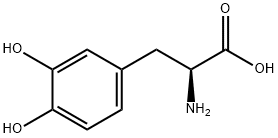
Levodopa
- CAS No.
- 59-92-7
- Chemical Name:
- Levodopa
- Synonyms
- L-DOPA;3,4-DIHYDROXY-L-PHENYLALANINE;L-3,4-DIHYDROXYPHENYLALANINE;DIHYDROXYPHENYLALANINE;L-Dihydroxyphenylalanine;Levedopa;Dopar;Bendopa;Larodopa;3-HYDROXY-L-TYROSINE
- CBNumber:
- CB2402938
- Molecular Formula:
- C9H11NO4
- Molecular Weight:
- 197.19
- MOL File:
- 59-92-7.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2025/4/15 18:16:32
| Melting point | 276-278 °C (lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 334.28°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | -11.7 º (c=5.3, 1N HCl) |
| Density | 1.3075 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | -12 ° (C=5, 1mol/L HCl) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Slightly soluble in water, practically insoluble in ethanol (96 per cent). It is freely soluble in 1 M hydrochloric acid and sparingly soluble in 0.1 M hydrochloric acid . |
| pka | 2.32(at 25℃) |
| form | Crystalline Powder |
| color | White to creamy |
| Odor | at 100.00 %. odorless |
| Odor Type | odorless |
| optical activity | -39.5 (H2O) -12.025 (1 mol dm-3 HCl) |
| Water Solubility | Slightly soluble in water, dilute hydrochloric acid and formic acid. Insoluble in ethanol. |
| Merck | 14,5464 |
| BRN | 2215169 |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. Light and air sensitive. |
| InChIKey | WTDRDQBEARUVNC-LURJTMIESA-N |
| LogP | -1.154 (est) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 59-92-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Levodopa(59-92-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Levodopa (59-92-7) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS07 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Warning | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P261-P264-P270-P301+P312-P302+P352-P305+P351+P338 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xn | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 22-36/37/38-20/21/22 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 26-36-24/25 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | AY5600000 | |||||||||
| F | 10-23 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29225090 | |||||||||
| Hazardous Substances Data | 59-92-7(Hazardous Substances Data) | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 in mice (mg/kg): 3650 ±327 orally, 1140 ±66 i.p., 450 ±42 i.v., >400 s.c.; in male, female rats (mg/kg): >3000, >3000 orally; 624, 663 i.p.; >1500, >1500 s.c. (Clark) | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Levodopa price More Price(14)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | D9628 | 3,4-Dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine ≥98% (TLC) | 59-92-7 | 5G | ₹3637.2 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | D9628 | 3,4-Dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine ≥98% (TLC) | 59-92-7 | 25G | ₹12557 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | D9628 | 3,4-Dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine ≥98% (TLC) | 59-92-7 | 100G | ₹36140 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | PHR1271 | Levodopa Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material | 59-92-7 | 500MG | ₹9818.28 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | D9628 | 3,4-Dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine ≥98% (TLC) | 59-92-7 | 500G | ₹125321.03 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Levodopa Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Levodopa is an amino acid precursor of dopamine with antiparkinsonian properties. Levodopa is a prodrug that is converted to dopamine by DOPA decarboxylase and can cross the blood-brain barrier. When in the brain, levodopa is decarboxylated to dopamine and stimulates the dopaminergic receptors, thereby compensating for the depleted supply of endogenous dopamine seen in Parkinson's disease. To assure that adequate concentrations of levodopa reach the central nervous system, it is administered with carbidopa, a decarboxylase inhibitor that does not cross the blood-brain barrier, thereby diminishing the decarboxylation and inactivation of levodopa in peripheral tissues and increasing the delivery of dopamine to the CNS.
Chemical Properties
L-Dopa [59-92-7], levodopa, crystallizes as colorless, odorless, and tasteless needles from water, mp 276-278℃(decomp.). It is freely soluble in dilute hydrochloric and formic acids but practically insoluble in ethanol, benzene, chloroform, and ethyl acetate. Solubility in water is 66 mg/40 mL. In the presence of moisture, l-dopa is rapidly oxidized by atmospheric oxygen, with darkening.
Uses
Levodopa is an immediate precursor of dopamine and product of tyrosine hydroxylase. It derived from vanillin is widely used for treatment of Parkinson’s disease, most often in combination with peripheral decarboxylase inhibitors such as benserazide and carbidopa.
Definition
ChEBI: Levodopa is an optically active form of dopa having L-configuration. Used to treat the stiffness, tremors, spasms, and poor muscle control of Parkinson's disease.
Biological Functions
Levodopa (L-DOPA), the most reliable and effective drug used in the treatment of parkinsonism, can be considered a form of replacement therapy. Levodopa is the biochemical precursor of dopamine. It is used to elevate dopamine levels in the neostriatum of parkinsonian patients. Dopamine itself does not cross the blood-brain barrier and therefore has no CNS effects. However, levodopa, as an amino acid, is transported into the brain by amino acid transport systems, where it is converted to dopamine by the enzyme L-aromatic amino acid decarboxylase.
If levodopa is administered alone, it is extensively metabolized by L-aromatic amino acid decarboxylase in the liver, kidney, and gastrointestinal tract. To prevent this peripheral metabolism, levodopa is coadministered with carbidopa (Sinemet), a peripheral decarboxylase inhibitor. The combination of levodopa with carbidopa lowers the necessary dose of levodopa and reduces peripheral side effects associated with its administration.
