Lead acetate
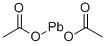
- CAS No.
- 301-04-2
- Chemical Name:
- Lead acetate
- Synonyms
- LEAD (II) ACETATE;PbAc2;unichempba;LEAD ACETATE 3H2O;ACETIC ACID LEAD SALT;Diacetic acid lead(II);LEAD SUGAR;bleiacetat;Sugaroflead;LEAD ACETATE
- CBNumber:
- CB3750317
- Molecular Formula:
- C4H6O4Pb
- Molecular Weight:
- 325.29
- MOL File:
- 301-04-2.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/3/14 15:18:26
| Melting point | 75 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | decomposes at >280℃ [KIR78] |
| Density | 3.3 g/cm3 |
| vapor pressure | 15.7hPa at 25℃ |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Clear colorless |
| Water Solubility | g/100g H2O: 19.7 (0°C), 55.2 (25°C); equilibrium solid phase, Pb(CH3COO)2 ·3H2O [KRU93]; g/100mL H2O: 44.3 (20°C), 221 (50°C) [KIR78] |
| λmax | 260nm(H2O)(lit.) |
| Merck | 14,5397 |
| Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) | pKsp: 2.75 |
| Dielectric constant | 2.5(0.0℃) |
| LogP | -0.17 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 301-04-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Lead(II) acetate (301-04-2) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS08,GHS09 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H360Df-H373-H410 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P260-P314-P501-P273-P391-P501 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | T,N | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 61-33-48/22-50/53-62 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 53-45-60-61 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 1616 6.1/PG 3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 2 | |||||||||
| RTECS | OF8050000 | |||||||||
| HS Code | 2915.29.5000 | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 6.1(b) | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 i.p. in rats: 15 mg Pb/100g (Bradley, Fredrick) | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Lead acetate price More Price(3)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCI Chemicals (India) | L0315 | Lead(II) Acetate [for Perovskite precursor] | 301-04-2 | 1G | ₹2000 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
| TCI Chemicals (India) | L0315 | Lead(II) Acetate [for Perovskite precursor] | 301-04-2 | 5G | ₹4800 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
| TCI Chemicals (India) | L0315 | Lead(II) Acetate [for Perovskite precursor] | 301-04-2 | 25G | ₹11200 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
Lead acetate Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Lead acetate is stable under ordinary conditions of use and storage. Lead acetate is incompatible with bromates, phenol, chloral hydrate, sulphides, hydrogen peroxide, resorcinol, salicylic acid, sulphites, vegetable infusions, alkalis, tannin, phosphates, citrates, chlorides, carbonates, tartrates, and acids. Lead (II) acetate, as well as white lead, has been used in cosmetics throughout history, though this practice has ceased in Western countries. It is still used in men’s hair colouring. Lead (II) acetate paper is used to detect the poisonous gas hydrogen sulphide. The gas reacts with lead (II) acetate on the moistened test paper to form a grey precipitate of lead (II) sulphide.
Chemical Properties
Lead acetate is a white, flaky crystalline substance with a slight odor of acetic acid. Commercial grades may be powdered granules, or brown or gray lumps. Diacetate: Powder.
Uses
2 – 1 - Sweetener
Like other lead (II) salts, lead (II) acetate has a sweet taste, which has led to its use as a sugar substitute throughout history. The ancient Romans, who had few sweeteners besides honey, would boil must (grape juice) in lead pots to produce a reduced sugar syrup called defrutum, concentrated again into sapa. This syrup was used to sweeten wine and to sweeten and preserve fruit. It is possible that lead(II) acetate or other lead compounds leaching into the syrup might have caused lead poisoning in anyone consuming it . Lead acetate is no longer used in the production of sweeteners in most of the world because of its recognized toxicity. Modern chemistry can easily detect it, which has all but stopped the illegal use that continued decades after legal use as a sweetener was banned .
