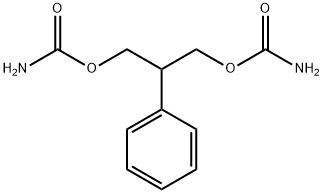
Felbamate
- CAS No.
- 25451-15-4
- Chemical Name:
- Felbamate
- Synonyms
- W-554;Talox;Taloxa;Felbamyl;felbatol;felbamato;ADD-03055;FELBAMATE;Sch-54388;Felbanmate
- CBNumber:
- CB6689427
- Molecular Formula:
- C11H14N2O4
- Molecular Weight:
- 238.24
- MOL File:
- 25451-15-4.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2023/7/21 14:17:16
| Melting point | 148-1500C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 511.9±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.275±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| Flash point | 9℃ |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,Room temperature |
| solubility | alcohol: soluble |
| pka | 12.99±0.50(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White |
| BCS Class | 2 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 25451-15-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Felbamate(25451-15-4) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS02,GHS06,GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H225-H301+H311+H331-H370 |
| Precautionary statements | P210-P260-P280-P301+P310-P311 |
| RIDADR | UN1230 - class 3 - PG 2 - Methanol |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | TZ1070000 |
| HS Code | 2924296000 |
| Toxicity | LD50 i.p. in mice: 4000 mg/kg (Ludwig et al.) |
Felbamate price More Price(3)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | F0778 | Felbamate | 25451-15-4 | 10MG | ₹14711.18 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | F0778 | Felbamate | 25451-15-4 | 50MG | ₹53107.45 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | F-029 | Felbamate solution 2.0?mg/mL in methanol, ampule of 1?mL, certified reference material, Cerilliant? | 25451-15-4 | 1ML | ₹17103.8 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Felbamate Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Felbamate, characterized by its low toxicity and wide margin of safety, is efficacious in treating refractory patients with generalized tonic-clonic and complex partial seizures as monotherapy and adjunctive therapy.It has also been demonstrated to have a neuroprotective effect in cerebral ischemia and hypoxia. It has been suggested that the mechanism of its anticonvulsant activity is possibly through an interaction with the strychnineinsensitive receptor site on the NMDA receptor complex.
Chemical Properties
White Powder. Solubility in water 0.33 mg/mL, in ethanol 5.0 mg/mL, and in DMF 333.4 mg/mL.
Definition
ChEBI: The bis(carbamate ester) of 2-phenylpropane-1,3-diol. An anticonvulsant, it is used in the treatment of epilepsy.
Biological Functions
Felbamate (Felbatol) was introduced with the expectation
that it would become a major drug in the treatment
of epilepsy. Felbamate exhibited few manifestations of
serious toxicity in early clinical trials. Soon after its introduction,
however, it became apparent that its use was
associated with a high incidence of aplastic anemia.
Consequently, felbamate is indicated only for patients
whose epilepsy is so severe that the risk of aplastic anemia
is considered acceptable.
While its mechanism of action has not been clearly
established, felbamate shows some activity as an inhibitor
of voltage-dependent sodium channels in a manner
similar to that of phenytoin and carbamazepine.
Felbamate also interacts at the strychnine-insensitive
glycine recognition site on the NMDA receptor–
ionophore complex.Whether this effect is important to
its anticonvulsant activity is not clear.
Hazard
Low toxicity by ingestion. Human systemic effects.
Biological Activity
Anticonvulsant, acting as an antagonist at the NMDA-associated glycine binding site.
Mechanism of action
Gabapentin is a water-soluble amino acid originally designed to be a GABA-mimetic analogue capable of penetrating the CNS.
Surprisingly, it has no direct GABA-mimetic activity, nor is it active on sodium channels. The mechanism of action remains
unknown, although it has been suggested that gabapentin may alter the metabolism or release of GABA. Gabapentin
raises brain GABA levels in patients with epilepsy. Recent studies have demonstrated gabapentin binding to calcium
channels in a manner that can be allosterically modulated.
Gabapentin is indicated as an adjunct for use against partial seizures with or without secondary generalization, in patients
older than 12 years, and as adjunct for the treatment of partial seizures in children 3 to 12 years of age. It also is approved for
the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetic properties for gabapentin generally are favorable, with a bioavailability of 60% when given in low doses and somewhat less when given at higher doses because of saturable intestinal uptake by the L-amino-acid transporter. The L-amino-acid transporter is very susceptible to substrate saturation (low Km value). Its absorption and distribution into the CNS appears to be dependent on this amino acid transporter. Following the administration of an oral dose, gabapentin reaches peak plasma concentration in 2 to 3 hours. Additionally, it exhibits linear pharmacokinetics. Moreover, it is not extensively metabolized, nor is it an inducer of hepatic metabolizing enzymes. The elimination of unmetabolized gabapentin occurs by the renal route. Although its therapeutic range is not well characterized, gabapentin has a broad therapeutic index. This implies that a wide range of doses can be used, based on individual patient needs, without significant limitation because of dose-dependent side effects. Protein binding is negligible. Its elimination half-life of 5 to 7 hours is not affected by the dose or by other drugs, and its short half-life necessitates multiple daily administration.