General Description
Levodopa belongs to a group of the most effective drugs for treating the type of Parkinsonism not caused by medicinal agents. The first significant breakthrough in the treatment of PDcame about with the introduction of high-dose levodopa. Fahn referred to this as a revolutionary development intreating parkinsonian patients. The rationale for the use oflevodopa for the treatment of PD was established in theearly 1960s. Parkinsonian patients were shown to have decreasedstriatal levels of DA and reduced urinary excretionof DA. Since then, levodopa has shown to be remarkablyeffective for treating the symptoms of PD.
Side effects
Get medical help immediately if you have any symptoms: fever, unusual muscle stiffness, severe confusion, sweating, fast/irregular heartbeat, and rapid breathing. A severe allergic reaction to this drug is rare. This medication may cause saliva, urine, or sweat to turn dark. This effect is harmless.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion. Moderately toxic by intravenous and intraperitoneal routes. Human systemic effects by ingestion: somnolence, hallucinations and distorted perceptions, toxic psychosis, motor activity changes, ataxia, dyspnea. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. Questionable human carcinogen producing skin tumors. Human mutation data reported. An anticholinergic agent used as an anti Parhnsonian drug. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx
Metabolism
Metabolism of levodopa and dopamine may proceed by four pathways: decarboxylation, O-methylation, transamination, and oxidation. Levodopa is decarboxylated to dopamine by the enzyme AAAD. This enzyme is ubiquitously distributed in the gut, liver, and kidney. The gastric and intestinal wall contains AAAD, which significantly metabolizes levodopa. At least half of an oral levodopa dose is decarboxylated during absorption and first-pass hepatic metabolism. Further decarboxylation may occur by AAADC during successive circulation through these tissues. Approximately 70% of the levodopa metabolites appear as dopamine and its degradation products, indicating that decarboxylation is the primary route of metabolism.
Purification Methods
Likely impurities are vanillin, hippuric acid, 3-methoxytyrosine and 3-aminotyrosine. DOPA recrystallises from large volumes of H2O forming colourless white needles; its solubility in H2O is 0.165%, but it is insoluble in EtOH, *C6H6, CHCl3, and EtOAc. Also crystallise it by dissolving it in dilute HCl and adding dilute ammonia to give pH 5, under N2. Alternatively, crystallise it from dilute aqueous EtOH. It is rapidly oxidised in air when moist, and darkens, particularly in alkaline solution. Dry it in vacuo at 70o in the dark, and store it in a dark container preferably under N2. It has at 220.5nm (log 3.79) and 280nm (log 3.42) in 0.001N max HCl. [Yamada et al. Chem Pharm Bull Jpn 10 693 1962, Bretschneider et al. Helv Chim Acta 56 2857 1973, NMR: Jardetzky & Jardetzky J Biol Chem 233 383 1958, Beilstein 4 IV 2492, 2493.]
Levodopa Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of2
chevron_rightPreparation Products
1of2
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BTC pharm India | +918790379245 | AndhraPradesh, India | 1262 | 58 | Inquiry |
| JIVICHEM SYNTHESIS PVT LTD | +91-7028392790 +91-7028392790 | Maharashtra, India | 335 | 58 | Inquiry |
| KARPSCHEM LABORATORIES | +91-7249203006 +91-7249203006 | Maharashtra, India | 786 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Varanous Labs Pvt Ltd | +91-7036248882 +91-7036248882 | Hyderabad, India | 1537 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Embio Limited | +91-9004390567 +91-9004390567 | Maharashtra, India | 33 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Divis Laboratories Ltd | +91-4066966413 +91-4066966413 | Hyderabad, India | 34 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Aruvi Labs | +91-8056181939 +91-8056181939 | Tamil Nadu, India | 149 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Maithri Drugs Pvt Ltd | +91-9059204566 +91-9848881740 | Telangana, India | 64 | 58 | Inquiry |
| ARRAKIS INDUSTRIES LLP | +91 74995 32711 | Maharashtra, India | 1353 | 58 | Inquiry |
| JSK Chemicals | +919879767970 | Gujarat, India | 3756 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| BTC pharm India | 58 |
| JIVICHEM SYNTHESIS PVT LTD | 58 |
| KARPSCHEM LABORATORIES | 58 |
| Varanous Labs Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| Embio Limited | 58 |
| Divis Laboratories Ltd | 58 |
| Aruvi Labs | 58 |
| Maithri Drugs Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| ARRAKIS INDUSTRIES LLP | 58 |
| JSK Chemicals | 58 |
Related articles
- Levodopa: A Breakthrough in Parkinson's Disease Treatment
- Levodopa, is a cornerstone in the treatment of Parkinson's disease (PD), a neurodegenerative disorder that affects millions wo....
- Jun 25,2024
- The review of levodopa
- Levodopa is a precursor drug of dopamine (DA), which has no pharmacological activity.
- Mar 29,2022
- Side effects of Levodopa
- Levodopa is the precursor to dopamine. Most commonly, clinicians use levodopa as a dopamine replacement agent for the treatmen....
- Jan 17,2022
59-92-7(Levodopa)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




