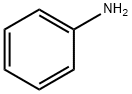
아닐린 C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
물성
순수한 아닐린은 상온에서 특유의 냄새가 나고 무색투명한 액체 상태로 존재한다. 그러나 공기 중에서는 서서히 붉게 변하고 마지막에는 불투명한 흑색으로 변하게 된다. 끓는점은 184°C, 녹는점은 -6°C이다. 밀도는 1.0215g/ml이다. 인화점은 76°C이다. 물에는 약간 녹고 에탄올, 에테르, 벤젠 등의 유기 용매에는 잘 녹는다. 알칼리 금속이나 알칼리 토금속을 아닐린에 녹이면 수소가 발생하면서 C6H5HNNa 등의 금속 화합물이 생성된다.
용도
아닐린은 다음과 같은 용도로 사용된다. 용매: 구두약, 향료의 제조 원료. 우레탄 중합체의 원료. 제초제, 살충제, 곰팡이 제거제의 원료. 알루미늄, 크롬(III), 철(III), 납 등의 정량 시약.
안전성
아닐린은 강력한 독성이 있기 때문에 취급에 주의해야 한다. 아닐린은 헤모글로빈과 결합하여 산소의 운반을 방해한다. 지속적인, 또는 반복적인 노출은 식욕감소, 빈혈, 체중감소, 신경계 이상, 신장 이상, 간이나 연골의 손상을 야기할 수 있다. 흡입하거나 피부를 통해서 흡수될 경우 중독을 일으킬 수 있다. 아닐린을 보관할 때는 마개를 단단히 막아 어두운 곳에 두어야 한다.
개요
First produced in 1826 by Otto Unverdorben through
destructive distillation of indigo, the first industrial use
was as a purple dye, Mauveine, formulated by William
Henry Perkin accidentally in an attempt to isolate quinone.
The name aniline was given in deference to the indigoyielding
plant, Indigofera suffruticosa, commonly named
anil.
화학적 성질
Aniline,C6H5NH2, is slightly soluble in water,miscible in alcohol and ether,and turns yellow to brown in air. Aniline may be made(1) by the reduction, with iron or tin in HCI, of nitrobenzene, and(2) by the amination of chlorobenzene by heating with ammonia to a high temperature corresponding to a pressure of over 200 atmospheres in the presence of a catalyst(a mixture of cuprous chlorideandoxide).Aniline is the end point of reduction of most mononitrogen substituted benzene nuclei,as nitro benzene beta-phenyl hydroxylamine, azoxybenzene, azobenzene, hydrazobenzene. Aniline is detected by the violet coloration produced by a small amountof sodium hypochlorite. Aniline is used as a solvent, in the preparation of compound in the manufacture of dyes and their intermediates, and in the manufacture of medicinal chemicals.
물리적 성질
Colorless, oily liquid with a faint ammonia-like odor and burning taste. Gradually becomes yellow
to reddish-brown on exposure to air or light. The lower and upper odor thresholds are 2 and 128
ppm, respectively (quoted, Keith and Walters, 1992). An odor threshold of 1.0 ppm
v was reported
by Leonardos et al. (1969).
용도
A thin, colorless oil prepared by reducing benzene with iron
filings in the presence of hydrochloric or acetic acid and then
separating the aniline formed by distillation. It is slightly
soluble in water but dissolves easily in alcohol, ether, and
benzene. Aniline is the base for many dyes used to increase
the sensitivity of emulsions.
정의
ChEBI: A primary arylamine in which an amino functional group is substituted for one of the benzene hydrogens.
생산 방법
Aniline was obtained in 1826 by Unverdorben from distillation of indigo and was given the name aniline in 1841 by Fritzsche (Windholz et al 1983). The chemical was manufactured in the U. S. by the Bechamp reaction involving reduction of nitrobenzene in the presence of either copper/silica or hydrochloric acid/ferrous chloride catalysts; but in 1966, amination of chlorobenzene with ammonia was introduced (IARC 1982; Northcott 1978). Currently, aniline is produced in the U.S., several European countries and Japan by the catalytic hydrogenation of nitrobenzene in either the vapor phase or solvent system. This chemical is also produced by reacting phenol with ammonia (HSDB 1989). Production in 1982 amounted to 331,000 tons (HSDB 1989).
일반 설명
A yellowish to brownish oily liquid with a musty fishy odor. Melting point -6°C; boiling point 184°C; flash point 158°F. Denser than water (8.5 lb / gal) and slightly soluble in water. Vapors heavier than air. Toxic by skin absorption and inhalation. Produces toxic oxides of nitrogen during combustion. Used to manufacture other chemicals, especially dyes, photographic chemicals, agricultural chemicals and others.
공기와 물의 반응
Darkens on exposure to air and light. Polymerizes slowly to a resinous mass on exposure to air and light. Slightly soluble in water.
위험도
An allergen. Toxic if absorbed through the
skin. Combustible. Skin irritant. Questionable car-
cinogen.
