CHLOROTRIFLUOROMETHANE
- CAS No.
- 75-72-9
- Chemical Name:
- CHLOROTRIFLUOROMETHANE
- Synonyms
- CFC;f13;r13;F 13;R 13;CF3Cl;CClF3;CFC13;FKW13;Arcton
- CBNumber:
- CB6202231
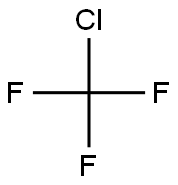
- Molecular Formula:
- CClF3
- Molecular Weight:
- 104.46
- MOL File:
- 75-72-9.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2023/5/4 15:16:44
| Melting point | -181°C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | -81,4°C |
| Density | (-130℃)1.703g/cm3 |
| refractive index | 1.1990 |
| storage temp. | -70°C |
| EPA Substance Registry System | CFC-13 (75-72-9) |
CHLOROTRIFLUOROMETHANE Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Strictly speaking, fluorocarbon compounds contain only the elements carbon, fluorine, and sometimes hydrogen. However, in industrial applications such as refrigerants and aerosol propellants, the term fluorocarbon has been used to include compounds containing chlorine and bromine atoms, or both. These industrial products have somewhat similar chemical and physical properties. Their relatively inert character and wide range of vapor pressures and boiling points make them especially well suited as refrigerants in a variety of applications, blowing agents for plastic foams, and aerosols.
Chemical Properties
Colorless gas; ethereal odor. heavier than air. Nonflammable
Uses
Dielectric and aerospace chemical, hardening of metals, pharmaceutical processing.
General Description
CHLOROTRIFLUOROMETHANE is a colorless odorless gas. CHLOROTRIFLUOROMETHANE is shipped as a liquefied gas under its own vapor pressure. CHLOROTRIFLUOROMETHANE is noncombustible. CHLOROTRIFLUOROMETHANE can asphyxiate by the displacement of air. Contact with the liquid can cause frostbite. Exposure of the container to prolonged heat or fire may cause CHLOROTRIFLUOROMETHANE to rupture violently and rocket.
Reactivity Profile
The reaction of aluminum with various halogenated hydrocarbons produces a self-sustaining reaction with sufficient heat to melt aluminum pieces, examples of other halogenated hydrocarbons are fluorotrichloromethane, dichlorodifluoromethane, chlorodifluoromethane, tetrafluoromethane. The vigor of the reaction appears to be dependent on the combined degree of fluorination and the vapor pressure, [Chem. Eng. News 39(27):44(1961)].
Hazard
Toxic by inhalation; slightly irritant.
Health Hazard
Exposure may cause nausea, dizziness, and headache, and rapid suffocation. Contact with skin may cause frostbite.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Toxic fumes of Cl and F
Materials Uses
The fluorocarbons are generally compatible with most of the common metals except at high temperatures. At elevated temperatures, the following metals resist fluorocarbon corrosion (and are named in decreasing order of their corrosive resistance): Inconel, stainless steel, nickel, steel, and bronze. Water or water vapor in fluorocarbon systems will corrode magnesium alloys or aluminum containing over 2 percent magnesium. These metals are not recommended for use with fluorocarbon systems in which water may be present.
Safety Profile
A mild irritant. Narcotic in high concentrations. Reacts violently with Al. When heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of Fand Cl-.
storage
Use forced ventilation and local exhaust, or both, to prevent an accumulation of gas that could reduce the oxygen level to below 19.5%. Ensure good floor ventilation. Use a check valve or trap in the discharge line to prevent back flow into the cylinder. Where applicable, use a pressure-reducing regulator when connecting a cylinder to a low-pressure piping system. For flammable fluorocarbons, adherence to pertinent electrical standards is necessary. Personnel should not weld, solder, braze, or have an open flame of any type in atmospheres containing flammable or nonflammable fluorocarbons.
Purification Methods
Main impurities are CO2, O2, and N2. The CO2 is removed by passage through saturated aqueous KOH, followed by conc H2SO4. The O2 is removed using a tower packed with activated copper on Kieselguhr at 200o, and the gas is dried over P2O5. [Miller & Smyth J Am Chem Soc 79 20 1957, Beilstein 1 III 42, 1 IV 34.] TOXIC GAS.
CHLOROTRIFLUOROMETHANE Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of2
chevron_rightPreparation Products
75-72-9(CHLOROTRIFLUOROMETHANE)Related Search:
1of3
chevron_right





