Diethyl ether
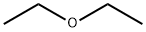
- CAS No.
- 60-29-7
- Chemical Name:
- Diethyl ether
- Synonyms
- ETHER;Ethyl ether;Anhydrous ether;Anhydrous diethyl ether;1-Ethoxyethane;ETHYL ETHER pure;Aether;(C2H5)2O;ALCOHOL - ETHER;DiethylEtherForHplc
- CBNumber:
- CB6853949
- Molecular Formula:
- C4H10O
- Molecular Weight:
- 74.12
- MOL File:
- 60-29-7.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2025/2/27 17:16:38
| Melting point | -116 °C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 34.6 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.714 |
| vapor density | 2.6 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 28.69 psi ( 55 °C) |
| refractive index |
n |
| Flash point | -40 °F |
| storage temp. | Store at RT. |
| solubility | Soluble in water, miscible with ethanol (96 per cent), with methylene chloride and with fatty oils. It is highly flammable. |
| form | Liquid |
| Specific Gravity | 0.714 (20/4℃) ; 0.712 (25℃) |
| color | clearAPHA: ≤10 |
| Odor | Pungent odor detectable at 0.33 ppm |
| Relative polarity | 2.9 |
| explosive limit | 1.7-36%(V) |
| Water Solubility | 69 g/L (20 ºC) |
| FreezingPoint | -116.3℃ |
| Merck | 14,3806 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 12.50(x 10-4 atm?m3/mol at 25 °C) (Signer et al., 1969) |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 1200 mg/m3 (400 ppm) (ACGIH and OSHA); STEL 1500 mg/m3 (500 ppm) (ACGIH). |
| Dielectric constant | 4.0(40℃) |
| Stability | Stable, but light-sensitive, sensitive to air. May contain BHT (2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol) as a stabilizer. Substances to be avoided include zinc, halogens, halogen-halogen compounds, nonmetals, nonmetallic oxyhalides, strong oxidizing agents, chromyl chloride, turpentine oils, turps substitutes, nitrates, metallic chlorides. Extre |
| LogP | 0.890 |
| Surface tension | 17.153mN/m at 293.15K |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 60-29-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Ethoxy ethane(60-29-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ethyl ether (60-29-7) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS02,GHS07 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H224-H302-H336 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P210-P233-P240-P241-P301+P312-P403+P233 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | F+,Xn,T,F | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 12-19-22-66-67-39/23/24/25-23/24/25-11 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 9-16-29-33-45-36/37-7 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 1155 3/PG 1 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 1 | |||||||||
| RTECS | KI5775000 | |||||||||
| F | 10 | |||||||||
| Autoignition Temperature | 160 °C | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HS Code | 2909 11 00 | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 3 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | I | |||||||||
| Hazardous Substances Data | 60-29-7(Hazardous Substances Data) | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 oral (rat) 1215 mg/kg LC50 inhal (rat) 73,000 ppm (2 h) PEL (OSHA) 400 ppm STEL (ACGIH) 500 ppm |
|||||||||
| IDLA | 1,900 ppm [10% LEL] | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Diethyl ether price More Price(53)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 673811 | Diethyl ether anhydrous, ACS reagent, ≥99.0%, contains BHT as inhibitor | 60-29-7 | 1L | ₹15588 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 673811 | Diethyl ether anhydrous, ACS reagent, ≥99.0%, contains BHT as inhibitor | 60-29-7 | 4L | ₹29844.53 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 676845 | Diethyl ether ACS reagent, ≥98.0%, contains ≤2% ethanol and ≤10ppm BHT as inhibitor | 60-29-7 | 1L | ₹12004.93 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 673811 | Diethyl ether anhydrous, ACS reagent, ≥99.0%, contains BHT as inhibitor | 60-29-7 | 200L | ₹180452.75 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | 346136 | Diethyl ether ACS reagent, anhydrous, ≥99.0%, contains BHT as inhibitor | 60-29-7 | 100ML | ₹4524.85 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Diethyl ether Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Diethyl ether is a component of starting fluids and is used as a solvent in the manufacture of synthetic dyes and plastics. Because of its characteristics, diethyl ether was widely used in many countries as an anesthetic agent, but was then replaced by other substances in the 1960s.
Chemical Properties
Ether, (C2H5)2,also known as ethyl ether, is a colorless liquid. It is used as a solvent,a denaturant, and as an anesthetic in medicine. lt is an organic compound in which two hydrocarbon radicals are joined by an atom of oxygen.
Chemical Properties
Diethyl ether has very diffusive, sweet-ethereal odor. Actually a poor odorant, it gives impression of power by its very high vapor pressure at room temperature.
