FERROUS SULFATE
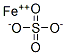
- CAS No.
- 7720-78-7
- Chemical Name:
- FERROUS SULFATE
- Synonyms
- FeSO4;FERROUS SULPHATE;Iron sulfate;IRON(II) SULFATE;FERROIN SOLUTION;DRIED FERROUS SULPHATE;Iron(Ⅱ) sulfate;kesuka;Irosul;slowfe
- CBNumber:
- CB7450570
- Molecular Formula:
- FeO4S
- Molecular Weight:
- 151.91
- MOL File:
- 7720-78-7.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2025/1/27 9:38:02
| Melting point | decomposes at 671℃ [JAN85] |
|---|---|
| Density | 3.650 |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 20℃ |
| storage temp. | Store at +15°C to +25°C. |
| solubility | Water (Slightly) |
| form | white orthorhombic crystals |
| color | white orthorhombic crystals, crystalline; hygroscopic |
| PH | 2.5 (20°C, 50g/L in H2O) |
| Odor | at 100.00?%. odorless |
| Water Solubility | g/100g solution H2O: 13.6 (0°C), 22.8 (25°C), 24.0 (100°C); solid phase, FeSO4 · 7H2O (0°C, 25°C), FeSO4 ·H2O (100°C) [KRU93] |
| Dielectric constant | 14.2(14℃) |
| InChI | InChI=1S/Fe.H2O4S/c;1-5(2,3)4/h;(H2,1,2,3,4)/q+2;/p-2 |
| InChIKey | BAUYGSIQEAFULO-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
| SMILES | [Fe+2].S([O-])([O-])(=O)=O |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7720-78-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Ferrous sulfate(7720-78-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ferrous sulfate (7720-78-7) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H302-H315-H319 |
| Precautionary statements | P264-P270-P301+P312-P330-P501-P264-P280-P302+P352-P321-P332+P313-P362-P264-P280-P305+P351+P338-P337+P313P |
| Risk Statements | 25 |
| Safety Statements | 45 |
| HS Code | 28332910 |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 7720-78-7(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| Toxicity | LD50 oral in rat: 319mg/kg |
FERROUS SULFATE price
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 1.09193 | Ferroin solution (1,10-phenanthroline iron(II) sulfate) 1/40 mol/l redox indicator | 7720-78-7 | 100ML | ₹6400 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 1.09193 | Ferroin solution (1,10-phenanthroline iron(II) sulfate) 1/40 mol/l redox indicator | 7720-78-7 | 500ML | ₹27430 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
FERROUS SULFATE Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Green vitriol, FeSO4.7H20, has been known since the thirteenth century ; it crystallizes from solutions of iron or iron bases in dilute sulphuric acid. The heptahydrate forms green monoclinic crystals of density 1·88, very soluble in water (296 g litre-1 FeS04 at 25°C). By precipitating the aqueous solution with ethanol, heating the heptahydrate to 140° in vacuo or by crystallizing it from 50 % sulphuric acid, the white monohydrate is obtained. This can be further dehydrated to the white, amorphous FeSO4 by heating to 300° in a current of hydrogen. At red heat the sulphate decomposes : 2FeS04 -> Fe203+S02+S03 A tetrahydrate, FeS04.4H20, crystallizes from aqueous solutions above 56°.
Chemical Properties
Ferrous sulfate is a greenish or yellowish solid in fine or lumpy crystals.
Physical properties
White orthorhombic crystal; hygroscopic; density 3.65 g/cm3; soluble in water (26.6g/100g water at 20°C). The monohydrate is a yellowish-white monoclinic crystal; density 3.0 g/cm3; decomposes at 300°C; soluble in water. Heptahydrate is bluish-green monoclinic crystal; refractive index 1.47; hardness 2 Mohs; density 1.89g/cm上3; decomposes at about 60°C; very soluble in water; soluble in absolute methanol; slightly soluble in ethanol.
Occurrence
Iron(II) sulfate is probably the most important salt of iron, as well as the longest-known iron(II) compound. The compound is used as a mordant in dyeing; as a component of writing ink; in electroplating baths; in radiation dosimeters; in lithography and engraving; as a weed-killer; and in water purification. A major application of this compound is in the manufacture of other iron(II) salts including Prussian blue or ferric ferrocyanide. Iron(II) sulfate also is used as a reducing agent and an analytical reagent (in brown ring test for nitrate).
Uses
Ferrous Sulfate is a nutrient and dietary supplement that is a source of iron. it is a white to grayish odorless powder. ferrous sulfate hep- tahydrate contains approximately 20% iron, while ferrous sulfate dried contains approximately 32% iron. it dissolves slowly in water and has high bioavailability. it can cause discoloration and rancidity. it is used for fortification of baking mixes. in the encapsulated form it does not react with lipids in cereal flours. it is used in infant foods, cereals, and pasta products.
