Dichlorodifluoromethane
- CAS No.
- 75-71-8
- Chemical Name:
- Dichlorodifluoromethane
- Synonyms
- f12;r12;CF12;F 12;f-12;HC12;R 12;R-12;FC-12;fcc12
- CBNumber:
- CB1202887
- Molecular Formula:
- CCl2F2
- Molecular Weight:
- 120.91
- MOL File:
- 75-71-8.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2024/3/14 15:18:25
| Melting point | -158°C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | -29.79°C |
| Density | 1.329 |
| vapor pressure | 4,306 at 20 °C (McConnell et al., 1975) |
| refractive index | 1.2850 |
| Flash point | 11 °C |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | Soluble in acetic acid, acetone, chloroform, ether (Weast, 1986), and ethanol (ITII, 1986) |
| form | buffered aqueous glycerol solution |
| color | Colorless gas with an ethereal odor |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble. 0.028 g/100 mL |
| Henry's Law Constant | 1.72, 2.63, and 3.91 at 10, 20, and 30 °C, respectively (Munz and Roberts, 1987) |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH REL: TWA 1,000 ppm (4,950 mg/m3), IDLH 15,000 ppm; OSHA PEL: TWA 1,000 ppm; ACGIH TLV: TWA 1,000 ppm (adopted). |
| Dielectric constant | 2.4(21℃) |
| Stability | Stable. Non-flammable. May react violently with aluminium. |
| InChIKey | PXBRQCKWGAHEHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | 2.160 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 75-71-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Dichlorodifluoromethane(75-71-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | CFC-12 (75-71-8) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS02,GHS06,GHS08 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H225-H301+H311+H331-H370-H420 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P210-P260-P280-P301+P310-P311 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xn;N,Xi,N,Xn,T,F | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 20-59-23/25-11-39/23/24/25-23/24/25-22 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 23-24/25-59-61-45-24-16-7-36/37 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | 1028 | |||||||||
| OEB | A | |||||||||
| OEL | TWA: 1000 ppm (4950 mg/m3) | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 1 | |||||||||
| Hazard Note | Irritant | |||||||||
| DOT Classification | 2.2 (Nonflammable gas) | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 2.2 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 for rats >1 g/kg (quoted, Verschueren, 1983). | |||||||||
| IDLA | 15,000 ppm | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Dichlorodifluoromethane price More Price(5)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | SAB4501251 | Anti-GPR17 antibody produced in rabbit affinity isolated antibody | 75-71-8 | 100μG | ₹50560.5 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | SAB4501250 | Anti-GPR17 antibody produced in rabbit affinity isolated antibody | 75-71-8 | 100μG | ₹50560.5 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | SAB2501541 | Anti-GPR17 (C-terminal) antibody produced in goat affinity isolated antibody, buffered aqueous solution | 75-71-8 | 100μG | ₹53135.7 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | HPA029766 | Anti-GPR17 antibody produced in rabbit Prestige Antibodies? Powered by Atlas Antibodies, affinity isolated antibody, buffered aqueous glycerol solution | 75-71-8 | 100μL | ₹41436.3 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 40346 | Dichlorodifluoromethane solution 5000?μg/mL in methanol, certified reference material | 75-71-8 | 1ML | ₹5400 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Dichlorodifluoromethane Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Dichlorodifluoromethane is known as CFC-12, also called R-12, or Freon-12. R-12 is a general name for Refrigerant-12. Freon is a trade name for DuPont. CFC stands for chlorofl uorocarbons, which are nontoxic, nonfl ammable, synthetic chemicals containing atoms of carbon, chlorine, and fluorine.CFC use climbed steadily worldwide as it was incorporated in refrigeration and air conditioning, as well as being used as propellants, blowing agents, and solvents.

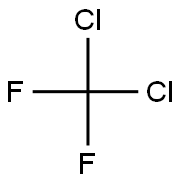
dichlorodifluoromethane structure
Chemical Properties
Dichlorodifluoromethane is a liquefied gas and exists as a liquid at room temperature when contained under its own vapor pressure, or as a gas when exposed to room temperature and atmospheric pressure. The liquid is practically odorless and colorless. The gas in high concentrations has a faint etherlike odor. Dichlorodifluoromethane is noncorrosive, nonirritating, and nonflammable. Ethereal odor at .20% by volume. Shipped as a compressed gas.
Dichlorotetrafluoroethane is a colorless, nonflammable liquefied gas with a faint, ethereal odor.
Trichloromonofluoromethane is a clear, volatile liquid at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. It has a characteristic carbon tetrachloride-like odor and is nonirritating and nonflammable.
History
CFCs were developed in the 1930s as coolants for refrigerator, freezer, and motor vehicle air conditioners.they subsequently found use as metal cleaners, degreasers, propellants, solvents, and blowing agents in the production of foams. CFCs have received widespread environmental attention because of their potential to deplete stratospheric ozone.
Uses
Refrigerant, aerosol propellant.
Dichlorodifluoromethane is used as a refrigerant gas in refrigerators and air conditioners.
Dichlorodifluoromethane is also used in aerosol sprays, in plastics, and as an aid in detecting leaks.
Dichlorodifluoromethane harms the ozone layer, which protects the earth from the sun’s ultraviolet radiation.