Clinical Use
Felbamate is a dicarbamate that is structurally similar to the antianxiety drug meprobamate. It was approved by the U.S. FDA for antiseizure use in 1993. Following the occurrence of rare cases of aplastic anemia and of severe hepatotoxicity associated with the use of felbamate during early 1994, however, a black box warning was added to the drug's package insert). Despite this, felbamate continues to be used in many patients, although not as a first-line treatment. These toxicity effects may be attributed to the formation of toxic metabolites. Although felbamate use is now uncommon, it is used for severe refractory seizures, either partial, myoclonic, or atonic, or in Lennox-Gastaut syndrome
Side effects
Adverse effects of gabapentin are uncommon and not serious. The CNS effects include mild to moderate sedation, fatigue,
ataxia, headache, dizziness, and diplopia. Gabapentin may exacerbate myoclonus, but the effect is mild and does not require
discontinuance of the drug. It has been associated with the development of neuropsychiatric adverse events in
children.
Drug interactions are infrequent with gabapentin. It does not induce hepatic metabolizing enzymes, nor do other AEDs affect its
metabolism and elimination. Antacids may decrease absorption. Gabapentin dosage may need to be decreased in patients with
renal disease or in the elderly.
Synthesis
The synthesis of felbamate was first published in 1959. 2-Phenyl-1,3-propanediole is reacted with ethylcarbamate to yield felbamate.
Metabolism
Although the metabolism of felbamate has not been fully characterized, felbamate is esterase hydrolyzed to its monocarbamate metabolite, 2-phenyl-1,3-propanediol monocarbamate, which subsequently is oxidized via aldehyde dehydrogenase to its major human metabolite 3-carbamoyl-2-phenylpropionic acid. Other metabolites include the p-hydroxy and mercapturic acid metabolites of felbamate, which have been identified in human urine. Felbamate is a substrate for CYP2C19, with minor activity for CYP3A4 and CYP2E1. Thompson et al. has provided evidence for the formation of the reactive metabolite, 3-carbamoyl-2-phenylpropionaldehyde (CBMA), from the alcohol oxidation of 2-phenyl-1,3-propanediol monocarbamate. CBMA then undergoes spontaneous elimination to another reactive intermediate, 2-phenylpropenal (more commonly known as atropaldehyde), which is proposed to play a role in the development of toxicity during felbamate therapy. CBMA or a further product has been shown to provoke an immune response in mice. Evidence for in vivo atropaldehyde formation was confirmed with the identification of its mercapturic acid conjugates in human urine after felbamate administration. This is consistent with the hypothesis that atropaldehyde reacts rapidly with thiol nucleophiles, such as glutathione, to form mercapturates. More recently, a fluorine analogue of felbamate was synthesized in which the benzylic C2 hydrogen of the propane chain was replaced with fluorine, preventing the formation of atropaldehyde and confirming that the acidic benzylic hydrogen plays a pivotal role in its formation. This analogue is presently undergoing drug development. Felbamate administration exhibited linear kinetics, with a half-life of 20 to 23 hours in the absence of enzyme-inducing AEDs. Approximately 50% of an oral dose of felbamate is excreted unchanged.
Felbamate Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of2
chevron_rightPreparation Products
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TYNDAL LABS PVT LTD | +91-8008166674 +91-8008166674 | AndhraPradesh, India | 95 | 58 | Inquiry |
| KARPSCHEM LABORATORIES | +91-7249203006 +91-7249203006 | Maharashtra, India | 786 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Hetero Drugs Limited | +91-4023704923 +91-4023704923 | Telangana, India | 296 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Mylan Laboratories Ltd | +91-4023550543 +91-4030866666 | Telangana, India | 150 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Apicore Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd | +91-2662267177 +91-2662267166 | Gujarat, India | 181 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Arch Pharmalabs Ltd | +91-2242871210 +91-2242871210 | Maharashtra, India | 51 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Solara Active Pharma Sciences Ltd | +91-8046632100 +91-7075706520 | Bangalore, India | 65 | 58 | Inquiry |
| A.J Chemicals | 91-9810153283 | New Delhi, India | 6124 | 58 | Inquiry |
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | +91-22-45045900 | Hyderabad, India | 6351 | 58 | Inquiry |
| SynZeal Research Pvt Ltd | +1 226-802-2078 | Gujarat, India | 6522 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| TYNDAL LABS PVT LTD | 58 |
| KARPSCHEM LABORATORIES | 58 |
| Hetero Drugs Limited | 58 |
| Mylan Laboratories Ltd | 58 |
| Apicore Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| Arch Pharmalabs Ltd | 58 |
| Solara Active Pharma Sciences Ltd | 58 |
| A.J Chemicals | 58 |
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | 58 |
| SynZeal Research Pvt Ltd | 58 |





