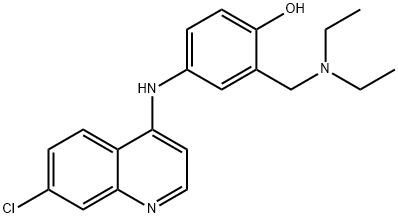
Amodiaquine
- CAS No.
- 86-42-0
- Chemical Name:
- Amodiaquine
- Synonyms
- CAM-AQI;CAM-AQ1;Miaquin;Camoquin;Camochin;Camoquine;SN 10,751;NSC 13453;Camoquinal;Flavoquine
- CBNumber:
- CB8344720
- Molecular Formula:
- C20H22ClN3O
- Molecular Weight:
- 355.86
- MOL File:
- 86-42-0.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2023/6/8 9:01:57
| Melting point | 208°C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 478.0±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.258 |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly, Sonicated), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 9.43±0.50(Predicted) |
| color | Pale Yellow to Light Yellow |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 86-42-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Amodiaquine(86-42-0) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS07 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Warning | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H302 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P264-P270-P301+P312-P330-P501 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 oral in mouse: 550mg/kg | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Amodiaquine Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Amodiaquine is a prodrug form of the antimalarial compound N-desethyl amodiaquine . It is active against several strains of P. falciparum in vitro (EC50s = 0.23-0.52 nM) and exhibits a synergistic effect when used in combination with N-desethyl amodiaquine. Amodiaquine dose-dependently inhibits development of parasitemia in a mouse model of P. berghei infection.
Chemical Properties
Cyrstalline Solid
Uses
An antimalarial
Indications
Amodiaquine (Camoquin) is another 4-aminoquinoline derivative whose antimalarial spectrum and adverse reactions are similar to those of chloroquine, although chloroquine-resistant parasites may not be amodiaquine- resistant to the same degree. Prolonged treatment with amodiaquine may result in pigmentation of the palate, nail beds, and skin. There is a 1:2000 risk of agranulocytosis and hepatocellular dysfunction when the drug is used prophylactically.
Definition
ChEBI: A quinoline having a chloro group at the 7-position and an aryl amino group at the 4-position.
World Health Organization (WHO)
Amodiaquine, an antimalarial agent related to chloroquine, was introduced over 40 years ago for the treatment and prophylaxis of malaria. The drug was voluntarily withdrawn in the United Kingdom in 1975 for commercial reasons but was subsequently reintroduced in 1985 to meet the medical demand for an antimalarial drug to deal with the rapid spread of chloroquine-resistant falciparum malaria in Asia and Africa. By 1986 a significant number of cases of agranulocytosis associated with prophylactic use, some of which were fatal, had been reported there and it has been estimated that the frequency of this risk is of the order of 1:2,000. Although most cases occurred when amodiaquine had been used in combination with other antimalarials, the major manufacturer decided to withdraw the prophylactic indication worldwide following discussions with experts. Preparations remain available for the treatment of acute attacks of malaria which involves only a short period of exposure to the drug. (Reference: (WHODI) WHO Drug Information, 1, 5, 1987)
Pharmaceutical Applications
A mono-Mannich-base 4-aminoquinoline, formulated as the dihydrochloride dihydrate or free base for oral administration. It is active against P. falciparum and P. vivax and is more active than chloroquine for the treatment of uncomplicated P. falciparum malaria. Chloroquine-resistant strains may remain susceptible, but resistance to amodiaquine is also spreading in some regions of Africa. The pharmacological properties are similar to those of chloroquine. The terminal elimination halflife is 1–3 weeks. It is rapidly and extensively metabolized to the desethyl derivative which has reduced antiplasmodial activity. Prophylactic use has been abandoned because of agranulocytosis and hepatotoxicity due to formation of a quinoneimine metabolite. A fixed dose combination with artesunate and derivatives (for example, isoquine) with altered metabolism and reduced toxicity is in development.
Clinical Use
Mechanistically, it is very similar to chloroquine and does nothave any advantages over the other 4-aminoquinoline drugs.When used for prophylaxis of malaria, it had a higher incidenceof hepatitis and agranulocytosis than that was chloroquine.There is evidence that the hydroquinone (phenol)amine system readily oxidizes to a quinone imine either autoxidatively and/or metabolically, and this productmay contribute to amodiaquine’s toxicity.
Purification Methods
Amodiaquin crystallises from 2-ethoxyethanol or EtOH. [Burckhalter et al. J Am Chem Soc 70 1363 1948, Beilstein 22 III/IV 4647.]
Amodiaquine Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Micro Orgo Chem | +91-91-022-24969510 +91-9082984052 | Mumbai, India | 66 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Jigs Chemical ltd | +919099003427 | Gujarat, India | 239 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Ipca Laboratories Ltd | +91-2262105000 +91-2262105000 | Maharashtra, India | 61 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Rivashaa Agrotech Biopharma Pvt. Ltd. | +91-26463395 +91-7926462688 | Gujarat, India | 1615 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Ralington Pharma | +91-7948911722 +91-9687771722 | Gujarat, India | 1350 | 58 | Inquiry |
| KPS Chemicals And Pharmaceuticals | +91-9870076629 +91-8469484608 | Gujarat, India | 33 | 58 | Inquiry |
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | +91-22-45045900 | Hyderabad, India | 6351 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Pharmaffiliates Analytics and Synthetics P. Ltd | +91-172-5066494 | Haryana, India | 6773 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Triveni chemicals | 08048762458 | New Delhi, India | 6093 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Celogen Pharma Private Limited | 08048371985Ext 399 | Mumbai, India | 1 | 58 | Inquiry |
Related articles
- Side effects of Amodiaquine
- Amodiaquine is a 4-aminoquinoline which has been used widely since the early 1950s to treat and prevent Plasmodium falciparum ....
- Apr 1,2022
86-42-0(Amodiaquine)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




