solubility | Insoluble. |
| form | rod |
| Specific Gravity | 1.8~2.1 (amorphous) |
| color | Black |
| PH | 6-9 |
| Odor | at 100.00?%. odorless |
| Resistivity | 1375 μΩ-cm, 20°C (graphite) |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble in water. |
| Merck | 14,1807 |
| BRN | 4360473 |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. Combustible. Highly flammable in powdered form. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7440-44-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Carbon(7440-44-0) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Carbon (7440-44-0) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS02 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H251 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P235-P280-P403+P235-P407-P420 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | F,Xn,Xi | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 36/37-36/37/38-20-10-11 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 26-36-24/25-22-36/37 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 1325 4.1/PG 3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | FF5250100 | |||||||||
| Autoignition Temperature | 842 °F | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 4.2 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| HS Code | 38021000 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 intravenous in mouse: 440mg/kg | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Carbon price More Price(509)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | C9157 | Activated charcoal suitable for cell culture, suitable for plant cell culture | 7440-44-0 | 500G | ₹5888.8 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | C7606 | Activated Charcoal meets USP testing specifications | 7440-44-0 | 125G | ₹5585.7 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | C9157 | Activated charcoal suitable for cell culture, suitable for plant cell culture | 7440-44-0 | 2.5KG | ₹18229.3 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | C7606 | Activated Charcoal meets USP testing specifications | 7440-44-0 | 500G | ₹12838.45 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | C7606 | Activated Charcoal meets USP testing specifications | 7440-44-0 | 2.5KG | ₹54882.75 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Carbon Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
All our SWNTs come packed as dry powders, which can be dispersed within the user's solvent of choice.
Chemical Properties
Carbon, C, is a nonmetallic element, grey solid. It is found in nature as graphite (specific gravity2.25), diamond(specific gravity 3.51), and coal (specific gravity 1.88). Carbon is found in all living things, is insoluble in common solvents,and forms an almost infinite numberof organic compounds. Anaturally occurring radioactive isotope,14C, has a half-life of 5780 years and is used in archaeo logical investigations to date artifacts and ancient documents. Other uses of carbon depend on its form. For example, diamonds for jewels and abrasives,graphite for lubricants, activated carbon to absorb color and gases, and wood carbon for fuel are some common examples.
Isotopes
There are 15 isotopes of carbon, two of which are stable. Stable carbon-12makes up 98.89% of the element’s natural abundance in the Earth’s crust, and carbon-13 makes up just 1.11% of carbon’s abundance in the Earth’s crust. All the otherisotopes of carbon are radioactive with half-lives varying from 30 nanoseconds (C-21) to5,730 years (C-14).
Origin of Name
Carbon’s name is derived from the Latin word carbo, which means, “charcoal.”
Occurrence
Carbon is the 14th most abundant element, making up about 0.048% of the Earth’s crust.It is the sixth most abundant element in the universe, which contains 3.5 atoms of carbonfor every atom of silicon. Carbon is a product of the cosmic nuclear process called fusion,through which helium nuclei are “burned” and fused together to form carbon atoms withthe atomic number 12. Only five elements are more abundant in the universe than carbon:hydrogen, helium, oxygen, neon, and nitrogen.
Characteristics
Carbon is, without a doubt, one of the most important elements on Earth. It is the majorelement found in over one million organic compounds and is the minor component in mineralssuch as carbonates of magnesium and calcium (e.g., limestone, marble, and dolomite),coral, and shells of oysters and clams.The carbon cycle, one of the most essential of all biological processes, involves the chemicalconversion of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates in green plants by photosynthesis.
Animalsconsume the carbohydrates and, through the metabolic process, reconvert the carbohydratesback into carbon dioxide, which is returned to the atmosphere to continue the cycle.
Uses
Crucibles, retorts, foundry facings, molds, lubricants, paints and coatings, boiler compounds, powder glazing, electrotyping, monochromator in X-ray diffraction analysis, fluorinated graphite polymers with fluorine-to-carbon ratios of 0.1–1.25, electrodes, bricks, chemical equipment, motor and generator brushes, seal rings, rocket nozzles, moderator in nuclear reactors, cathodes in electrolytic cells, pencils, fibers, self-lubricating bearings, intercalation compounds.
Definition
The crystalline allotropic form of carbon.
General Description
Black grains that have been treated to improve absorptive ability. May heat spontaneously if not properly cooled after manufacture.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Dust is explosive when exposed to heat or flame. Freshly prepared material can heat and spontaneously ignite in air. The presence of water assists ignition, as do contaminants such as oils. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Carbon is incompatible with very strong oxidizing agents such as fluorine, ammonium perchlorate, bromine pentafluoride, bromine trifluoride, chlorine trifluoride, dichlorine oxide, chlorine trifluoride, potassium peroxide, etc. . Also incompatible with air, metals, unsaturated oils. [Lewis].
Hazard
(Powder, natural) Fire risk.
