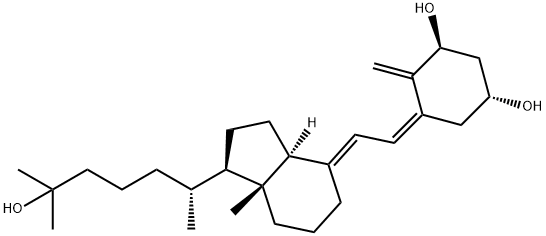
Calcitriol: Function, Mechanism of Action and Side Effects
May 6,2024
Function of Calcitriol
Calcitriol is an active metabolite of vitamin D and a vitamin D receptor (VDR) agonist. It has the effect of helping the body use more calcium from food or supplements and regulating the body's parathyroid hormone production. Often sold as tablets or capsules, it is used to treat hypocalcaemia, osteoporosis, and to prevent corticosteroid-induced osteoporosis. The FDA has approved systemic calcitriol for the control of hypocalcaemia in patients on chronic renal dialysis, secondary hyperparathyroidism in patients with chronic kidney disease who are not yet on dialysis, and hypocalcaemia in patients with hypoparathyroidism and pseudohyperparathyroidism. In addition, studies have shown that it has anticancer, antidepressant and neuroprotective effects. However, it lacks sufficient clinical therapeutic proof and is in the pre-development stage. Topical Calcitriol ointment is also used to treat mild to moderate plaque psoriasis. Calcitriol has also been used systemically for the treatment of conditions other than those specified, including type 1, vitamin D-dependent rickets and pseudo-vitamin D-deficiency rickets.
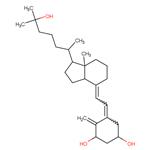
Mechanism of Action
Calcitriol is a vitamin D receptor (VDR) agonist that regulates the expression of hundreds of human genes by activating the VDR. In vivo, calcitriol binds to the VDR in the kidneys, parathyroid glands, intestines, and bones to increase serum blood calcium levels by promoting intestinal absorption, renal tubular reabsorption, and skeletal release. Calcitriol is a transcription factor encoding a calcium-binding protein that transports both calcium and phosphorus ions to intestinal epithelial cells. Together with parathyroid hormone, calcitriol stimulates bone resorption by activating osteoclasts through the release of the nuclear factor kappa-B ligand receptor activator of osteoblasts (RANKL). Calcitriol was found to significantly inhibit the proliferation of normal human epidermal keratinocytes and T-lymphocytes by inducing apoptosis and suppressing gene expression of chemokines and epidermal proteins involved in psoriasis.
Recently, it has been found that VDR-mediated transcriptional regulation does not fully explain the various phenotypic effects of calcitriol. calcitriol also appears to regulate the mitochondrial large conductance calcium-modulated potassium channel, a novel target of calcitriol. In addition, Calcitriol inhibits P2X7R/NLRP3/caspase-1 signalling, thereby attenuating LPS-induced microglia activation and exerting antidepressant and neuroprotective effects.
Side Effects of Calcitriol
Common side effects of Calcitriol include: dry mouth, headache, loss of appetite, metallic taste in the mouth, upset stomach. They are usually not too serious and resolve on their own. Other possible serious side effects include:
High phosphorus levels: back/bone/joint/muscle pain, numbness and tingling around the mouth.
Hypercalcaemia: increased thirst or urination, nausea, vomiting, confusion, unusual weakness or fatigue, sensory disturbances, apathy, renal calcium deposits, urinary tract infections and high blood pressure.
Altered heart rhythm: rapid or irregular heartbeat, dizziness, lightheadedness or lightheadedness, chest pain, and dyspnoea.
Allergic reactions: rash, itching, hives, swelling of the face, lips, tongue or throat.
References:
[1] ANNA M OLSZEWSKA. Mitochondrial potassium channels: A novel calcitriol target.[J]. Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters, 2022. DOI:10.1186/s11658-021-00299-0.
[2] CHANGSHUI WANG. Calcitriol attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation and depressive-like behaviors by suppressing the P2X7R/NLRP3/caspase-1 pathway.[J]. Psychopharmacology, 2024. DOI:10.1007/s00213-024-06565-1.
[3] KHUZAMA A ALJUNIDEE; Sanaa K B. Combination therapy of calcitriol inhibits the proliferation of breast cancer cells: new concept of nonclassical function of calcitriol.[J]. Hormone Molecular Biology and Clinical Investigation, 2021. DOI:10.1515/hmbci-2021-0031.
[4] S. EBRAHIMI. Calcitriol versus Calcitriol and Low Dose Cinacalcet for Treating Severe Secondary Hyperparathyroidism in Hemodialysis Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial[J]. Journal of Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences, 2023. DOI:10.5812/jkums-134173.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- The Mechanism of Calcitriol in Cancer Treatment Jan 30, 2024
Calcitriol regulates cell cycle, induces apoptosis, and promotes cell differentiation, contributing to its anti-cancer effects.
- Calcitriol: Activity, Mechanisms, Application, Toxicity and Contraindications Studies Mar 1, 2023
Calcitriol, the hormonally active form of vitamin D3, It produced in the skin, and dietary vitamin D3 are metabolized first in the liver to 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 and then in the kidney to calcitriol.
- Biological function and synthesis of Calcitriol Jun 17, 2022
Calcitriol is a calciotropic hormone secreted by renal proximal tubular cells. It stimulates intestinal calcium absorption and bone mineralization.
Yes. The therapeutic fluoropyrimidines 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and 5-fluorocytosine (5-FC) have long been used to treat human cancer and severe invasive fungal infections, respectively.....
Nov 1,2024Biochemical EngineeringSilane, (3-isocyanatopropyl)dimethoxymethyl, represents a significant advancement in the field of silane chemistry.....
May 6,2024APICalcitriol
32222-06-3You may like
- Synthesis of Vitamin D from β-Sitosterol
Jul 23, 2024
- What is the effect of Retinoic acid on the skin?
May 8, 2024
- Vitamin A: Properties, Production process and Uses
Mar 13, 2024
- Calcitriol
-
- $0.00 / 10g
- 2024-11-03
- CAS:32222-06-3
- Min. Order: 1g
- Purity: 99.0%min. HPLC
- Supply Ability: 10000
- Calcitriol
-

- $0.00 / 1g
- 2024-11-02
- CAS:32222-06-3
- Min. Order: 1g
- Purity: 99%min;EP
- Supply Ability: 100G
- Calcitriol
-

- $66.00 / 2mg
- 2024-11-01
- CAS:32222-06-3
- Min. Order:
- Purity: 99.64%
- Supply Ability: 10g