건강위험
Aniline is a moderate skin irritant, a moderate to severe eye irritant, and a skin sensitizer
in animals. Aniline is moderately toxic via inhalation and ingestion. Symptoms of
exposure (which may be delayed up to 4 hours) include headache, weakness, dizziness,
nausea, difficulty breathing, and unconsciousness. Exposure to aniline results in the
formation of methemoglobin and can thus interfere with the ability of the blood to
transport oxygen. Effects from exposure at levels near the lethal dose include
hypoactivity, tremors, convulsions, liver and kidney effects, and cyanosis.
Aniline has not been found to be a carcinogen or reproductive toxin in humans. Some
tests in rats demonstrate carcinogenic activity. However, other tests in which mice,
guinea pigs, and rabbits were treated by various routes of administration gave negative
results. Aniline produced developmental toxicity only at maternally toxic dose levels but
did not have a selective toxicity for the fetus. It produces genetic damage in animals and
in mammalian cell cultures but not in bacterial cell cultures.
화재위험
Combustion can produce toxic fumes including nitrogen oxides and carbon monoxide. Aniline vapor forms explosive mixtures with air. Aniline is incompatible with strong oxidizers and strong acids and a number of other materials. Avoid heating. Hazardous polymerization may occur. Polymerizes to a resinous mass.
인화성 및 폭발성
Aniline is a combustible liquid (NFPA rating = 2). Smoke from a fire involving
aniline may contain toxic nitrogen oxides and aniline vapor. Toxic aniline vapors are
given off at high temperatures and form explosive mixtures in air. Carbon dioxide or
dry chemical extinguishers should be used to fight aniline fires.
화학 반응
Reactivity with Water No reaction; Reactivity with Common Materials: No reaction; Stability During Transport: Stable; Neutralizing Agents for Acids and Caustics: Flush with water and rinse with dilute acetic acid; Polymerization: Not pertinent; Inhibitor of Polymerization: Not pertinent.
잠재적 노출
Aniline is widely used as an intermediate
in the synthesis of dyestuffs. It is also used in the
manufacture of rubber accelerators and antioxidants, pharmaceuticals,
marking inks; tetryl, optical whitening agents;
photographic developers; resins, varnishes, perfumes, shoe
polishes, and many organic chemicals.
Carcinogenicity
The IARC has classified aniline as a Group 3 carcinogen,
that is, not classifiable as to its carcinogenicity. However,
NIOSH has determined that there is sufficient evidence
to recommend that OSHA require labeling this substance a
potential occupational carcinogen. This position followed an
evaluation of a high-dose feeding study of aniline hydrochloride in F344 rats and B6C3F1 mice (3000 or
6000 ppm and 6000 or 12,000 ppm, respectively). The test
was negative in both sexes of mice; however, hemangiosarcomas
of the spleen and combined incidence of fibrosarcomas
and sarcomas of the spleen were statistically significant
in the male rats; the number of female rats having fibrosarcomas
of the spleen was also significant.
비 호환성
May form explosive mixture with air.
Unless inhibited (usually methanol), aniline is readily able
to polymerize. Fires and explosions may result from contact
with halogens, strong acids; oxidizers, strong base organic
anhydrides; acetic anhydride, isocyanates, aldehydes,
sodium peroxide. Strong reaction with toluene diisocyanate.
Reacts with alkali metals and alkali earth metals. Attacks
some plastics, rubber and coatings; copper and copper
alloys.
폐기물 처리
Consult with environmental
regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal
practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing
storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal.
Incineration with provision for nitrogen oxides removal from
flue gases by scrubber, catalytic or thermal device.
아닐린 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
준비 용품
N-PHENYLISONICOTINAMIDE
Modified MDI
2-아닐리노에탄올
적색 208 염료
Acid Black 234
Direct Dark Brown NM
Direct Bordeaux NGB
염산 아닐린
1,3-Diphenylurea
2,4,6-트라이클로로아닐린
Pigment Red 175
항-산화제 RD
UREA, N-(2,6-DIMETHYLPHENYL)-N'-[IMINO(METHYLAMINO)METHYL]-
N-페닐-1-나프틸아민
자색 005 반응염료
2-CHLOROMALONALDEHYDE
3-히드록시디페닐아민
산성블랙26
4-N-DECYLANILINE
N,N-비스(시아노에틸)아닐린
Direct Orange S
라나솔블루3R
C.I. 솔벤트 BLACK 5
3-BROMOPYRIDINE-2-CARBOXYLIC ACID
디사이클로헥실아민
산성황색79
Disperse Scarlet S-3GFL
4-하이드록시-2-(트리플루오로로메틸)퀴놀린
N,N'-다이페닐-파라-페닐렌다이아민
C.I. 리엑티브 블루 222
다이렉트그린89
N-페닐-2-나프틸아민
4-브로모-2-(트리플루오로메틸)퀴놀린
8-아닐리노-1-나프탈렌술폰 산
페닐하이드라지늄설페이트(2:1)
4,4'-비스((4-아닐리노-6-(비스(2-하이드록시에틸)아미노)-1,3,5-트리아진-2-일)아미노) 스틸벤-2,2'-디설 폰산
2 BASIC ORANGE 2
Bronze Red
sodium dibenzyl amine enzene sulfonate
용제 황색 14