Production Methods
Iron(II) sulfate in industrial scale is mostly produced in the pickling process as a by-product of the steel industry. It is obtained when the surface of steel is cleaned with dilute sulfuric acid to remove metal impurities. In the laboratory iron(II) sulfate heptahydrate may be prepared by dissolving iron in dilute sulfuric acid in a reducing atmosphere, followed by crystallization:
Fe + H2SO4 → FeSO4 + H2
Alcohol may be added to the aqueous solution to speed up crystallization; iron(II) may otherwise oxidize to iron(III) during a slow crystallization process.
Iron(II) oxide or carbonate may be used instead of iron metal to prepare the heptahydrate.
.
Definition
A rusty-brown solid prepared by the action of heat on iron(III) hydroxide or iron(II) sulfate. It occurs in nature as the mineral hematite. Industrially it is obtained by roasting iron pyrites. Iron(III) oxide dissolves in dilute acids to produce solutions of iron(III) salts. It is stable at red heat, decomposes around 1300°C to give triiron tetroxide, and can be reduced to iron by hydrogen at 1000°C. Iron(III) oxide is not ionic in character but has a structure similar to that of aluminum(III) oxide.
Hazard
Ingestion causes intestinal disorders.
Agricultural Uses
Copperas, also called green vitriol, is ferrous sulphate heptahydrate. It is an iron salt fertilizer, which is most effective in overcoming iron deficiency.
Safety Profile
A human poison by ingestion. Moderately toxic to humans by an unspecified route. An experimental poison by ingestion, intraduodenal, intraperitoneal, intravenous, and subcutaneous routes. Human systemic effects by ingestion: aggression, somnolence, brain recorlng changes, diarrhea, nausea or vomiting, bleedmg from the stomach, coma. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. Potentially explosive reaction with methyl isocyanoacetate at 25'. May igmte on contact with arsenic trioxide + sodium nitrate. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of SOx. See also IRON COMPOUNDS.
Potential Exposure
It is used as a fertilizer, food or feed additive; and in herbicides; process engraving; dyeing, and water treatment. A byproduct of various chemical and metal treating operations.
Incompatibilities
Aqueous solution is acidic. Contact with alkalies form iron. Keep away from alkalies, soluble carbo nates; gold and silver salts; lead acetate; lime water, potassium iodide; potassium and sodium tartrate; sodium borate; tannin.
FERROUS SULFATE Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of2
chevron_rightPreparation Products
1of4
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LABDHI CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES | +91-9322229293 +91-9322229293 | Mumbai, India | 21 | 58 | Inquiry |
| S.V ENTERPRISES | +919322701159 | Mumbai, India | 150 | 58 | Inquiry |
| ANWITA APIS | +919000311012 | Hyderabad, India | 195 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Rishi Chemical Works Pvt Ltd | +91-3322290068 +91-3322290071 | Kolkata, India | 43 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Evans Fine Chem | +91-9821340302 +91-9821340302 | Maharashtra, India | 286 | 58 | Inquiry |
| VITRAG CHEMICALS PVT LTD | +91-7490053194 +91-7490053194 | Gujarat, India | 47 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Ultra Chemical Works | +91-9820078105 +91-9820078105 | Mumbai, India | 124 | 58 | Inquiry |
| India Phosphate | +91-9993319656 +91-9993319656 | Madhya Pradesh, India | 61 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Dhara Industries | +91-9322395199 +91-9322395199 | Mumbai, India | 190 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Ions Pharma | +912266707500 | Maharashtra, India | 89 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| LABDHI CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES | 58 |
| S.V ENTERPRISES | 58 |
| ANWITA APIS | 58 |
| Rishi Chemical Works Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| Evans Fine Chem | 58 |
| VITRAG CHEMICALS PVT LTD | 58 |
| Ultra Chemical Works | 58 |
| India Phosphate | 58 |
| Dhara Industries | 58 |
| Ions Pharma | 58 |
Related articles
- The Comprehensive Guide to Ferrous Sulfate Monohydrate: Synthesis, Composition, and Applications
- Ferrous sulfate monohydrate, a derivative of iron sulfate, is a chemical compound that plays a crucial role in various industr....
- May 21,2024
- Application of Ferrous sulfate
- Ferrous sulfate appears as a greenish or yellow-brown crystalline solid. Density 15.0 lb /gal. Melts at 64°C and loses the sev....
- May 24,2022
7720-78-7(FERROUS SULFATE)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




