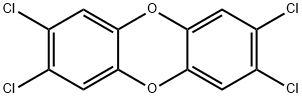
2,3,7,8-테트라클로로디벤조-P-디옥신
|
|
2,3,7,8-테트라클로로디벤조-P-디옥신 속성
- 녹는점
- 284-287°C
- 끓는 점
- 407.62°C (rough estimate)
- 밀도
- 1.6430 (estimate)
- 증기압
- 340 at 25 °C (Rodorf, 1985)
- 굴절률
- 1.6430 (estimate)
- 인화점
- 4 °C
- 저장 조건
- Refrigerator
- 용해도
- Chloroform: Slightly soluble
- 물리적 상태
- 무색 고체 또는 결정
- 색상
- 무색~백색 바늘
- 수용성
- 0.0193ug/L(22℃)
- Henry's Law Constant
- 5.40 at 20 °C (approximate - calculated from water solubility and vapor pressure)
- 노출 한도
- An IDLH of 1 ppb was recommended by Schroy et al. (1985).
- CAS 데이터베이스
- 1746-01-6(CAS DataBase Reference)
- IARC
- 1 (Vol. Sup 7, 69, 100F) 2012
안전
- 위험 및 안전 성명
- 위험 및 사전주의 사항 (GHS)
| 위험품 표기 | F,Xn | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 위험 카페고리 넘버 | 11-38-48/20-63-65-67 | ||
| 안전지침서 | 36/37-62-46 | ||
| 유엔번호(UN No.) | 2811 | ||
| WGK 독일 | 3 | ||
| 위험 등급 | 6.1(a) | ||
| 포장분류 | I | ||
| 유해 물질 데이터 | 1746-01-6(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| 독성 | LD50 in male, female rats (mg/kg): 0.022, 0.045 orally (Schwetz) |
2,3,7,8-테트라클로로디벤조-P-디옥신 C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
화학적 성질
White Solid용도
A toxic polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin detected in domestic meat and poultry.일반 설명
White crystals or tan crystalline powder.공기와 물의 반응
Insoluble in water.반응 프로필
2,3,7,8-TETRACHLORODIBENZO-P-DIOXIN reaacts when exposed to ultraviolet light in solution in isooctane or n-octanol. Undergoes catalytic perchlorination .건강위험
Chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (CDDs) cause chloracne, may cause hepatotoxicity, immunotoxicity, reproductive toxicity, developmental toxicity, and central nervous system toxicity, and are considered to be a human carcinogen.The most obvious health effect in humans for exposure to CDDs is chloracne, a severe skin disease characterized by follicular hyperkeratosis (comedones) occurring with or without cysts and pustules.2–4 Unlike adolescent acne, chloracne may affect almost every follicle in an involved area, and it may be more disfiguring than adolescent acne.
화재위험
Literature sources indicate that 2,3,7,8-TETRACHLORODIBENZO-P-DIOXIN is nonflammable.Pharmacology
TCDD and other chlorinated dibenzodioxins, dibenzofurans, and planar PCBs are thought to operate through a common mechanism. For humans and rodents, there is an initial binding to the aryl hydrocarbon (Ah) receptor. Binding to the receptor is a necessary (but not sufficient) event for the biological response. TCDD induces many responses, including induction of gene expression, altered metabolism, altered cell growth and differentiation, and disruption of steroid hormone and growth factor signal transduction pathways. The very diversity of tissue-selective and species-selective responses elicited by TCDD requires that the receptor (Ah) is part of a multicomponent system, and it is unlikely that the differences in dose-response are related solely to differences in Ah receptor concentrations or affinities in various species or tissues (29). It is considered that there is an inducible protein-binding site in the liver (30,31) known as CYP1A1 (30–34) because TCDD was not sequestered in the liver of transgenic mice that lack P450 1A2 gene.Safety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic, neoplastigenic, tumorigenic, and teratogenic data. One of the most toxic synthetic chemicals. A deadly experimental poison by ingestion, skin contact, and intraperitoneal routes. Human systemic effects by skin contact: allergic dermatitis. Experimental reproductive effects. Human mutation data reported. An eye irritant. TCDD is the most toxic member of the 75 dioxins. It causes death in rats by hepatic cell necrosis. Death can follow a lethal dose by weeks. Acute and subacute exposure result in wasting, hepatic necrosis, thymic atrophy, hemorrhage, lymphoid depletion, chloracne. A by-product of the manufacture of polychlorinated phenols. It is found at low levels in 2,4,5-T, 2,4,5-trichlorophenol, and hexachlorophene. It is also formed during various combustion processes. Incineration of chemical wastes, including chlorophenols, chlorinated benzenes, and biphenyl ethers, may result in the presence of TCDD in flue gases, fly ash, and soot particles. It is immobile in contaminated soil and may be retained for years. TCDD has the potential for bio-accumulation in animals. An accident in Seveso, Italy, and inadvertent soil contamination in Mmouri have resulted in abandonment of the contaminated areas. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Cl-.잠재적 노출
