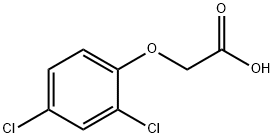
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- CAS No.
- 94-75-7
- Chemical Name:
- 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- Synonyms
- 2,4-D;Estone;For;2,4-D ACID;Amidox;Miracle;Crotilin;Fernimine;Transamine;2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic
- CBNumber:
- CB8762041
- Molecular Formula:
- C8H6Cl2O3
- Molecular Weight:
- 221.04
- MOL File:
- 94-75-7.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/7/26 15:15:06
| Melting point | 136-140 °C (lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 160 °C (0.4 mmHg) |
| Density | 1.563 |
| vapor pressure | 0.4 mm Hg ( 160 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.5000 (estimate) |
| Flash point | 160°C/0.4mm |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Soluble in organic solvents (ethanol, acetone, dioxane) |
| pka | pK1:2.64 (25°C) |
| form | crystalline |
| color | off-white to tan |
| PH Range | Acidic |
| Odor Threshold | 3.13 ppm |
| Water Solubility | Slightly soluble. Decomposes. 0.0890 g/100 mL |
| Merck | 14,2796 |
| BRN | 1214242 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 6.72 and 0.84 x 10-5 atm?m3/mol were reported at pH values of 1 and 7, respectively (wetted-wall column, Rice et al., 1997a) |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH REL: TWA 10 mg/m3, IDLH 100 mg/m3; OSHA PEL: TWA 10 mg/m3; ACGIH TLV: TWA 10 mg/m3. |
| Stability | Stable, but moisture-sensitive and may be light-sensitive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, corrodes many metals. Decomposes in water. |
| LogP | 2.810 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 94-75-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. 113) 2018 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | (2,4-Dichlorophenoxy)acetic acid(94-75-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2,4-D (94-75-7) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS05,GHS07,GHS09 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H302-H317-H318-H335-H410 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P261-P273-P280-P301+P312-P302+P352-P305+P351+P338 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xn,Xi,T,F | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 22-37-41-43-52/53-39/23/24/25-23/24/25-36/37/38-11-36-20/21/22-67-66 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 24/25-26-36/37/39-46-61-2-45-36/37-27-16-7-9 | |||||||||
| OEB | B | |||||||||
| OEL | TWA: 10 mg/m3 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 3077 9/PG 3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 2 | |||||||||
| RTECS | AG6825000 | |||||||||
| Autoignition Temperature | > 180 °C | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 6.1 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29189090 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 (oral): rat [free] 375 mg/kg, [-Na] 666-805 mg/kg. | |||||||||
| IDLA | 100 mg/m3 | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid price More Price(19)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | D7299 | 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid ≥95%, crystalline | 94-75-7 | 100G | ₹3702.15 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | D7299 | 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid ≥95%, crystalline | 94-75-7 | 250G | ₹7371.83 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | D70724 | 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid 97% | 94-75-7 | 5G | ₹3723.8 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 8.20451 | 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid for synthesis | 94-75-7 | 5G | ₹3600 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | D70724 | 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid 97% | 94-75-7 | 100G | ₹4687.23 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
2,4-D free acids, esters, amines, and salts are formulated in water suspensions or solutions, or in various organic solvents, for application as systemic herbicides that are used postemergence for selective control of broadleaf weeds.
Chemical Properties
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid is a white to yellow crystalline powder with a slight phenolic odor. It is used as a herbicide for the selective control of broad-leaved weeds in agriculture, and for the control of woody plants along roadsides, railways, and utilities rights of way. It is one of the most widely used herbicides in the world and is commonly used on crops such as wheat and corn, and on pasture and rangelands. It is also used to control broad-leaved aquatic weeds.
Physical properties
Odorless, white to pale yellow, powder or prismatic crystals. Impure formulations containing 2,4- D as the main component may have a phenolic odor.
Uses
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid is often formulated as various forms of inorganic salts or esters. 2,4-D was first registered as a herbicide in 1948, and its annual production was estimated at 52–67 million lb in 1990. The primary use of 2,4-D is for control of broadleaf weeds, and as such, it is used for a large spectrum of applications in agriculture, forestry, and lawn care. 2,4-D also is used along right-ofways, on rangelands, parks, and in aquatic environments.
Definition
ChEBI: A chlorophenoxyacetic acid that is phenoxyacetic acid in which the ring hydrogens at postions 2 and 4 are substituted by chlorines.
Preparation
Two processes are currently used for the production of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. In the first process, phenol is condensed with chloroacetic acid forming phenoxyacetic acid, which is subsequently chlorinated. In the second process, phenol is chlorinated, generating 2,4-dichlorophenol, which is subsequently condensed with chloroacetic acid. The butyl ester derivative of 2,4-D is produced by the esterification of the acid with butanol in the presence of a ferric chloride catalyst and chlorine (Liu et al., 2013).

Preparation of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
General Description
Odorless white to tan solid. Sinks in water.
Air & Water Reactions
Decomposes rapidly in water.
Reactivity Profile
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid is incompatible with strong oxidizers. 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid is corrosive to metals.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Toxic and irritating hydrogen chloride or phosgene gases may form.
Agricultural Uses
Herbicide, Plant growth regulator: 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid was introduced as a plant growth-regulator in 1942. 2, 4-D is the most widely used herbicide in the United States and its used in more than 100 countries. It is registered in the United States as a herbicide for control of broadleaf plants and as a plant growth-regulator. There are many forms or derivatives of 2,4-D including esters, amines, and salts. It is used in cultivated agriculture, in pasture and rangeland applications, forest management, home, garden, and to control aquatic vegetation. It may be found in emulsion form, in aqueous solutions (salts), and as a dry compound. The product Agent Orange, made by Monsanto Chemical and used extensively throughout Vietnam, was about 50% 2,4-D. However, the controversies associated with the use of Agent Orange involved a contaminant (dioxin) in the 2,4,5-T component of the defoliant. In 1964 Agent Orange replaced Agent Purple a mixture of the n-butyl esters of 2,4-D and 2,4,5-T plus the isobutyl ester of 2,4,5-T.
