Chloroplantinic acid
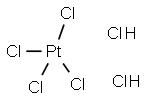
- CAS No.
- 16941-12-1
- Chemical Name:
- Chloroplantinic acid
- Synonyms
- CPA;CHLOROPLATINIC ACID;PLATINUM CHLORIDE;Chloroplatinic acid hexahydrate;PL 50T;nsc4958;atinic acid;speier’scatalyst;CHLORPLATINICACID;PLATINIC CHLORIDE
- CBNumber:
- CB2271499
- Molecular Formula:
- Cl6H2Pt
- Molecular Weight:
- 409.81
- MOL File:
- 16941-12-1.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2024/3/14 15:18:26
| Melting point | 60 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Density | 2.43 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 20℃ |
| refractive index |
n |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 0.5 M at 20 °C, clear, orange |
| form | powder and chunks |
| color | orange |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| Merck | 14,7526 |
| Exposure limits |
ACGIH: TWA 0.002 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 4 mg/m3; TWA 0.002 mg/m3 |
| Stability | May decompose on exposure to light, air or moisture. |
| InChIKey | GBFHNZZOZWQQPA-UHFFFAOYSA-J |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Platinate(2-), hexachloro-, hydrogen (1:2), (OC-6-11)- (16941-12-1) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |     GHS05,GHS06,GHS08,GHS09 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H290-H301-H314-H317-H334-H373-H411 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P234-P273-P280-P303+P361+P353-P304+P340+P310-P305+P351+P338 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | T,C,Xi | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 25-34-42/43-36/38-36/37/38-22 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 26-27-36/37/39-45-22-23 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 3264 8/PG 3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 1 | |||||||||
| RTECS | TP1510000 | |||||||||
| F | 3-8-10 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 8 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| HS Code | 28439000 | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Chloroplantinic acid price More Price(5)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 262587 | Chloroplatinic acid solution 8?wt. % in H2O | 16941-12-1 | 10ML | ₹18503.7 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 262587 | Chloroplatinic acid solution 8?wt. % in H2O | 16941-12-1 | 50ML | ₹48384.9 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 262587 | Chloroplatinic acid solution 8?wt. % in H2O | 16941-12-1 | 250ML | ₹171950.1 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| ALFA India | ALF-040177-NJ | Dihydrogen hexachloroplatinate(IV) solution, Pt 20% (cont. Pt) | 16941-12-1 | 0.5g | ₹14947 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
| ALFA India | ALF-040177-NA | Dihydrogen hexachloroplatinate(IV) solution, Pt 20% (cont. Pt) | 16941-12-1 | 2g | ₹29908 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
Chloroplantinic acid Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
Orange/Red Crystals
Uses
Chloroplantinic acid (H2PtCl6) is one of the most commercially important compounds of platinum. Its many uses include etching on zinc, making indelible ink, plating, and coloring in fine porcelains and use in photography, in mirrors, and as a catalyst.
Definition
chloroplatinic acid: A reddish crystallinecompound, H2PtCl6, made bydissolving platinum in aqua regia.
General Description
Chloroplatinic acid, is a reddish-brown solid. Chloroplatinic acid is soluble in water and will yield a mildly acidic solution. Chloroplatinic acid may cause illness from inhalation of the dust and Chloroplatinic acid is irritating to skin and eyes. When heated to high temperatures Chloroplatinic acid may decompose to toxic chloride fumes. Chloroplatinic acid may burn, but may be difficult to ignite. Chloroplatinic acid is used for manufacturing indelible ink and in electroplating processes.
Air & Water Reactions
Soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Oxidizing acids are generally soluble in water with the release of hydrogen ions. The resulting solutions have pH's of less than 7.0. Materials in this group react with chemical bases (for example: amines and inorganic hydroxides) to form salts. These neutralization reactions occur as the base accepts hydrogen ions that the acid donates. Neutralizations can generate dangerously large amounts of heat in small spaces. The dissolution of acids in water or the dilution of their concentrated solutions with water may generate significant heat. The addition of water acids often generates sufficient heat in the small region of mixing to boil some of the water explosively. The resulting "bumping" spatters acid widely. These materials have significant ability as oxidizing agents. but that ability varies (for example, from high for nitric acid to low for sulfuric acid and most sulfonic acids). They can react with active metals, including iron and aluminum, and also many less active metals, to dissolve the metal and liberate hydrogen and/or toxic gases. Like other acids, materials in this group can initiate polymerization in certain classes of organic compounds. Their reactions with cyanide salts and compounds release gaseous hydrogen cyanide. Flammable and/or toxic gases are also often generated by their reactions with dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, nitriles, sulfides, and weak or strong reducing agents. Additional gas-generating reactions occur with sulfites, nitrites, thiosulfates (to give H2S and SO3), dithionites (SO2), and even carbonates: the carbon dioxide gas from the last is nontoxic but the heat and spattering from the reaction can be troublesome. Acids often catalyze (increase the rate) of chemical reactions.
Health Hazard
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
Non-combustible, substance itself does not burn but may decompose upon heating to produce corrosive and/or toxic fumes. Some are oxidizers and may ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated.
Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous and intraperitoneal routes. Mutation data reported. See PLATINUM COMPOUNDS and CHLORIDES. Incompatible with BrF3. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Cl-.
Potential Exposure
Chloroplatinic acid has many uses, among them are platinum plating, photography, and catalysis.
Shipping
UN2507 Chloroplatinic acid, solid, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material.
Purification Methods
If it is to be purified, or regenerated from Pt recovered from catalytic hydrogenations, it should be dissolved in aqua regia followed by evaporation to dryness and dissolution in the minimum volume of H2O. Then the aqueous solution is treated with saturated ammonium chloride until all the ammonium hexachloroplatinate separates. The (NH4)2PtCl6 is filtered off and dried at 100o. Igniting this salt gives Pt sponge; dissolve the Pt sponge in aqua regia, boil to dryness, dissolve the residue in concentrated HCl, boil to dryness again and repeat the process. Protect it from light. [Hickers J Am Chem Soc 43 1268 1921, Adams et al. Org Synth Coll Vol I 463, 466 1941, Bruce J Am Chem Soc 58 687 1936.]
Incompatibilities
Oxidizing acids are generally soluble in water with the release of hydrogen ions. The resulting solutions have pH’s of <7.0. Materials in this group react with chemical bases (e.g., amines and inorganic hydroxides) to form salts. These neutralization reactions occur as the base accepts hydrogen ions that the acid donates. Neutralizations can generate dangerously large amounts of heat in small spaces. The dissolution of acids in water or the dilution of their concentrated solutions with water may generate significant heat. The addition of water acids often generates sufficient heat in the small region of mixing to boil some of the water explosively. The resulting “bumping” spatters acid widely. These materials have significant ability as oxidizing agents. but that ability varies (e.g., from high for nitric acid to low for sulfuric acid and most sulfonic acids). They can react with active metals, including iron and aluminum, and also many less active metals, to dissolve the metal and liberate hydrogen and/or toxic gases. Like other acids, materials in this group can initiate polymerization in certain classes of organic compounds. Their reactions with cyanide salts and compounds release gaseous hydrogen cyanide. Flammable and/or toxic gases are also often generated by their reactions with dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, nitriles, sulfides, and weak or strong reducing agents. Additional gas-generating reactions occur with sulfites, nitrites, thiosulfates (to give H2S and SO3), dithionites (SO2), and even carbonates: the carbon dioxide gas from the last is nontoxic but the heat and spattering from the reaction can be troublesome. Acids often catalyze (increase the rate) of chemical reactions.
Chloroplantinic acid Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evans Fine Chem | +91-9821340302 +91-9821340302 | Maharashtra, India | 286 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Otto Chemie Pvt Ltd | +91-2222070099 +91-2266382599 | Maharashtra, India | 429 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Vineeth Precious Catalysts Pvt Ltd | +91-9049600004 +91-9049600004 | Mumbai, India | 29 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Dhara Industries | +91-9322395199 +91-9322395199 | Mumbai, India | 190 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Metal Chem India | +91-8999856889 +91-9011882000 | Maharashtra, India | 46 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Umicore India Private Ltd | 91-22-66275640 | Maharashtra, India | 10 | 58 | Inquiry |
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | +91-22-45045900 | Hyderabad, India | 6351 | 58 | Inquiry |
| FINAR LTD | +91 - 2717 - 616717 | New Delhi, India | 660 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Alfa Aesar | 1 800 209 7001 | Maharashtra, India | 6913 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Noble Catalyst Private Limited | 08048265569 | Gujarat, India | 8 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Evans Fine Chem | 58 |
| Otto Chemie Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| Vineeth Precious Catalysts Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| Dhara Industries | 58 |
| Metal Chem India | 58 |
| Umicore India Private Ltd | 58 |
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | 58 |
| FINAR LTD | 58 |
| Alfa Aesar | 58 |
| Noble Catalyst Private Limited | 58 |
16941-12-1(Chloroplantinic acid)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