TCDD is primarilly a research chemical. As noted above, TCDD is an inadvertent contaminant in herbicide precursors and thus in the herbicides themselves. It is also formed during various combustion processes including the incineration of chemical wastes (chlorophenols, chlorinated benzenes, and biphenyl ethers). It may be found in flue gases, fly ash, and soot particles. It is highly persistent in soil, and contamination may be retained for years. TCDD is the most toxic of all the dioxins, and has the potential for bio-accumulation in animals. Thus, it is applied in herbicide formulations, but is not used per se. It has been estimated that approximately 2 million acres in the United States have been treated for weed control on one or more occasions with approximately 15 million pounds of TCDD contaminated 2,4,5,-T, 2,4,-D, or combinations of the two.Carcinogenicity
2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) is known to be a human carcinogen based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in humans, both epidemiological and on the mechanism of carcinogenesis. TCDD was first listed in the Second Annual Report on Carcinogens as reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen. Subsequently, a number of studies were published that examined cancer in human populations exposed to TCDD occupationally or through industrial accidents. A concerted research effort examined the molecular and cellular events that occur in tissues of humans and animals exposed to TCDD. Based on the new information, the listing was revised to known to be a human carcinogen in the January 2001 addendum to the Ninth Report on Carcinogens.신진 대사
Absorption. TCDD is retained in all tissues. The highest retention is in fat and liver. Penetration values into human skin are low. For example, a dose of 6.5 ng/cm2 in acetone gave a rate of 5 g/cm2/h. Transfer to the fetus has been observed (43). Absorption rates after single dose in the diet were 50 to 70–90% (44–48). Rates in rats were lower (50–60%) when administered in the diet for more than 6 weeks (49), compared with a single-dose absorption rate of 70% (46).Distribution. The major storage sites are liver and adipose tissue. The skin can act as an important storage site, and high concentrations can also be found in the adrenals (1). After one day of exposure for rats, mice, hamsters and guinea pigs, 25–70% of the dose was stored in the liver (41).
Excretion. Excretion is mostly fecal. Breast milk can be a route of elimination. Whole body half-lives were from 17 to 31 days in rat studies (46–52). Mice had lower halflives (53,54). Female rhesus monkeys with four years of dietary exposure had a longer half-life (391 days) (55,56). These half-lives are very fast considering human half-lives of 5.8–11.3 years (cited earlier).
비 호환성
Decomposes in ultraviolet (UV) light.2,3,7,8-테트라클로로디벤조-P-디옥신 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
준비 용품
2,3,7,8-테트라클로로디벤조-P-디옥신 관련 검색:
2,3,7,8-테트라클로로디벤조-P-디옥신 설프로포스 헥사클로로디벤조디옥신
1,2,3,4,7,8-HEXACHLORODIBENZO-P-DIOXIN
1,2,3,4,6,7,8,9-OCTACHLORODIBENZO-P-DIOXIN
1,2,3,7,8-PENTACHLORODIBENZO-P-DIOXIN
1,2,3,4,6,7,8-HEPTACHLORODIBENZO-P-DIOXIN
1,2,7,9-Tetrachlorooxanthrene,1,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-para-dioxin,1,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-4-dioxin
1,2,3,4-Tetrachlorodibenzo-para-dioxin,1,2,3,4-Tetrachlorooxanthrene
1,2,3,7,8,9-HEXACHLORODIBENZO-P-DIOXIN
1,3,7,9-TETRACHLORODIBENZO-P-DIOXIN
1,3,6,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-para-dioxin,1,3,6,8-Tetrachlorooxanthrene
TETRACHLORODIBENZO-PARA-DIOXIN,1,2,6,7-TETRACHLORODIBENZO-P-DIOXIN
1,2,6,8-TETRACHLORODIBENZO-P-DIOXIN
1,2,7,8-TETRACHLORODIBENZO-PARA-DIOXIN,2,3,6,7-TETRACHLORODIBENZO-PARA-DIOXIN
DIBENZO-P-DIOXIN
1,3,7,9-TETRACHLORODIBENZO-PARA-DIOXIN
1,2,3,7-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin