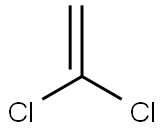
VINYLIDENE CHLORIDE
- CAS No.
- 75-35-4
- Chemical Name:
- VINYLIDENE CHLORIDE
- Synonyms
- 1,1-DICHLOROETHENE;1,1-DICHLOROETHYLENE;VDC;vinylidene;Vinylidine chloride;1,1-Dichlorethen;1,1-Dichlorethylen;Ethene,1,1-dichloro-;1,1-dichloroethylene vinylidene chloride;VDCM
- CBNumber:
- CB8292656
- Molecular Formula:
- C2H2Cl2
- Molecular Weight:
- 96.94
- MOL File:
- 75-35-4.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2025/1/27 9:38:02
| Melting point | -122 °C (lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 30-32 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1.213 g/mL at 20 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 3.46 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 9.68 psi ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index |
n |
| Flash point | −9 °F |
| storage temp. | Store at +2°C to +8°C. |
| solubility | 2.5g/l |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Clear colorless |
| explosive limit | 8.4-16.5%(V) |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water (2.5g/L at 20°C). |
| Sensitive | Light Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,9996 |
| BRN | 1733365 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 0.86, 1.00, 1.27, 1.97, and 2.66 at 2.0, 6.0, 10.0, 18.0, and 25.0 °C, respectively (EPICS-SPME, Dewulf et al., 1999) |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 5 ppm (~20 mg/m3) (ACGIH); TLV-STEL 20 ppm (ACGIH); carcinogenic ity: Animal Limited Evidence, Human Inad equate Evidence (IARC). |
| Dielectric constant | 4.7(16℃) |
| Stability | Stable. Very flammable - note low flash point. Vapour may travel considerable distances to a source of ignition. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, alcohols, halides, sopper, aluminium. Rapidly absorbs oxygen from the air and forms explosive peroxides. Light and water promote self-polymerisation. May form explosive mix |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 75-35-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. 39, Sup 7, 71, 119) 2019 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1,1-Dichloroethylene (75-35-4) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |     GHS02,GHS06,GHS08,GHS09 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H224-H301-H319-H332-H351-H372-H373-H411 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P210-P233-P273-P301+P310-P304+P340+P312-P403+P233 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | F+,Xn,T,F | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 12-20-40-39/23/24/25-23/24/25-11 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 7-16-29-36/37-46-45 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 1303 3/PG 1 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | KV9275000 | |||||||||
| F | 1-8-10 | |||||||||
| Autoignition Temperature | 968 °F | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HS Code | 2903 29 00 | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 3 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | I | |||||||||
| Hazardous Substances Data | 75-35-4(Hazardous Substances Data) | |||||||||
| Toxicity | Acute oral LD50 for rats 1,550 mg/kg, male mice 194 mg/kg, female mice 217 mg/kg (Jones and Hathway, 1978):dogs 5,750 mg/kg (Tierney et al., 1979). Heitmuller et al. (1981) reported a NOEC of 80 ppm. | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
VINYLIDENE CHLORIDE price More Price(8)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 8.03209 | 1,1-Dichloroethylene (stabilised with hydroquinone monomethyl ether) for synthesis | 75-35-4 | 100ML | ₹5880 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 8.03209 | 1,1-Dichloroethylene (stabilised with hydroquinone monomethyl ether) for synthesis | 75-35-4 | 1L | ₹11700 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 8.03209 | 1,1-Dichloroethylene (stabilised with hydroquinone monomethyl ether) for synthesis | 75-35-4 | 30KG | ₹104500 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 40027 | 1,1-Dichloroethene solution certified reference material, 1000?μg/mL in methanol | 75-35-4 | 1ML | ₹3830.4 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | 163023 | 1,1-Dichloroethylene contains 200?ppm MEHQ as inhibitor, 99% | 75-35-4 | 25ML | ₹4736.95 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
VINYLIDENE CHLORIDE Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
Vinylidene chloride is a volatile liquid. Mild, sweet odor resembling chloroform. The odor threshold in air is 500 ppm.
Physical properties
Colorless liquid or gas with a mild, sweet, chloroform-like odor. The average least detectable odor threshold concentration in water at 60 °C and in air at 40 °C was 1.6 mg/L (Alexander et al., 1982).
Uses
VDC is used to make various kinds of chemical intermediates, agricultural chemicals, SARAN?polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) resins and films, PVDC latex coatings, and photographic and X-ray films.
Production Methods
VDC is prepared commercially by the dehydrochlorination of 1,1,2-trichloroethane using a slight excess of lime or caustic as shown in the reaction schematic. About 200 ppm of monomethyl ether of hydroquinone (MEHQ) is added to prevent polymer formation and preserve product quality.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of chloroethenes that is ethene in which both of the hydrogens attached to one of the carbons are replaced by chlorines.
General Description
A clear colorless liquid with a chloroform-like odor. Flash point 0°F. Boiling point 99°F. Denser (at 10.1 lb / gal) than water and insoluble in water. Hence sinks in water. May polymerize exothermically if heated or contaminated. If the polymerization takes place inside a container, the container may rupture violently. Vapors heavier than air.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Peroxidizable monomer, such as VINYLIDENE CHLORIDE, may initiate exothermic polymerization of the bulk material [Bretherick 1979. p. 160, 187]. Mixing vinylidene chloride in equal molar portions in a closed container with any of the following substances caused the temperature and pressure to increase: chlorosulfonic acid, nitric acid, or oleum [NFPA 1991]. It's reaction products with ozone are particularly dangerous, [Dow Chemical, 1968]. This may extend to other powerful oxidants, as various peroxides are produced.
Health Hazard
Vapor can cause dizziness and drunkenness; high levels cause anesthesia. Liquid irritates eyes and skin.
Fire Hazard
Flammable liquid; flash point (closed cup) -18°C(0°F) (flash point data reported in the
literature differ); vapor pressure 500 torr at
20°C (68°F); vapor density 3.34 (air=1);
the vapor is heavier than air and can travel
a considerable distance to a source of igni tion and flash back; autoignition temperature 570°C (1058°F); fire-extinguishing agent: dry
chemical, CO2, or foam; use water to keep
fire-exposed containers cool and to flush any
spill.
1,1-DCE vapors form explosive mixtures
with air within the range 7.3–16.0% by
volume in air. It polymerizes at elevated
temperatures. If polymerization occurs in
a closed container, the container may rup ture violently. Polymerization is inhibited in
the presence of 200 ppm of hydroquinone
monomethyl ether (Aldrich 1997). It forms
a white deposit of peroxide on long stand ing which may explode. It decomposes when
involved in fire, producing toxic hydrogen
chloride. Reactions with concentrated min eral acids are exothermic.
Safety Profile
Suspected carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic, neoplastigenic, tumorigenic, and teratogenic data. Poison by inhalation, ingestion, and intravenous routes. Moderately toxic by subcutaneous route. Human systemic effects by inhalation: general anesthesia, liver and hdney changes. Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. See also VINYL CHLORIDE. A very dangerous fire hazard when exposed to heat or flame. Moderately explosive in the form of gas when exposed to heat or flame. It forms explosive peroxides upon exposure to air. Potentially explosive reaction with chlorotrifluoroethylene at 18O℃. Reaction with ozone forms dangerous products. Explosive reaction with perchloryl fluoride when heated above 100℃. Also can explode spontaneously. Reacts violently with chlorosulfonic acid, HNO3, oleum. Can react vigorously with oxidizing materials. To fight fire, use alcohol foam, CO2, dry chemical. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Cl-. See also CHLORINATED HYDROCARBONS, ALIPHATIC.
Potential Exposure
Vinylidene chloride is used in the manufacture of 1,1,1-trichloroethane (methyl chloroform). However, the manufacture of polyvinylidene copolymers is the major use of VDC. The extruded films of the copolymers are used in packaging and have excellent resistance to water vapor and most gases. The chief copolymer is Saran (polyvinylidene chloride/vinyl chloride), a transparent film used for food packaging. The films shrink when exposed to higher than normal temperatures. This characteristic is advantageous in the heat-shrinking of overwraps on packaged goods and in the sealing of the wraps. Applications of VDC latexes include mixing in cement to produce highstrength mortars and concretes, and as binders for paints and nonwoven fabrics providing both water resistance and nonflammability. VDC polymer lacquers are also used in coating films and paper. VDC is also used to produce fibers. Monofilaments, made by extruding the copolymer, are used in the textile industry as furniture and automobile upholstery; drapery fabric; outdoor furniture; venetian-blind tape; and filter cloths.
