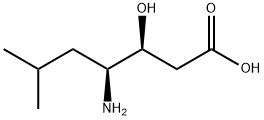
STATINE
- CAS No.
- 49642-07-1
- Chemical Name:
- STATINE
- Synonyms
- STATIN;STATINE;H-STA-OH;S)-Statine;LEU-STATINE;4S)-Statine;(S,S)-Statine;H-STA(3S,4S)-OH;(3S,4S)-STATINE;H-(3S,4S)-STA-OH
- CBNumber:
- CB9272763
- Molecular Formula:
- C8H17NO3
- Molecular Weight:
- 175.23
- MOL File:
- 49642-07-1.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/7/2 8:55:41
| Melting point | 209 °C |
|---|---|
| alpha | D15 -20° (c = 0.64 in water) |
| Boiling point | 306.53°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.1233 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4476 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | 0.5 M HCl: 50 mg/mL, clear, very faintly yellow |
| pka | 3.97±0.10(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to off-white |
| Merck | 13,8879 |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H319-H315-H335 |
| Precautionary statements | P264-P280-P305+P351+P338-P337+P313P-P264-P280-P302+P352-P321-P332+P313-P362 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Statements | 36/37/38 |
| Safety Statements | 26-36 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
STATINE Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
white powder
Clinical Use
With the possible exception of atorvastatin, the
statins are used to lower LDL cholesterol in familial or
polygenic ( multifactorial) hypercholesterolemia (type
IIa) and in combination with triglyceride-lowering
drugs to treat combined hyperlipidemia (type IIb) when
both LDL and VLDL (very low density lipoproteins)
are elevated. However, the statins probably
should not be given with the fibrates (triglyceridelowering
drugs, discussed later), since this combination
may greatly increase statin toxicity. Atorvastatin, the
most potent of the available statins, has also
been shown to lower blood triglycerides significantly.
This effect may be due to decreasing hepatic cholesterol
and cholesterol ester levels to such an extent that
hepatic formation of VLDL is impaired.The statins also
have been claimed to reduce blood cholesterol levels
modestly in some patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia,
a condition often fatal in childhood
or in early adulthood.
The statins may lower the risk of CHD by decreasing
inflammation, an important component of atherogenesis.
Lovastatin decreased elevated plasma levels of Creactive
protein, a marker for cellular inflammation, and
acute coronary events in patients with relatively low
plasma cholesterol levels. Recent studies also suggest
that use of statins may decrease the risk of stroke, dementia,
and Alzheimer’s disease and may improve bone density in postmenopausal women. These broad actions
may be related to the hypocholesterolemic, antiproliferative,
antiinflammatory, or antioxidant properties of the
statins or some combination of these properties.
Side effects
The statins generally appear to be well tolerated, with muscle pain and liver dysfunction seen in 1 to 2% of patients. However, the consequences of 20 to 30 years of continuous use are unknown. This fact has been dramatically reinforced by the recent recognition of a potentially fatal consequence of statin use. A relatively common side effect of the statins (perhaps 1% of patients) is myositis, that is, inflammation of skeletal muscle accompanied by pain, weakness, and high levels of serum creatine kinase. Rhabdomyolysis, i.e., disintegration of muscle with urinary excretion of myoglobin and kidney damage, was considered to be a rare and extreme toxic outcome. However, cerivastatin (Baycol) has now been withdrawn from the market by its manufacturer (Bayer) because of 31 deaths linked to fatal rhabdomyolysis. The risk of muscle damage is said to increase with simultaneous use of the triglyceride-lowering fibrates. Pravastatin may be less toxic than other statins because it does not readily penetrate extrahepatic cells and may be more confined to the liver after oral dosage.
STATINE Preparation Products And Raw materials
STATINE Suppliers
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TargetMol Chemicals Inc. | +1-781-999-5354 +1-00000000000 | United States | 19892 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Career Henan Chemica Co | +86-0371-86658258 +8613203830695 | China | 30253 | 58 | Inquiry |
| BOC Sciences | 16314854226; +16314854226 | United States | 19743 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Nextpeptide Inc | +86-0571-81612335 +8613336028439 | China | 19915 | 58 | Inquiry |
| LEAPCHEM CO., LTD. | +86-852-30606658 | China | 43348 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Hangzhou Peptidego Biotech Co.,Ltd. | 0571-87213919 | China | 6526 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Hangzhou Sinoda Pharmaceutical Technology Co. LTD | 0571-87213919 17306812703 | China | 6213 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Beijing Ouhe Technology Co., Ltd | 010-82967028 13552068683 | China | 12439 | 60 | Inquiry |
| Combi-Blocks Inc. | 858 635 8950 | United States | 6632 | 69 | Inquiry |
| MedChemExpress | 021-58955995 | United States | 6398 | 58 | Inquiry |
49642-07-1(STATINE)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