Physical properties
Colorless, hygroscopic, volatile liquid with a sweet, pungent odor. Odor threshold concentration is 330 ppb (quoted, Keith and Walters, 1992).
History
Ether was supposedly discovered by Raymundus Lullus (1232–1315) around 1275, although there is no extant evidence of this in his writings. The discoverer of ether is often credited to the German physician and botanist Valerius Cordus (1515–1554), who gave the first description of the preparation of ether in the mid-16th century. Cordus called the substance oleum vitrioli dulce, which is translated as sweet oil of vitriol. Cordus used sulfuric acid (oil of vitriol) to catalyze the conversion of alcohol to ether. At approximately the same time Paracelsus (1493–1541), a Swiss physician who is also cited as a discoverer of ether, observed that chickens were safely put to sleep by breathing vapors from sweet oil of vitriol. In 1730, August Siegmund Frobenius changed the name of sweet vitriol to ether.
Uses
Diethyl ether has been used extensively as a general anesthetic.
Uses
Ethyl ether is a solvent that may cause skin irritation. Although considered a non-comedogenic raw material, it is rarely used in cosmetics.
However, being a useful extraction
solvent for natural perfume and flavor materials, diethyl ether is often found in traces in the commercial, evaporated extracts. It is easier to remove
ether from natural extracts, than it is to remove Hexane and other, more common solvents for perfume raw materials.
Production Methods
Ether is produced by the dehydration of ethanol using sulfuric acid: 2CH3CH2OH +2H2SO4 → (CH3CH2)2O + H2SO4 + H2O.the temperature of the reaction is carriedout at about 140°C to control for unwanted products.the volatile ether is distilled from themixture. Ether can also be prepared by Williamson synthesis. In this reaction, ethanol reactswith sodium to form sodium ethanolate (Na+C2H5O?). Sodium ethanolate then reacts withchloroethane to form ether and sodium chloride: Na+C2H5O? +C2H5Cl → C2H5OC2H5 +NaCl. Ether is also produced as a by-product in the production of ethanol.
Definition
diethyl ether: A colourless flammablevolatile ether, C2H5OC2H5; r.d. 0.71;m.p. –116°C; b.p. 34.5°C. It can bemade by Williamson’s synthesis. Itis an anaesthetic and useful organicsolvent.
General Description
A clear colorless liquid with an anesthetic odor. Flash point -49°F. Less dense than water and slightly soluble in water. Hence floats on water. Vapors are heavier than air. Used as a solvent and to make other chemicals.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Oxidizes readily in air to form unstable peroxides that may explode spontaneously [Bretherick, 1979 p.151-154, 164]. A mixture of liquid air and Diethyl ether exploded spontaneously, [MCA Case History 616(1960)].
Reactivity Profile
Occasional explosions have occurred when aluminum hydride was stored in ether. The explosions have been blamed on the presence of carbon dioxide impurity in the ether, [J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 70:877(1948)]. Diethyl ether and chromium trioxide react violently at room temperature. Solid acetyl peroxide in contact with ether or any volatile solvent may explode violently. A 5-gram portion in ether detonated while being carried, [Chem. Eng. News 27:175(1949)]. Nitrosyl perchlorate ignites and explodes with Diethyl ether. A mixture of ether and ozone forms aldehyde and acetic acid and a heavy liquid, ethyl peroxide, an explosive, [Mellor 1:911(1946-1947)].
Hazard
CNS depressant by inhalation and skin absorption. Very flammable, severe fire and explosion hazard when exposed to heat or flame. Forms explosive peroxides. Explosive limits in air 1.85– 48%.
Health Hazard
The acute toxicity of diethyl ether is low. Inhalation of high concentrations can cause sedation, unconsciousness, and respiratory paralysis. These effects are usually reversible upon cessation of exposure. Diethyl ether is mildly irritating to the eyes and skin, but does not generally cause irreversible damage. Repeated contact can cause dryness and cracking of the skin due to removal of skin oils. The liquid is not readily absorbed through the skin, in part because of its high volatility. Diethyl ether is slightly toxic by ingestion. Diethyl ether is regarded as having adequate warning properties. There is no evidence for carcinogenicity of diethyl ether, and no reproductive effects have been reported. Chronic exposure to diethyl ether vapor may lead to loss of appetite, exhaustion, drowsiness, dizziness, and other central nervous system effects.
