Lead(II) nitrate
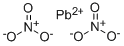
- CAS No.
- 10099-74-8
- Chemical Name:
- Lead(II) nitrate
- Synonyms
- PB(NO3)2;LEAD NITRATE;LEAD STANDARD;Blei(II)-nitrat;Pb solution;Lead Nitrale;LeadNitrateGr;LeadNitrateAr;leaddinitrate;LeadNitrateAcs
- CBNumber:
- CB4690009
- Molecular Formula:
- N2O6Pb
- Molecular Weight:
- 331.21
- MOL File:
- 10099-74-8.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/2/18 17:28:16
| Melting point | 470 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 500℃[at 101 325 Pa] |
| Density | 1.00 g/mL at 20 °C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: soluble |
| form | Solid |
| Specific Gravity | 4.53 |
| color | White |
| PH | 3-4 (50g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Water Solubility | 343 g/L |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Hydrolytic Sensitivity | 0: forms stable aqueous solutions |
| Merck | 14,5414 |
| Dielectric constant | 37.7(0.0℃) |
| Exposure limits |
ACGIH: TWA 0.05 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 100 mg/m3; TWA 0.050 mg/m3 |
| Stability | Stable. Strong oxidizer. Incompatible with combustible materials, organics, strong reducing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 10099-74-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Lead nitrate (Pb(NO3)2) (10099-74-8) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |      GHS03,GHS05,GHS07,GHS08,GHS09 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H272-H302+H332-H317-H318-H360FD-H372-H410 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P210-P273-P280-P304+P340+P312-P305+P351+P338-P308+P313 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | O,T,N,Xi,C | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 61-8-20/22-33-50/53-62-52/53-36/38-51/53-35-41-34 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 53-45-60-61-17-26-36/37-36/37/39-39 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 1469 5.1/PG 2 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | OG2100000 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HS Code | 2834 29 20 | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 5.1 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | II | |||||||||
| Toxicity | guinea pig,LDLo,oral,500mg/kg (500mg/kg),BLOOD: PIGMENTED OR NUCLEATED RED BLLOD CELLSBEHAVIORAL: CONVULSIONS OR EFFECT ON SEIZURE THRESHOLD,Archiv fuer Hygiene und Bakteriologie. Vol. 125, Pg. 273, 1941. | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Lead(II) nitrate price More Price(27)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 467790 | Lead(II) nitrate ≥99.95% trace metals basis | 10099-74-8 | 50G | ₹10078.08 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 467790 | Lead(II) nitrate ≥99.95% trace metals basis | 10099-74-8 | 250G | ₹24626.88 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 228621 | Lead(II) nitrate ACS reagent, ≥99.0% | 10099-74-8 | 100G | ₹2294.9 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 228621 | Lead(II) nitrate ACS reagent, ≥99.0% | 10099-74-8 | 500G | ₹2944.4 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 41318 | Lead Standard for ICP TraceCERT?, 1000?mg/L Pb in nitric acid | 10099-74-8 | 100ML | ₹18554.05 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Lead(II) nitrate Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
The lead nitrate appears as a white cubic crystal or monoclinic crystalline powder. It is soluble in water and liquid ammonia, being slightly soluble in the ethanol, being insoluble in concentrated nitric acid (produce protective film); it can react with concentrated hydrochloric acid or concentrated alkali chloride solution to form complex chlorinated lead acid or chlorinated lead acid salt; it has strong oxidizing property and may cause the risk of inducing combustion and explosion if mixed with organic matter, reducing agent and combustible substance such as sulfur and phosphorus or even subject to slightly friction. The dry lead nitrate can be subject to decomposition at around 205 ~223 while a temperature of 100 is enough to trigger the decomposition of wet lead nitrate. Its decomposition can emit toxic nitric oxide gas.
Physical properties
Colorless cubic or monoclinic crystals; refractive index 1.782; density 4.53 g/cm3 at 20°C; decomposes at 470°C; soluble in cold water; very soluble in boiling water 127 g/100 mL at 100°C; also soluble in caustic soda, caustic potash and ammonia solution, and moderately soluble in alcohol.
Uses
Lead(II) nitrate is employed in industrial applications such as heat stabilization in nylon and polyesters and coatings of photothermographic paper. It is utilized to improve the leaching process in the gold cyanidation. It finds applications as a lead paint as well as a source of dinitrogen tetroxide. As an oxidant, it is used in the oxidation of benzylic halides to aldehydes in organic synthesis. It is also used in the preparation of dithiocarbamates from isothiocyanates. It acts as a scavenger of bromide in nucleophilic substitution reactions.
Preparation
Lead nitrate is prepared by dissolving lead metal, lead monoxide or lead carbonate in excess dilute nitric acid followed by evaporation of and/or cooling the solution for crystallization.
General Description
Lead dinitrate is a white crystalline solid. The material is soluble in water. Lead dinitrate is noncombustible but Lead dinitrate will accelerate the burning of combustible materials. If large quantities of the material are involved in the fire an explosion may result. Prolonged exposure of the material to fire or heat may result in an explosion. Toxic oxides of nitrogen are produced in fires involving Lead dinitrate.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Mixtures of metal/nonmetal nitrates with alkyl esters may explode because of the formation of alkyl nitrates; mixtures of nitrate with phosphorus, tin (II) chloride or other reducing agents may react explosively [Bretherick 1979. p. 108-109]. An explosion of guanidine nitrate demolished an autoclave built to withstand 50 atmospheres, in which Lead dinitrate was being made from ammonium thiocyanate and Lead dinitrate [C. Angew. Chem. 49:23. 1936].
Hazard
The toxic effects are greater than other lead salts because lead nitrate is more soluble. Moderately toxic by ingestion and other routes of exposure. The compound also is an irritant to eye, skin, and mucous membranes.
Health Hazard
Early symptoms of lead intoxicatin via inhalation or ingestion are most commonly gastrointestinal disorders, colic, constipation, etc.; weakness, which may go on to paralysis, chiefly of the extensor muscles of the wrists and less often the ankles, is noticeable in the most serious cases. Ingestion of a large amount causes local irritation of the alimentary tract; pain, leg cramps, muscle weakness, paresthesias, depression, coma, and death may follow in 1 or 2 days. Contact with eyes causes irritation.
Industrial uses
This is a white to colorless fine crystalline compound, extremely soluble in water (34% at 20 °C). Commercial production is based on dissolution of lead metal or lead compounds in nitric acid (36–40% solution). Lead nitrate is considered to be an activator in mineral processing. Although lead may activate sphalerite, similar to CuSO4, the use of Pb(NO3)2 is limited to the activation of stibnite during beneficiation of antimony ores. Lead nitrate is the most widely used chemical in cyanidation of precious metals as an accelerator.
Purification Methods
Precipitate it twice from a hot (60o) concentrated aqueous solution by adding HNO3. The precipitate is sucked dry on a sintered-glass funnel, then transferred to a crystallising dish which is covered by a clock glass and left in an electric oven at 110o for several hours [Beck et al. Trans Faraday Soc 55 331 1959]. After two recrystallisations of ACS grade, no metals above 0.001ppm were detected.
Lead(II) nitrate Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
1of4
chevron_right