Production Methods
Dichlorodifluoromethane is prepared by the reaction of hydrogen
fluoride with carbon tetrachloride in the presence of a suitable
catalyst, such as polyvalent antimony. The dichlorodifluoromethane
formed is further purified to remove all traces of water
and hydrochloric acid as well as traces of the starting and
intermediate materials.
Trichloromonofluoromethane is also obtained by this process.
Dichlorotetrafluoroethane is prepared by the reaction of
hydrogen fluoride with chlorine and perchloroethylene in the
presence of a suitable catalyst such as polyvalent antimony.
General Description
A colorless gas having a faint ethereal odor. Shipped as a liquid confined under its own vapor pressure. Contact with the unconfined liquid can cause frostbite. Both components are noncombustible. Can asphyxiate by the displacement of air. Exposure of the closed container to prolonged heat or fire can cause Dichlorodifluoromethane to rupture violently and rocket.
Air & Water Reactions
The liquefied gas poured into water can be violently explosive. This is due to the phase transition from superheated liquid to vapor.
Reactivity Profile
The reaction of aluminum with various halogenated hydrocarbons produces a self-sustaining reaction with sufficient heat to melt aluminum pieces, examples of other halogenated hydrocarbons are fluorotrichloromethane, Dichlorodifluoromethane, chlorodifluoromethane, tetrafluoromethane. The vigor of the reaction appears to be dependent on the combined degree of fluorination and the vapor pressure, [Chem. Eng. News 39(27):44(1961)].
Health Hazard
INHALATION: some narcosis when 10% in air is breathed.
Safety Profile
Dichlorodifluoromethane is a colorless, non-flammable gas that can affect you when breathed in. Acute (short-term) exposure to dichlorodifluoromethane can cause dizziness, lightheadedness, and trouble with concentration. Exposure to high concentrations of the gas can cause the heart to beat irregularly or to stop. The health effects of chronic (long-term) exposure to dichlorodifluoromethane are unknown at this time. There is no evidence of an increase in cancer risk due to exposure to dichlorodifluoromethane.
Potential Exposure
Dichlorodifluoromethane is used as an aerosol propellant, refrigerant and foaming agent
Carcinogenicity
There was no evidence of carcinogenicity when groups of 50 male and 50 female rats were given oral doses of 15 or 150 mg/kg of CFC 12 daily for 2 years. As described above, there was no evidence of carcinogenicity when groups of 90 male and 90 female rats and of 60 male and 60 female mice were exposed by inhalation to levels of 1000 and 5000 ppm, 4 h/day, 5 days/ week.
Environmental Fate
Surface Water. Estimated half-lives of dichlorodifluoromethane from an experimental marine mesocosm during the spring (8–16 °C) and winter (3–7 °C) were 20 and 13 d, respectively (Wakeham et al., 1983).
storage
Chlorofluorocarbon propellants are nonreactive and stable at temperatures up to 5508℃. The liquefied gas is stable when used as a propellant and should be stored in a metal cylinder in a cool, dry place.
Shipping
UN1028 Dichlorodifluoromethane or Refrigerant gas R-12, Hazard class: 2.2; Labels: 2.2-Nonflammable compressed gas. Cylinders must be transported in a secure upright position, in a well-ventilated truck. Protect cylinder and labels from physical damage. The owner of the compressed gas cylinder is the only entity allowed by federal law (49CFR) to transport and refill them. It is a violation of transportation regulations to refill compressed gas cylinders without the express written permission of the owner
Purification Methods
Pass the gas through saturated aqueous KOH then conc H2SO4, and a tower packed with activated copper on Kielselguhr at 200o removed CO2 and O2. A trap cooled to -29o removed a trace of high boiling material. It is a non-flammable propellant.
Incompatibilities
The presence of greater than 5% water in solutions that contain
trichloromonofluoromethane may lead to hydrolysis of the
propellant and the formation of traces of hydrochloric acid, which
may be irritant to the skin or cause corrosion of metallic canisters.
Trichloromonofluoromethane may also react with aluminum, in the
presence of ethanol, to cause corrosion within a cylinder with the
formation of hydrogen gas. Similarly, alcohols in the presence of
trace amounts of oxygen, peroxides, or other free-radical catalysts
may react with trichloromonofluoromethane to form trace quantities
of hydrochloric acid.
Both dichlorodifluoromethane and dichlorotetrafluoroethane
are compatible with most ingredients used in pharmaceutical
aerosols. Because of their poor miscibility with water, most MDIs
are formulated as suspensions. However, solution MDIs can be
prepared through the use of ethanol as a cosolvent for water and
propellant, resulting in a clear solution (provided the water content
is less than 5%).
Waste Disposal
Return refillable compressed gas cylinders to supplier. Incineration, preferably after mixing with another combustible fuel. Care must be exercised to assure complete combustion to prevent the formation of phosgene. An acid scrubber is necessary to remove the halo acids produced. Because of potential ozone decomposition in the stratosphere, R-12 should be released to the atmosphere only as a last resort. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal
Regulatory Status
Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (aerosol formulations for inhalation, nasal, oral, and topical applications). With few exceptions for existing MDIs, the FDA and EPA have banned the use of CFCs in the USA after 31st December 2008, with all CFCs to be phased out by 2010–2015. Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK.
Dichlorodifluoromethane Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
75-71-8(Dichlorodifluoromethane)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




