|
|
| | Rhodium(III) chloride hydrate Basic information |
| | Rhodium(III) chloride hydrate Chemical Properties |
| Melting point | 100 °C (dec.)(lit.) | | storage temp. | Store below +30°C. | | solubility | Methanol (Slightly), Water (Slightly) | | form | crystalline | | color | White to off-white | | Water Solubility | soluble | | Sensitive | Hygroscopic | | Merck | 14,8188 | | Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 0.01 mg/m3
NIOSH: IDLH 2 mg/m3; TWA 0.001 mg/m3 | | Stability: | hygroscopic | | InChIKey | HSSMNYDDDSNUKH-UHFFFAOYSA-K | | CAS DataBase Reference | 20765-98-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| Hazard Codes | Xn,Xi | | Risk Statements | 22-41 | | Safety Statements | 26-36/39 | | RIDADR | 1759 | | WGK Germany | 3 | | TSCA | Yes | | HS Code | 28439000 |
| | Rhodium(III) chloride hydrate Usage And Synthesis |
| Chemical Properties | red-brown to dark brown crystalline powder, easily soluble in water, hydrochloric acid, alcohol and alkali solution, insoluble in ether and aqua regia, lose crystal water by strong heat and become insoluble, and then decompose into rhodium and chlorine. | | Uses | Rhodium(III) chloride hydrate is used as a catalyst to prepare acetic acid. It is also used as a catalyst for the isomerization of alkenes, the reduction of aromatic rings, the oxidation ofalkenes, the hydration of acetylene. It is involved in the hydrosilylation of α,β-unsaturated esters to form dimethylketene trimethylsilyl acetals. | | Application | Rhodium(III) chloride is often used in synthetic chemistry as a hydrogenation catalyst. Rhodium(III) chloride is also used to make transition metal complexes, some of which are used as reagents in the decarbonylation dehydration reactions of fatty acids to alkenes. | | Reactions | Catalyst in conjunction with "pybox" for the asymmetric hydrosilylation of ketones.
C-C bond forming reactions.
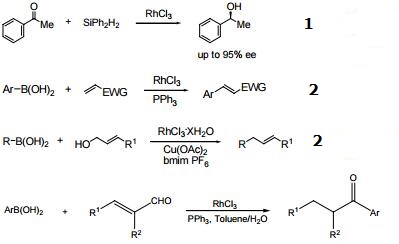 |
| | Rhodium(III) chloride hydrate Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|