Lead monoxide
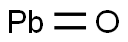
- CAS No.
- 1317-36-8
- Chemical Name:
- Lead monoxide
- Synonyms
- LITHARGE;LEAD(II) OXIDE;RED LEAD;ow;massicot;Lead oxid;c.i. 77577;plumbanone;massicotite;powder, <
- CBNumber:
- CB4119629
- Molecular Formula:
- OPb
- Molecular Weight:
- 223.1994
- MOL File:
- 1317-36-8.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/5/20 18:13:44
| Melting point | 886 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 1470 °C |
| Density | 9.53 |
| vapor pressure | 10 mm Hg ( 0 °C) |
| refractive index | 2.67 |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | Soluble in concentrated alkali, HCl and ammonium chloride. Insoluble in dilute alkali and alcohol. |
| form | powder |
| color | yellow |
| Specific Gravity | 9.53 |
| PH | 8-9 (100g/l, H2O, 20℃)(slurry) |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in concentrated alkali, hydrochloric acid, and ammonium chloride. Insoluble in water, dilute alkali and alcohol. |
| Hydrolytic Sensitivity | 4: no reaction with water under neutral conditions |
| Merck | 14,5413 |
| Exposure limits |
ACGIH: TWA 0.05 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 100 mg/m3; TWA 0.050 mg/m3 |
| Stability | Stable. Reacts violently with hydrogen peroxide, strong oxidizing agents, aluminium, zirconium, halogens, sulphur trioxide, boron, silicon, sodium, zinc. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1317-36-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Lead monoxide(1317-36-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Lead monoxide (1317-36-8) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS07,GHS08,GHS09 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H302+H332-H351-H360D-H362-H372-H410 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P260-P263-P273-P301+P312-P304+P340+P312-P308+P313 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | T,N | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 61-20/22-33-50/53-62 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 53-45-60-61 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 2291 6.1/PG 3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | OG1750000 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HS Code | 2824 10 00 | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 6.1(b) | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 i.p. in rats: 40 mg Pb/100g (Bradley, Fredrick) | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Lead monoxide price More Price(41)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich | 402982 | Lead(II) oxide ACS reagent, ≥99.0% | 1317-36-8 | 250G | ₹5423.33 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 402982 | Lead(II) oxide ACS reagent, ≥99.0% | 1317-36-8 | 250G | ₹5423.33 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 402982 | Lead(II) oxide ACS reagent, ≥99.0% | 1317-36-8 | 1KG | ₹17839.6 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 211907 | Lead(II) oxide powder, <10?μm, ReagentPlus?, ≥99.9% trace metals basis | 1317-36-8 | 500G | ₹4319.18 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 211907 | Lead(II) oxide powder, <10?μm, ReagentPlus?, ≥99.9% trace metals basis | 1317-36-8 | 100G | ₹4730.53 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Lead monoxide Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Lead(II) oxide occurs in two polymorphs, red, having a tetragonal crystal structure and yellow, having an orthorhombic crystal structure. Both forms occur naturally as rare minerals. The red form is known as “Litharge” and the yellow form is known as “Massico”.
Chemical Properties
Lead monoxide, litharge, PbO, exists in a reddish alpha form up to 489 °C; it then transforms to a yellow beta form (massicot), which is stable at high temperatures. It has a water solubility of 17 mg/L at 20 °C, and is soluble in nitric acid, alkalies, lead acetate, ammonium chloride, and chlorides of calcium and strontium. In alkalies, it forms the plumbite ion, [PbO2]2? . Lead oxides are produced industrially by thermal processes in which lead is directly oxidized with air. In the ball mill process, metallic lead balls are tumbled in air to produce a “leady” oxide, which typically contains 20-35% free lead. The Barton pot process oxidizes droplets of molten lead at ca. 430°C to produce either litharge or leady litharge.
