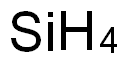Fun Facts About Silicon
May 27,2024
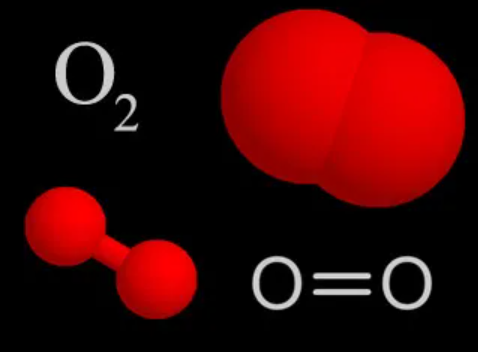
After an attempt to isolate silicon in 1808, Cornish chemist and inventor Sir Humphry Davy (December 17, 1778 to May 29, 1829) suggested the name “silicium” for silicon, from the Latin silex, silicis for flint, and adding the “-ium” ending because he thought it to be a metal (Davy, 1808a). In the universe, Si is the seventh most abundant element, after H, He, C, N, O, and Ne. These abundances are not replicated well on earth due to considerable separation of the elements during the formation of the Solar System. Silicon makes up 27.2% of the earth’s crust by weight, second only to oxygen at 45.5%, with which it always is bonded in nature. Silicon of 96%- 99% purity is produced by reducing quartzite (a metamorphic rock consisting mainly of the mineral quartz) or sand (mainly quartz grains) with highly pure coke.

Major Uses
Most silicon is used industrially without purification and frequently with relatively little processing. More than 90% of the earth’s crust is composed of silicate minerals. Numerous silicate minerals have direct commercial applications, for example, clays, silica sand, and most kinds of building stone. Hence, most uses for silicon are as structural compounds, either as the silicate minerals or silica (crude silicon dioxide).
Silicon forms an important element of electrical steel, modifying its resistivity and ferromagnetic properties. The properties of Si can be utilized to modify alloys with metals other than Fe. “Metallurgical-grade” silicon has between 95% and 99% purity. Approximately 55% of the global use of metallurgical purity Si is used in the manufacture of Al-Si alloys (silumin alloys) for Al part casts, primarily for use in the automotive industry.
Pure Si is an intrinsic semiconductor, which means that different to metals, it conducts electron holes and electrons released from atoms by heat; its electrical conductivity increases with higher temperatures. Pure Si has too low a conductivity (i.e., too high a resistivity) to be applied as a circuit element in electronics. In fact, pure Si is doped with small concentrations of particular other elements, which significantly enhance its conductivity and adjust its electrical response by adjusting the number and charge (positive or negative) of activated carriers. Such control is required for transistors, solar cells, semiconductor detectors, and other semiconductor devices used in the computer industry and other technical uses.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Silicon--diamond cubic crystal structure May 8, 2024
Silicon (Si) is a nonmetallic chemical element in the carbon family. Silicon makes up 27.7 percent of Earth's crust, the second most abundant element, surpassed only by oxygen.
- What is the ionic charge of silicon? Feb 7, 2024
Silicon typically forms ions with a charge of +4. This means it can lose four electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration similar to that of noble gases.
Oxygen constitutes 49.2% of the Earth's crust by mass as part of oxide compounds such as silicon dioxide, and SiO2, and is the most abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust.....
May 27,2024Inorganic chemistrySulfamic Acid Cleaner contains concentrated crystals that mix with water to make a mild, safe-to-use acid cleaner. Removes dried Portland cement, grout haze, and mortar residue from tile, concrete, and masonry.....
May 27,2024Organic AcidsSilicon
7440-21-3You may like
- The niobium oxide nanomaterials
Jul 4, 2024
- Rhenium:Discovery,Minerals,Chemistry,Uses,Toxicity
May 31, 2024
- How are Lead Minerals Distributed?
May 31, 2024
- Silicon powder
-

- $100.00 / 25kg
- 2023-05-31
- CAS:7440-21-3
- Min. Order: 25kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 500t/month
- Silicon
-

- $15.00 / 1KG
- 2021-07-02
- CAS:7440-21-3
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%+ HPLC
- Supply Ability: Monthly supply of 1 ton
- Silicon
-

- $1.00 / 1kg
- 2019-07-06
- CAS:7440-21-3
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: Customized