Trade name
Hedonal; 2,4-D; Estone; Agrotect; Fernesta; Fernimine; Netagrone; Tributon; Vergemaster; Amoxone; Dicopur; Dormone; Ipaner; Moxone; Phenox; Pielik; Rhodia; Weedone; B-Selektonon.
Potential Exposure
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, was introduced as a plant growth-regulator in 1942. It is registered in the United States as a herbicide for control of broadleaf plants and as a plant growth-regulator. Thus, workers engaged in manufacture, formulation or application are affected, as may be citizens in areas of application. The Vietnam war era defoliant, Agent Orange, was a mixture of 2,4-D and 2,4,5-T.
Carcinogenicity
Collectively, the epidemiological and toxicological data show that 2,4-D is not likely to be carcinogenic in humans unless it is acting through an unknown mechanism that is not evident in animals. According to the calculated RfD and data from exposure studies, the general public should not experience toxic effects from exposure to 2,4-D. Because workers involved in the manufacture or application of 2,4-D may be exposed to levels above the RfD, appropriate protective equipment should be used.
Environmental Fate
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-d) is rapidly degraded by microbes in soil and water, with a half-life of 3-22 days in different soils. 2,4-d is weakly sorbed by soil with sorption generally increasing with increasing soil organic carbon content. Leaching to groundwater is most likely in coarse-grained sandy soils with low organic content or with very basic soils. In general, little runoff occurs with 2,4-d or its amine salts.
Metabolism
Chemical. 2,4-D and its salts are very stable, but
esters are sensitive to hydrolysis under acidic and basic conditions. In the field, 2,4-D losses due to
photodegradation are minor. 2,4-D is a strong acid and
forms water-soluble salts with amines and alkali metals.
A sequestering agent is included in 2,4-D formulations to
prevent precipitation of Ca2+ andMg2+ salts in hard water.
Plant. 2,4-D detoxification occurs relatively slowly in
plants. There are many possible routes of detoxification,
and these are usually grouped into those reactions that are
consistent with phase I metabolism and those that are consistent
with phase II metabolism. Phase I reactions that
have been observed to occur with 2,4-D include dechlorination,
decarboxylation, hydroxylation, and dealkylation.
Phase II reactions that have been observed to occur
with 2,4-D include conjugation of the side chain to
amino acids, particularly glutamate and aspartate, and glucose conjugation following hydroxylation of the phenoxy
ring. Selectivity differences among broadleaf species
may be accounted for by differences in the rates of 2,4-D
detoxification.
Soil. Microbial degradation in the soil involves cleavage
of the acid side chain, decarboxylation, hydroxylation, and
ring opening.
Shipping
UN3345 Phenoxyacetic acid derivative pesticide, solid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials. A DOT regulated marine pollutant.
Purification Methods
Crystallise 2,4-D from MeOH. It is a plant growth substance, a herbicide and is TOXIC. [Beilstein 6 IV 908.]
Incompatibilities
A weak acid, incompatible with bases. Decomposes in sunlight or heat, forming hydrogen chloride and phosgene. Contact with strong oxidizers may cause fire and explosions.
Waste Disposal
Incineration of phenoxys is effective in 1 second @ 982 C, using a straight combustion process or @ 482℃ using catalytic combustion. Over 99% decomposition was reported when small amounts of 2,4-D were burned in a polyethylene bag. See "References" for additional detail. In accordance with 40CFR165, follow (31); recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by follow- ing (100) Package (2) label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal.
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of2
chevron_rightPreparation Products
1of2
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suryaprabha Pharmachem | +91-9850308282 +91-9850308282 | Maharashtra, India | 38 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Prayag Pharmachem | +91-9921873418 +91-9921873418 | Maharashtra, India | 16 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Oriental Crop Care Co. P Ltd. | 91-9896350799 | Haryana, India | 14 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Titan Biotech Limited | 09711169006 | Delhi, India | 196 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Agrowallied Ventures Pvt. Ltd. | 91-124-4600414 | Haryana, India | 5 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Loba Chemie Pvt., Ltd. | 91-22-66636663 | Maharashtra, India | 766 | 58 | Inquiry |
| ALPHA CHEMIKA | +91-22-22061123 +91-22-66382501 | Mumbai, India | 1681 | 43 | Inquiry |
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | +91-22-45045900 | Hyderabad, India | 6351 | 58 | Inquiry |
| TCI Chemicals (India) Pvt. Ltd. | 1800 425 7889 | New Delhi, India | 6778 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Otto Chemie Pvt. Ltd. | +91 9820041841 | Mumbai, India | 5873 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Suryaprabha Pharmachem | 58 |
| Prayag Pharmachem | 58 |
| Oriental Crop Care Co. P Ltd. | 58 |
| Titan Biotech Limited | 58 |
| Agrowallied Ventures Pvt. Ltd. | 58 |
| Loba Chemie Pvt., Ltd. | 58 |
| ALPHA CHEMIKA | 43 |
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | 58 |
| TCI Chemicals (India) Pvt. Ltd. | 58 |
| Otto Chemie Pvt. Ltd. | 58 |
Related articles
- Applications of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, esters, amines, and salts are formulated in water suspensions or solutions, or in various orga....
- Jan 13,2022
94-75-7(2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