Health Hazard
Fire may produce irritating and/or toxic gases. Contact may cause burns to skin and eyes. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Runoff from fire control may cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
Flammable/combustible material. May be ignited by friction, heat, sparks or flames. Some may burn rapidly with flare burning effect. Powders, dusts, shavings, borings, turnings or cuttings may explode or burn with explosive violence. Substance may be transported in a molten form at a temperature that may be above its flash point. May re-ignite after fire is extinguished.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by intravenous route. Experimental reproductive effects. It can cause a dust irritation, particularly to the eyes and mucous membranes. See also CARBON BLACK, SOOT. Combustible when exposed to heat. Dust is explosive when exposed to heat or flame or oxides, peroxides, oxosalts, halogens, interhalogens, 02, (NH4NO3 + heat), (NH4ClO4 @ 240°), bromates, Ca(OCl)2, chlorates, (Cla + Cr(OCl)2), Cl0, iodates, 105, Pb(NO3)~, HgNO3, HNO3, (oils + air), (K + air), NaaS, Zn(NO3)a. Incompatible with air, metals, oxidants, unsaturated oils.
Potential Exposure
Natural graphite is used in foundry facings, steel making lubricants, refractories, crucibles, pencil “lead,” paints, pigments, and stove polish. Artificial graphite may be substituted for these uses with the excep tion of clay crucibles; other types of crucibles may be pro duced from artificial graphite. Additionally, it may be used as a high temperature lubricant or for electrodes. It is uti lized in the electrical industry in electrodes, brushes, con tacts, and electronic tube rectifier elements; as a constituent in lubricating oils and greases; to treat friction elements, such as brake linings; to prevent molds from sticking together; and in moderators in nuclear reactors. In addition, concerns have been expressed about synthetic graphite in fibrous form. Those exposed are involved in production of graphite fibers from pitch or acrylonitrile fibers and the manufacture and use of composites of plastics, metals, or ceramics reinforced with graphite fibers.
Shipping
UN1362 Carbon, activated, Hazard Class: 4.2; Labels: 4.2-Spontaneously combustible material, International.
Purification Methods
Charcoal (50g) is added to 1L of 6M HCl and boiled for 45minutes. The supernatant is discarded, and the charcoal is boiled with two more lots of HCl, then with distilled water until the supernatant no longer gives a test for chloride ion. The charcoal (now phosphate-free) is filtered onto a sintered-glass funnel and air dried at 120o for 24hours. [Lippin et al. J Am Chem Soc 76 2871 1954.] The purification can be carried out using a Soxhlet extractor (without cartridge), allowing longer extraction times. Treatment with conc H2SO4 instead of HCl has been used to remove reducing substances.
Incompatibilities
Graphite is a strong reducing agent and reacts violently with oxidizers, such as fluorine, chlorine trifluoride, and potassium peroxide. Forms an explosive mixture with air. May be spontaneously combustible in air.
Waste Disposal
Do not incinerate. Carbon (graphite) fibers are difficult to dispose of by incineration. Waste fibers should be packaged and disposed of in a land fill authorized for the disposal of special wastes of this nature, or as otherwise may be required by law.
Carbon Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
1of5
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANJI BIOSCIENCES | +91-9000100077 +91-9000100077 | Hyderabad, India | 430 | 58 | Inquiry |
| ADVENT CHEMBIO PRIVATE LIMITED | +91-9821524116 +91-9821524116 | Mumbai, India | 353 | 58 | Inquiry |
| JUVENUS DRUGS | +91-9655606404 +91-9655606404 | Tamil Nadu, India | 94 | 58 | Inquiry |
| UNILOSA INTERNATINAL PRIVATE LIMITED | +91-9999069917 +91-9999069917 | New Delhi, India | 152 | 58 | Inquiry |
| JSK Chemicals | +919879767970 | Gujarat, India | 3756 | 58 | Inquiry |
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | +91-22-45045900 | Hyderabad, India | 6351 | 58 | Inquiry |
| FINAR LTD | +91 - 2717 - 616717 | New Delhi, India | 660 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Scientific OEM | +91-22- 2343 7546 / 2341 3094 | New Delhi, India | 1996 | 38 | Inquiry |
| ALPHA CHEMIKA | +91-22-22061123 +91-22-66382501 | Mumbai, India | 1681 | 43 | Inquiry |
| Sisco Research Laboratories Pvt. Ltd. | +91-22-4268 5800 | Mumbai, India | 4317 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| ANJI BIOSCIENCES | 58 |
| ADVENT CHEMBIO PRIVATE LIMITED | 58 |
| JUVENUS DRUGS | 58 |
| UNILOSA INTERNATINAL PRIVATE LIMITED | 58 |
| JSK Chemicals | 58 |
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | 58 |
| FINAR LTD | 58 |
| Scientific OEM | 38 |
| ALPHA CHEMIKA | 43 |
| Sisco Research Laboratories Pvt. Ltd. | 58 |
Related articles
- The isotopes of Carbon
- Carbon isotopes are atomic nuclei with 6 protons plus several neutrons (between 2 and 16). Carbon has two stable, naturally oc....
- May 27,2024
- How to Prepare Corn Cob Activated Carbon
- Corn cob is a rich biomass resource, and many studies have been conducted on its various applications.
- Feb 4,2024
- Carbon:Occurrence,Uses,Reactions
- Carbon is the 15th most abundant element in the Earth's crust, and the fourth most abundant element in the universe by mass af....
- Feb 28,2023
7440-44-0(Carbon)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




