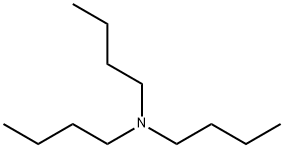
Tributylamine
- CAS No.
- 102-82-9
- Chemical Name:
- Tributylamine
- Synonyms
- TBA;TRI-N-BUTYLAMINE;TNBA;n-Tributylamine;N,N-Dibutylbutan-1-amine;ai3-15424;(n-C4H9)3N;Tributyamine;TRIBUTYLAMINE;Tributilamina
- CBNumber:
- CB5124462
- Molecular Formula:
- C12H27N
- Molecular Weight:
- 185.35
- MOL File:
- 102-82-9.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2023/11/28 16:31:44
| Melting point | −70 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 216 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.778 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 6.38 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 0.3 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index |
n |
| Flash point | 146 °F |
| storage temp. | Store at RT. |
| solubility | sparingly soluble in water; soluble in most organic solvents; soluble in acetone and benzene; very soluble in alcohol and ether |
| pka | 9.99±0.50(Predicted) |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Clear |
| Water Solubility | 0.386 g/L (25 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,9618 |
| BRN | 1698872 |
| Dielectric constant | 2.29 |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids. Hygroscopic. |
| LogP | 3.34 at 25℃ |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 102-82-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Tributylamine(102-82-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Tributylamine (102-82-9) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS06,GHS08 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H302-H310+H330-H315-H372 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P262-P280-P301+P312-P302+P352+P310-P304+P340+P310-P314 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | T,N,T+ | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 22-23/24-38-51/53-23/24/25-26-24 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 26-36/37-45-61-36/37/39-28A-28 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 2542 6.1/PG 2 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 2 | |||||||||
| RTECS | YA0350000 | |||||||||
| F | 10 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 6.1 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | II | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29211980 | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Tributylamine price More Price(14)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 8.08358 | Tributylamine for synthesis | 102-82-9 | 1L | ₹4000 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 8.08358 | Tributylamine for synthesis | 102-82-9 | 2.5L | ₹5300 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 8.08358 | Tributylamine for synthesis | 102-82-9 | 100ML | ₹5490 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 8.08358 | Tributylamine for synthesis | 102-82-9 | 40KG | ₹73030 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 471313 | Tributylamine ≥98.5% | 102-82-9 | 25ML | ₹2695.43 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Tributylamine Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
Pale-yellow liquid; amine odor. Slightly soluble in water; soluble in most organic solvents. Combustible.
Uses
Tributylamine is used as a solvent, an inhibitor in hydraulic fluids, a dental cement, and in isoprene polymerization.
Production Methods
Tributylamine (TBA) is manufactured by vapor phase alkylation of ammonia with butanol to produce a technical grade compound (Windholz et al 1983).
General Description
A pale yellow liquid with an ammonia-like odor. Less dense than water. Very irritating to skin, mucous membranes, and eyes. May be toxic by skin absorption. Low toxicity. Used as an inhibitor in hydraulic fluids.
Air & Water Reactions
Hygroscopic. Slightly soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Tributylamine can react with oxidizing materials . Neutralizes acids in exothermic reactions to form salts plus water. May be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen may be generated in combination with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides.
Health Hazard
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
Combustible material: may burn but does not ignite readily. When heated, vapors may form explosive mixtures with air: indoors, outdoors and sewers explosion hazards. Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated. Runoff may pollute waterways. Substance may be transported in a molten form.
Industrial uses
TBA is used as a solvent, an inhibitor in hydraulic fluids and a chemical intermediate. It is also used as a catalyst in a wide range of chemical reactions, as an insecticide, an emulsifying agent and in dental cements (HSDB 1988).
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, inhalation, skin contact, and subcutaneous routes. A central nervous system stimulant, irritant, and sensitizer. A corrosive irritant to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Flammable when exposed to heat, flame, or oxidmers. Can react with oxidizing materials. To fight fire, use foam, CO2, dry chemical. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx. See also AMINES.
Potential Exposure
Alert: (n-isomer): Possible risk of forming tumors, suspected of causing genetic defects, suspected reprotoxic hazard, Primary irritant (w/o allergic reaction), (sec-isomer): Drug. n-Butylamine is used in pharmaceuticals; dyestuffs, rubber, chemicals, emulsifying agents; photography, desizing agents for textiles; pesticides, and synthetic agents. sec-Butylamine is used as a fungistate. tert-Butylamine is used as a chemical intermediate in the production of tert-Butylaminoethyl methacrylate (a lube oil additive); as an intermediate in the production of rubber and in rust preventatives and emulsion deterrents in petroleum products. It is used in the manufacture of several drugs
Metabolism
Green and Large (1984) suggest that TBA is oxidized by a tertiary amine monooxygenase. The amine monooxygenases, located in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum, attack the amine group to give rise to the corresponding aldehyde product.
Shipping
UN1125 n-Butylamine, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3—Flammable liquid, 8—Corrosive material. UN2014 Isobutylamine, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3—Flammable liquid, 8—Corrosive material
Purification Methods
Purify the amine by fractional distillation from sodium under reduced pressure. Pegolotti and Young [J Am Chem Soc 83 3251 1961] heated the amine overnight with an equal volume of acetic anhydride, in a steam bath. The amine layer was separated and heated with water for 2hours on the steam bath (to hydrolyse any remaining acetic anhydride). The solution was cooled, solid K2CO3 was added to neutralize any acetic acid that had been formed, and the amine was separated, dried (K2CO3) and distilled at 44mm pressure. Davis and Nakshbendi [J Am Chem Soc 84 2085 1926] treated the amine with one-eighth of its weight of benzenesulfonyl chloride in aqueous 15% NaOH at 0-5o. The mixture was shaken intermittently and allowed to warm to room temperature. After a day, the amine layer was washed with aqueous NaOH, then water and dried with KOH. (This treatment removes primary and secondary amines.) It was further dried with CaH2 and distilled under vacuum. [Beilstein 4 IV 554.]
Incompatibilities
May form explosive mixture with air. May accumulate static electrical charges, and may causeignition of its vapors. n-Butylamine is a weak base; reacts with strong oxidizers and acids, causing fire and explosion hazard. Incompatible with organic anhydrides; isocyanates, vinyl acetate; acrylates, substituted allyls; alkylene oxides; epichlorohydrin, ketones, aldehydes, alcohols, glycols, phenols, cresols, caprolactum solution. Attacks some metals in presence of moisture. The tert-isomer will attack some forms of plastics
Waste Disposal
Use a licensed professional waste disposal service to dispose of this material. Dissolve or mix the material with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner andscrubber. All federal, state, and local environmental regulations must be observed.
Tributylamine Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
1of3
chevron_right102-82-9(Tributylamine)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