Physical properties
The oxide exhibits two crystalline modifications, the reddish or orange-red alpha form, known as litharge, and the yellow beta form, massicot. The alpha form constitutes tetragonal crystals while the beta modification is a yellow amorphous powder of orthorhombic crystal structure. The alpha form is stable at ordinary temperatures, converting to the beta form when heated at 489°C; density 9.35 g/cm3 (beta form); Moh’s hardness 2 (alpha form); the oxide melts at 888°C; vaporizes at 1,472°C with decomposition; vapor pressure 1 torr at 943°C and 5 torr at 1,039°C; practically insoluble in water (the solubility of alpha form is 17 mg/L at 20°C and that of beta form 23 mg/L at 22°C); insoluble in ethanol; soluble in dilute nitric acid and alkalies.
Uses
Lead(II) oxide is employed mostly in lead-based industrial glass and industrial ceramics, including computer components. It is used as an intermediate/precursor in the manufacture of several products, for example water proof cements, lubricants, lubricating oils, inorganic pigments, lead soaps, petroleum refining, rubber, cathode ray tube glass, and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). It is useful for lead acid batteries as cathode and anode. Lead monoxide scores significant applications in oil, gas and chemical manufactures. It is an efficient catalyst for condensation reactions in organic synthesis.
General Description
Odorless gray or yellow green or red-brown solid. Sinks in water.
Reactivity Profile
Lead monoxide has weak oxidizing or reducing powers. Redox reactions can however still occur. The majority of compounds in this class are slightly soluble or insoluble in water. If soluble in water, then the solutions are usually neither strongly acidic nor strongly basic. These compounds are not water-reactive. Aluminum carbide is oxidized with incandescence on warming with lead oxide, [Mellor, 1946, Vol. 5, 872]. Mixtures of lead oxide with aluminum powder(as with other metals: sodium, zirconium) give a violent explosions, [Mellor, 1946, Vol. 5, 217, 1941].
Health Hazard
General symptoms of lead poisoning (delayed). Inhalation or ingestion causes abdominal pain (lead colic), metallic taste in mouth, loss of weight, pain in muscles, and muscular weakness. Dust may irritate eyes.
Purification Methods
Higher oxides are removed by heating under vacuum at 550o with subsequent cooling under vacuum. It is red at room temperature but becomes yellow at high temperatures (~480o) reversibly. [Ray & Ogg J Am Chem Soc 78 5994 1956, Kwestroo et al. J Inorg Nucl Chem 29 39 1967.]
Lead monoxide Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
1of6
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLR Innovations | +91 9891111994 | New Delhi, India | 4542 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Shristab Pvt Ltd | +91-9414179987 +91-9414190109 | Rajasthan, India | 13 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Merck Ltd | +91-2262109800 +91-2262109000 | Maharashtra, India | 272 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Mittal Pigments Pvt Ltd | +91-9829626774 +91-9829626774 | Rajasthan, India | 7 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Gharda Chemicals Ltd | +919820134485 | Maharashtra, India | 32 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Kronox Lab Sciences Pvt Ltd | +91-9313231074 +91-9313231074 | Gujarat, India | 240 | 58 | Inquiry |
| L S Chemicals and Pharmaceuticals | +91-9820027610 +91-9820002565 | Maharashtra, India | 10 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Otto Chemie Pvt. Ltd. | +91 9820041841 | Mumbai, India | 5873 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Alfa Aesar | 1 800 209 7001 | Maharashtra, India | 6913 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Triveni chemicals | 08048762458 | New Delhi, India | 6093 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| GLR Innovations | 58 |
| Shristab Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| Merck Ltd | 58 |
| Mittal Pigments Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| Gharda Chemicals Ltd | 58 |
| Kronox Lab Sciences Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| L S Chemicals and Pharmaceuticals | 58 |
| Otto Chemie Pvt. Ltd. | 58 |
| Alfa Aesar | 58 |
| Triveni chemicals | 58 |
1317-36-8(Lead monoxide)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