Carcinogenicity
The IARC has concluded that
there is inadequate evidence in humans and limited evidence
in experimental animals for the carcinogenicity of VDC and
has placed it in its Group 3 category as not classifiable as to its
carcinogenicity to humans.
This conclusion is consistent with the evaluation by the
EPA, where VDC exhibits suggestive evidence of carcinogenicity
but not sufficient evidence to assess human carcinogenic
potential following inhalation exposure in studies in
rodents.
Environmental Fate
Biological. 1,1-Dichloroethylene significantly degraded with rapid adaptation in a static-culture
flask-screening test (settled domestic wastewater inoculum) conducted at 25 °C. Complete
degradation was observed after 14 d. At concentrations of 5 and 10 mg/L, the amount lost due to
volatilization at the end of 10 d was 24 and 15%, respectively (Tabak et al., 1981).
Soil. In a methanogenic aquifer material, 1,1-dichloroethylene biodegraded to vinyl chloride
(Wilson et al., 1986). Under anoxic conditions, indigenous microbes in uncontaminated sediments
degraded 1,1-dichloroethylene to vinyl chloride (Barrio-Lage et al., 1986).
Photolytic. Photooxidation of 1,1-dichloroethylene in the presence of nitrogen dioxide and air
yielded phosgene, chloroacetyl chloride, formic acid, HCl, carbon monoxide, formaldehyde, and
ozone (Gay et al., 1976). At 298 K, 1,1-dichloroethylene reacts with ozone at a rate of 3.7 x 10-21
cm3/molecule?sec (Hull et al., 1973).
Chemical/Physical. At temperatures exceeding 0 °C in the presence of oxygen or other
catalysts, 1,1-dichloroethylene will polymerize to a plastic (Windholz et al., 1983). The alkaline
hydrolysis of 1,1-dichloroethylene yielded chloroacetylene. The reported hydrolysis half-life at 25
°C and pH 7 is 1.2 x 108 yr (Jeffers et al., 1989).
Shipping
UN1303 Vinylidene chloride, stabilized, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3-Flammable liquid.
Incompatibilities
Readily forms explosive peroxides; violent polymerization from heat or on contact with oxidizers, chlorosulfonic acid; nitric acid; or oleum; or under the influence of oxygen, sunlight, alkali metals; aluminum, copper. Explosive on heating or on contact with flames. Inhibitors, such as the monomethyl ether of hydroquinone are added to prevent polymerization.
Waste Disposal
Return refillable compressed gas cylinders to supplier. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform to EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. Incineration, preferably after mixing with another combustible fuel. Care must be exercised to assure complete combustion to prevent the formation of phosgene. An acid scrubber is necessary to remove the halo acids produced.
VINYLIDENE CHLORIDE Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
1of2
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | +91-22-45045900 | Hyderabad, India | 6257 | 58 | Inquiry |
| SynZeal Research Pvt Ltd | +1 226-802-2078 | Gujarat, India | 6514 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Clearsynth Labs | 91-22-45045900 | Maharashtra, India | 3887 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Alfa Aesar | 1 800 209 7001 | Maharashtra, India | 6905 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Hebei Weibang Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +8615531157085 | China | 8805 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Hebei Mujin Biotechnology Co.,Ltd | +86 13288715578 +8613288715578 | China | 12829 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Henan Fengda Chemical Co., Ltd | +86-371-86557731 +86-13613820652 | China | 20262 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 | China | 21632 | 55 | Inquiry |
| CONIER CHEM AND PHARMA LIMITED | +8618523575427 | China | 49374 | 58 | Inquiry |
| career henan chemical co | +86-0371-86658258 +8613203830695 | China | 29810 | 58 | Inquiry |
75-35-4(VINYLIDENE CHLORIDE)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