Fire Hazard
Diethyl ether is extremely flammable (NFPA rating = 4) and is one of the most dangerous fire hazards commonly encountered in the laboratory, owing to its volatility and extremely low ignition temperature. Ether vapor may be ignited by hot surfaces such as hot plates and static electricity discharges, and since the vapor is heavier than air, it may travel a considerable distance to an ignition source and flash back. Ether vapor forms explosive mixtures with air at concentrations of 1.9 to 36% (by volume). Carbon dioxide or dry chemical extinguishers should be used for ether fires. Diethyl ether forms unstable peroxides on exposure to air in a reaction that is promoted by light; the presence of these peroxides may lead to explosive residues upon distillation.
Flammability and Explosibility
Diethyl ether is extremely flammable (NFPA rating = 4) and is one of the most dangerous fire hazards commonly encountered in the laboratory, owing to its volatility and extremely low ignition temperature. Ether vapor may be ignited by hot surfaces such as hot plates and static electricity discharges, and since the vapor is heavier than air, it may travel a considerable distance to an ignition source and flash back. Ether vapor forms explosive mixtures with air at concentrations of 1.9 to 36% (by volume). Carbon dioxide or dry chemical extinguishers should be used for ether fires. Diethyl ether forms unstable peroxides on exposure to air in a reaction that is promoted by light; the presence of these peroxides may lead to explosive residues upon distillation.
Chemical Reactivity
Reactivity with Water No reaction; Reactivity with Common Materials: No reaction; Stability During Transport: Stable; Neutralizing Agents for Acids and Caustics: Not pertinent; Polymerization: Not pertinent; Inhibitor of Polymerization: Not pertinent.
Industrial uses
Diethyl ether as a commercial product is available in several grades and is used as an extraction solvent, reaction solvent, and as a general anesthetic. Ethyl ether is an excellent solvent for alkaloids, dyes, fats, gums, oils, resins, and waxes. Blends of ethyl ether and ethanol are excellent solvents for cellulose nitrate used in the manufacture of guncotton, in collodion solutions and pyroxylin plastics. Ethyl ether is used in the recovery of acetic acid from aqueous solutions in the cellulose acetate and plastic industry. It is used as a starter fuel for diesel engines and as a denaturant in denatured ethanol formulations. Grignard and Wurtz-Fillig synthesis reactions use diethyl ether as an anhydrous, inert reaction medium.
Potential Exposure
Ethyl ether is used as a solvent for waxes, fats, oils, perfumes, alkaloids, dyes, gums, resins, nitrocellulose, hydrocarbons, raw rubber, and smokeless powder. It is also used as an inhalation anesthetic; a refrigerant; in diesel fuels; in dry cleaning; as an extractant; and as a chemical reagent for various organic reactions
Environmental Fate
Photolytic. The rate constant for the reaction of ethyl ether and OH radicals in the atmosphere at
300 K is 5.4 x 10-12 cm3/molecule?sec (Hendry and Kenley, 1979).
Chemical/Physical. The atmospheric oxidation of ethyl ether by OH radicals in the presence of
nitric oxide yielded ethyl formate as the major product. Minor products included formaldehyde
and nitrogen dioxide. In the absence of nitric oxide, the products were ethyl formate and
acetaldehyde (Wallington and Japar, 1991).
Ethyl ether will not hydrolyze (Kollig, 1993).
storage
ether should be used only in areas free of ignition sources (including hot plates, incandescent light bulbs, and steam baths), and this substance should be stored in tightly sealed metal containers in areas separate from oxidizers. Because of the tendency of diethyl ether to form peroxides on contact with air, containers should be dated upon receipt and at the time they are opened. Diethyl ether is generally supplied with additives that inhibit peroxide formation; distillation removes these inhibitors and renders the liquid more prone to peroxide formation. Material found to contain peroxides should be treated to destroy the peroxides before use or disposed of properly.
Shipping
UN1155 Diethyl ether or Ethyl ether, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3-Flammable liquid
Incompatibilities
May form explosive mixture with air. Incompatible with strong acids; strong oxidizers halogens, sulfur, sulfur compounds, causing fire and explosion hazard. Can form peroxides from air, heat, sunlight; may explode when container is unstoppered or otherwise opened. Attacks some plastics, rubber and coatings. Being a nonconductor, chemical may accumulate static electric charges that may result in ignition of vapor.
Waste Disposal
Concentrated waste containing no peroxides-discharge liquid at a controlled rate near a pilot flame. Concentrated waste containing peroxidesperforation of a container of the waste from a safe distance followed by open burning. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal
Diethyl ether Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of2
chevron_rightPreparation Products
1of8
chevron_rightRelated articles
- Is Diethyl ether Polar?
- Diethyl ether is consisting of two ethyl groups-C2H5-bonded to one oxygen atom. The structure of diethyl ether is C2H5-O-C2H5.....
- Dec 22,2023
60-29-7(Diethyl ether)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




