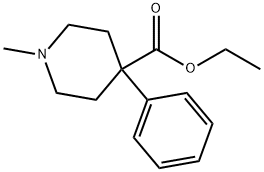
MEPERIDINE
- CAS No.
- 57-42-1
- Chemical Name:
- MEPERIDINE
- Synonyms
- Lydol;C07128;Dolsin;Demarol;Demerol;Nemerol;Petydyna;Pethidin;Pethanol;Petantin
- CBNumber:
- CB1121049
- Molecular Formula:
- C15H21NO2
- Molecular Weight:
- 247.33
- MOL File:
- 57-42-1.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2023/5/4 17:34:40
| Melting point | 270°C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 390.37°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.0267 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5130 (estimate) |
| Flash point | 11 °C |
| storage temp. | −20°C |
| pka | pKa 8.7 (Uncertain) |
| Water Solubility | 6.55g/L(25 ºC) |
| BCS Class | 1 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 4-Piperidinecarboxylic acid, 1-methyl-4-phenyl-, ethyl ester (57-42-1) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS02,GHS06,GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H225-H301+H311+H331-H370 |
| Precautionary statements | P210-P260-P280-P301+P310-P311 |
| Hazard Codes | F,T |
| Risk Statements | 11-23/24/25-39/23/24/25 |
| Safety Statements | 7-16-36/37-45 |
| RIDADR | UN 1230 3/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| Toxicity | A narcotic analgesic used for moderate to severe pain and during obstetrical anesthesia. Its oral LD50 in rats is 170 mg/kg. It has multiple actions qualitatively similar to those of morphine, and therapy is similar to that for morphine. Advantages over morphine concerning efficacy and reduced risk of addiction were largely illusory. This, and potential drug interactions, have resulted in a dramatic reduction in use. |
MEPERIDINE Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Uses
Analgesic (narcotic).
Biological Functions
Meperidine (Demerol) is a phenylpiperidine derivative
of morphine that was developed in the late 1930s as a
potential anticholinergic agent. It has some anticholinergic
side effects that lead to tachycardia, blurred vision,
and dry mouth. Meperidine is approximately onefifth
as potent as morphine and is absorbed only half as
well when administered orally as parenterally. It has a
rapid onset and short duration of action (2 hours), that
is, approximately one-fourth that of morphine.
Like morphine, meperidine has an active metabolite,
normeperidine, formed by N-demethylation of
meperidine. Normeperidine is not analgesic but is a
proconvulsant and a hallucinogenic agent. For this reason,
meperidine use in patients with renal or liver insufficiency
is contraindicated because of the decreased
clearance of the drug and its metabolite. Convulsant activity
has been documented in elderly patients given
meperidine and in patients using PCA who have decreased
renal function.
Meperidine differs from morphine in that it has far
less antitussive effect and little constipative effect. The
drug is particularly useful in cancer patients and in pulmonary
patients, in whom the cough reflex must remain
intact. However, it does have more seizure-inducing activity
than morphine. Although meperidine produces
spasms of the biliary tract and colon, such spasms are of
shorter duration than those produced by morphine.
Meperidine readily passes the placenta into the fetus.
However, respiratory depression in the newborn
has not been observed, and meperidine clearance in the
newborn is rapid in that it does not rely upon conjugation
to glucuronides. Meperidine, unlike morphine, has
not been associated with prolongation of labor; conversely,
it increases uterine contractions.
General Description
Meperidine (Demerol) was discovered in 1939 during a serendipitous screening of compounds being studied for antispasmodic activity. Mice given meperidine were noted to carry their tails in an erect position (the Straub tail reaction), which was indicative of narcotic analgesia. This led to the study of meperidine and derivatives as analgesic agents. Meperidine was found to have low potency at the receptor compared with morphine (0.2%) but much higher penetration into the brain resulting in a compound with about 10% of the potency of morphine.
Structural changes that increase the potency of meperidine include the introduction of an mhydroxyl on the phenyl ring, substituting the methyl on the N for a phenylethyl or a p-aminophenylethyl. Replacing the N-methyl with an N-allyl or N-cyclopropylmethyl group does not generate an antagonist, unlike the similar substitution of the morphine congeners. Meperidine quickly penetrates the blood-brain barrier and thus has a quick onset of activity and a high abuse potential.
Precautions
Contraindications are similar to those of morphine. In addition, because normeperidine accumulates in renal dysfunction and meperidine accumulates in hepatic dysfunction, meperidine is contraindicated in such patients because of convulsant effects. Similarly, the use of meperidine is contraindicated in patients who have a history of seizures or who are taking medication to prevent seizures. Phenytoin administered for seizures may reduce the effectiveness of meperidine by increasing the metabolism of the drug in the liver. Meperidine is not generally used in patients with cardiac dysfunction, since its anticholinergic effects can increase both heart rate and ectopic beats.
MEPERIDINE Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of2
chevron_rightPreparation Products
57-42-1(MEPERIDINE)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