2 – 1 - Sweetener2 – 1 – 1 - Resultant deaths
Pope Clement II died in October 1047. A toxicologic examination of his remains conducted in the mid – 20 th century confirmed centuries-old rumors that he had been poisoned with lead sugar.It is not clear if he was assassinated.
In 1787 painter Albert Christoph Dies swallowed, by accident, approximately 21 g of lead acetate. His recovery from this poison was slow and incomplete. He lived with illnesses until his death in 1822 .
Although the use of lead (II) acetate as a sweetener was already illegal at that time, composer Ludwig van Beethoven may have died of lead poisoning caused by wines adulterated with lead acetate.
Mary Seacole applied lead (II) acetate, among other remedies, against an epidemic of cholera in Panama.
Production Methods
Lead acetate is made by dissolving lead monoxide (litharge) or lead carbonate in strong acetic acid. Several types of basic salts are formed when lead acetates are prepared from lead monoxide in dilute acetic acid or at high pH. The basic salts of lead acetate are white crystalline compounds, which are highly soluble in water and dissolve in ethyl alcohol.
Lead acetate can be made by boiling elemental lead in acetic acid and hydrogen peroxide.
Definition
ChEBI: A lead coordination entity in which a central lead(2+) atom is coordinated to two acetate ions.
Potential Exposure
Lead acetate is used as a color additive in hair dyes; as a mordant in cotton dyes, in the lead coating of metals; as a drier in paints; varnishes and pigment inks; and in medicinals, such as astringents. Incompatibilities: A strong reducing agent. Reacts violently with strong oxidizers, bromates, strong acids; chemically active metals; phosphates, carbonates, phenols. Contact with strong acids forms acetic acid. Incompatible with strong bases: ammonia, amines, cresols, isocyanates, alkylene oxides; epichlorohydrin, sulfites, resorcinol, salicylic acid, and chloral hydrat
Shipping
UN1616 Lead acetate, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials
Purification Methods
Crystallise it twice from anhydrous acetic acid and dry it under vacuum for 24hours at 100o. The solubility in H2O is 63% (at ~20o) and 200% (at boiling point). [Beilstein 2 IV 118.]
Incompatibilities
A strong reducing agent. Reacts violently with strong oxidizers, bromates, strong acids; chemically active metals; phosphates, carbonates, phenols. Contact with strong acids forms acetic acid. Incompatible with strong bases: ammonia, amines, cresols, isocyanates, alkylene oxides; epichlorohydrin, sulfites, resorcinol, salicylic acid, and chloral hydrate
Waste Disposal
Convert to nitrate using nitric acid; evaporate, then saturate with H2S; wash and dry the sulfide and ship to the supplier. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal
Precautions
Lead (II) acetate, as with any other lead salts, causes lead poisoning.
Lead acetate Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of2
chevron_rightPreparation Products
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVA CHEMICALS PVT LTD | +91-8879390046 +91-8879390046 | Maharashtra, India | 74 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Kronox Lab Sciences Pvt Ltd | +91-9313231074 +91-9313231074 | Gujarat, India | 240 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Dhara Industries | +91-9322395199 +91-9322395199 | Mumbai, India | 190 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Nithyasri Chemicals (APURVA CHEMICALS) | +91-2512692130 +91-9323652199 | Maharashtra, India | 75 | 58 | Inquiry |
| L S Chemicals and Pharmaceuticals | +91-9820027610 +91-9820002565 | Maharashtra, India | 10 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Evans Fine Chem | +91-9821340302 +91-9821340302 | Maharashtra, India | 286 | 58 | Inquiry |
| TCI Chemicals (India) Pvt. Ltd. | 1800 425 7889 | New Delhi, India | 6778 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Vishnupriya Chemicals Private Limited | +91-8046041737 | Telangana, India | 220 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Central Drug House(P) Ltd. | 91-11-49404040 | New Delhi, India | 6160 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Euroasia Trans Continental | +91 22 56349035-36 | New Delhi, India | 519 | 47 | Inquiry |
301-04-2(Lead acetate)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




