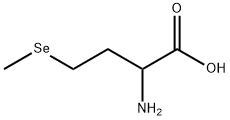
DL-Selenomethionine
- CAS No.
- 1464-42-2
- Chemical Name:
- DL-Selenomethionine
- Synonyms
- Selenomethionine;Selenium methionine;seleniummethionine;Seleno-DL-methionine;C05335;DL-Se-Met;methionine,seleno;Methionine, seleno;DL-SELENOMETHIONINE;SELENOMETHIONINE 98+%
- CBNumber:
- CB4505790
- Molecular Formula:
- C5H11NO2Se
- Molecular Weight:
- 196.11
- MOL File:
- 1464-42-2.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/3/28 16:55:20
| Melting point | 267-269 °C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 320.8±37.0 °C(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | almost transparency in 1mol/L HCl |
| pka | 2.26±0.10(Predicted) |
| form | solid |
| color | White to Almost white |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| Merck | 14,8441 |
| BRN | 1758204 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Butanoic acid, 2-amino-4-(methylseleno)-(1464-42-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Butanoic acid, 2-amino-4-(methylseleno)- (1464-42-2) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS06,GHS08,GHS09 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H301+H331-H373-H410 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P260-P264-P273-P301+P310-P304+P340+P311-P314 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | T,N | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 23/25-33-50/53 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 20/21-28-45-60-61 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 3283 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | ES7110000 | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 6.1 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| HS Code | 2931909000 | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
DL-Selenomethionine price More Price(7)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | S3875 | Seleno-DL-methionine ≥99% (TLC) | 1464-42-2 | 25MG | ₹3301.63 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | S3875 | Seleno-DL-methionine ≥99% (TLC) | 1464-42-2 | 100MG | ₹6462.53 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | S3875 | Seleno-DL-methionine ≥99% (TLC) | 1464-42-2 | 500MG | ₹16713.8 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | S3875 | Seleno-DL-methionine ≥99% (TLC) | 1464-42-2 | 1G | ₹37671 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | PHR2613 | Selenomethionine | 1464-42-2 | 200MG | ₹16995.25 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
DL-Selenomethionine Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Selenomethionine is the major form of selenium in plant foods. Selenomethionine is identical to methionine, except that selenium replaces the sulfur atom. The selenium consumed as selenocysteine is broken down to form alanine and hydrogen selenide (H2Se). The breakdown pathway of selenomethion- ine is not clear. Although selenium does not occur to a great extent as selenite in foods, selenite is readily used as a source of the element by humans and animals. Selenium also occurs as selenate in foods such as beet leaves, garlic, and cabbage.

DL-Selenomethionine is a selenium (Se) analogue of methionine in which sulfur is replaced with the trace element selenium. Selenomethionine (SeMet) can incorporate into proteins in place of methionine with no effects on protein structure and function, providing a mechanism for reversible Se storage in organs and tissues. Free selenium is incorporated into selenocysteine, an amino acid found in more than thirty selenoproteins including the glutathione peroxidases (GPx) enzymes, thioredoxin reductase (TR) and the iodothyronine deiodinase enzymes.
Uses
Selenium as selenite, DL-selenomethionine, and DL-selenocystine was equally effective in preventing liver necrosis, but factor 3 selenium was three times more effective than these forms (Burk, 1976; Schwarz and Foltz, 1958).
Biological Functions
Most selenium in animal tissues is present as selenomethionine or selenocysteine. Selenomethionine, which cannot be synthesized by humans and is initially synthesized in plants, is incorporated randomly in place of methionine in a variety of proteins obtained from plant and animal sources. Selenium is present in varying amounts in these proteins, which are called selenium-containing proteins.
Selenomethionine is not known to have a physiological function separate from that of methionine.
Selenocysteine is present in animal selenoproteins that have been characterized (see below) and is the form of selenium that accounts for the biological activity of the element. In contrast to selenomethionine, there is no evidence that selenocysteine substitutes for cysteine in humans.
Biological Activity
Most dietary selenium is highly bioavailable. Selenomethionine, which is estimated to account for at least half of the dietary selenium, is absorbed by the same mechanism as methionine, and its selenium is made available for selenoprotein synthesis when it is catabolized via the transsulfuration pathway (Esaki et al., 1982). The bioavailability of selenium in the form of selenomethionine is greater than 90 percent (Thomson and Robinson, 1986). The selenium in selenocysteine, another significant dietary form, is also highly bioavailable (Swanson et al., 1991). There appear to be some minor dietary forms of selenium (especially present in fish) that have relatively low bioavailability, but these forms have not been identified (Cantor and Tarino, 1982). Selenate and selenite, two inorganic forms of selenium, have roughly equivalent bioavailability which generally exceeds 50 percent (Thomson and Robinson, 1986). Although they are not major dietary constituents, these inorganic forms are commonly used as selenium supplements.
Metabolism
Selenomethionine, derived mainly from plants, enters the methionine pool in the body and shares the fate of methionine until catabolized by the transsulfuration pathway. The resulting free selenocysteine is further broken down with liberation of a reduced form of the element, which is designated selenide (Esaki et al., 1982). Ingested selenite, selenate, and selenocysteine are all apparently metabolized directly to selenide. This selenide may be associated with a protein that serves as a chaperone (Lacourciere and Stadtman, 1998). The selenide can be metabolized to selenophosphate, the precursor of selenocysteine in selenoproteins (Ehrenreich et al., 1992) and of selenium in transfer RNA (Veres et al., 1992), or it can be converted to excretory metabolites (Mozier et al., 1988), some of which have been characterized as methylated forms.
Purification Methods
It crystallises in hexagonal plates from MeOH and H2O. [Klosterman & Painter J Am Chem Soc 69 2009 1949.] The L-isomer [3211-76-5] is purified by dissolving it in H2O, adjusting the pH to 5.5 with aqueous NH3, evaporating to near-dryness, and the residue is washed several times with absolute EtOH till a solid is formed and then recrystallise from Me2CO. It has m 266-268o(dec) [also 275o(dec)], and [] D +18.1o(c 1, N HCl). [Pande et al. J Org Chem 35 1440 1970, Beilstein 4 IV 3216.]
DL-Selenomethionine Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | +91-22-45045900 | Hyderabad, India | 6351 | 58 | Inquiry |
| TCI Chemicals (India) Pvt. Ltd. | 1800 425 7889 | New Delhi, India | 6778 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Pharmaffiliates Analytics and Synthetics P. Ltd | +91-172-5066494 | Haryana, India | 6773 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Triveni chemicals | 08048762458 | New Delhi, India | 6093 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Prachi Pharmaceuticals Private Limited | 08048966305 | Mumbai, India | 20 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Pharma Affiliates | 172-5066494 | Haryana, India | 6761 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Souvenier Chemicals | 08048372762Ext 645 | Mumbai, India | 396 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Hebei Mojin Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +86 13288715578 +8613288715578 | China | 12459 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Henan Fengda Chemical Co., Ltd | +86-371-86557731 +86-13613820652 | China | 20361 | 58 | Inquiry |
| career henan chemical co | +86-0371-86658258 +8613203830695 | China | 29901 | 58 | Inquiry |
1464-42-2(DL-Selenomethionine)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




