Cesium
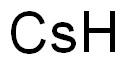
- CAS No.
- 7440-46-2
- Chemical Name:
- Cesium
- Synonyms
- CAESIUM;CESIUM;Cesium-133;CESIUM METAL;caesium atom;CESIUM: 99.9%;Cesium powder;Cesium (99.5%);Cesium, 99.95+%;CESIUM STANDARD
- CBNumber:
- CB9854189
- Molecular Formula:
- Cs
- Molecular Weight:
- 132.91
- MOL File:
- 7440-46-2.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2025/1/27 9:38:02
| Melting point | 28.5 °C (lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 705 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1.873 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 1 mm Hg ( 279 °C) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: soluble |
| form | ingot |
| color | Silver |
| Specific Gravity | 1.892 |
| PH | 0.5 (20°C in H2O) |
| Flame Color | Blue violet |
| Resistivity | 19 μΩ-cm, 0°C |
| Water Solubility | reacts with H2O to evolve H2; soluble liquid NH3 [MER06] |
| Sensitive | moisture sensitive |
| Merck | 13,2018 |
| Exposure limits |
ACGIH: TWA 2 ppm; STEL 4 ppm OSHA: TWA 2 ppm(5 mg/m3) NIOSH: IDLH 25 ppm; TWA 2 ppm(5 mg/m3); STEL 4 ppm(10 mg/m3) |
| Stability | Flammable solid; highly flammable in powder form. Moisture-sensitive. Incompatible with chlorine, phosphorus, water. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7440-46-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cesium (7440-46-2) |
| Bulk Modulus | 1.57 GPa |
|---|
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS02,GHS05 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H260-H314 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P223-P231+P232-P280-P305+P351+P338-P370+P378-P422 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xi,C,F | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 36/38-34-14/15-11 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 26-45-43-36/37/39-16-8 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 3264 8/PG 3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | FK9225000 | |||||||||
| F | 10 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 4.3 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | I | |||||||||
| HS Code | 28051990 | |||||||||
| Hazardous Substances Data | 7440-46-2(Hazardous Substances Data) | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Cesium price More Price(7)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 239240 | Cesium ingot, ≥99.95% trace metals basis | 7440-46-2 | 1G | ₹6583.2 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 239240 | Cesium ingot, ≥99.95% trace metals basis | 7440-46-2 | 5G | ₹34994.35 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 14714 | Cesium purum, ≥99.5% | 7440-46-2 | 1G | ₹8450.55 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 14714 | Cesium purum, ≥99.5% | 7440-46-2 | 5G | ₹16711.2 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| ALFA India | ALF-043005-18 | Cesium, 99.8% (metals basis) | 7440-46-2 | 50g | ₹51920 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
Cesium Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Cesium was discovered in 1860 by Robert Bunsen and Gustav Kirchoff. It is used in the most accurate atomic clocks. Cesium melts at 28.41°C (just below body temperature) and occurs in Earth’s crust at 2.6 ppm. Cesium is the rarest of the naturally occurring alkali metals as the isotope 133Cs. Its compounds are correspondingly rare. Granites contain about 1 ppm cesium and sedimentary rocks contain approximately 4 ppm cesium. The most common commercial source of cesium is pollucite, which contains between 5 and 32% cesium oxide. Radioactive forms of cesium (134Cs and 137Cs) can also be found in the environment. They are produced during nuclear fission, and are used in cancer treatment.
Chemical Properties
Cesium is silvery gold, soft ductile metal. It is the most electropositive and alkaline element. Cesium, gallium, and mercury are the only three metals that are liquid at or around room temperature. Cesium reacts explosively with cold water, and reacts with ice at temperatures above -116℃. Cesium hydroxide is a strong base and attacks glass and reacts with halogens to form a fluoride, chloride, bromide, and iodide. Cesium metal oxidizes rapidly when exposed to air and can form the dangerous superoxide on its surface. Most cesium compounds are water soluble.

Isotopes
Cs-133 is the only stable isotope of cesium, and it makes up all of the naturallyoccurring cesium found in the Earth’s crust. In addition to Cs-133 there are about 36radioactive isotopes of Cs, most of which are artificially formed in nuclear reactors. Allare produced in small numbers of atoms with relatively short half-lives. The range of Csisotopes is from Cs-113 (amu = 112.94451) to Cs-148 (amu = 147.94900). Most ofthese radioisotopes produce beta radiation as they rapidly decay, with the exception ofCs-135, which has a half-life of 3×106yr, which makes it a useful research tool. Cs-137,with a half-life of 33 years, produces both beta and gamma radiation.
Origin of Name
In 1860 Gustav Kirchhoff and Robert Bunsen named the element “Cesium,” using the Latin word caesius, which means bluish-gray.
Occurrence
The stable form of Cs-133 is the 48th most abundant element on Earth, but because it isso reactive, it is always in compound form. The Earth’s crust contains only about 7 ppm ofCs-133. Like the other alkali metals, it is found in mixtures of complex minerals. Its mainsource is the mineral pollucite (CsAlSi2O6). It is also found in lepidolite, a potassium ore.Pollucite is found in Maine, South Dakota, Manitoba, and Elba and primarily in Rhodesia,South Africa.One problem in refining cesium is that it is usually found along with rubidium; therefore,the two elements must be separated after they are extracted from their sources. The mainprocess to produce cesium is to finely grind its ores and then heat the mix to about 600°Calong with liquid sodium, which produces an alloy of Na, Cs, and Ru, which are separatedby fractional distillation. Cesium can also be produced by the thermochemical reduction of amixture of cesium chloride (CsCl) and calcium (Cs).
Characteristics
Cesium is located between rubidium and francium in group 1 of the periodic table. It isthe heaviest of the stable alkali metals and has the lowest melting point. It is also the mostreactive of the alkali metals.Cesium will decompose water, producing hydrogen, which will burn as it is liberated fromH2O. Cesium is extremely dangerous to handle and will burn spontaneously or explode whenexposed to air, water, and many organic compounds.
Uses
Cesium is used in photovoltaic cells, vacuum tubes, scintillation counters, and atomic clocks.
Preparation
Although Cesium metals have been prepared by fused salt electrolysis, the highly reactive nature of the metals complicates the collection step and favors the use of other preparative methods where the metals can be removed in vapor form from the reaction mixture. The oxides, hydroxides, carbonates, halides, sulphates, chromates and nitrates of Cesium have been reduced to the metals by strong reducing metals such as sodium, calcium, magnesium, barium, iron, zirconium, aluminum or silicon at moderately high temperatures. The preferred method, however, involves the reduction of the anhydrous metal chlorides with calcium metal under vacuum. Anhydrous cesium chloride is mixed with a large excess of calcium chips and heated under vacuum at 700-800°C. As the chloride is reduced, metal vapors issue from the reaction mixture and are led under the vacuum to a cooler portion of the vessel where they condense and drop into a collection vessel.
Definition
A soft golden highly reactive low-melting element of the alkali-metal group. It is found in several silicate minerals, including pollucite (CsAlSi2O6). The metal oxidizes in air and reacts violently with water. Cesium is used in photocells, as a catalyst, and in the cesium atomic clock. The radioactive isotopes 134Cs (half life 2.065 years) and 137Cs (half life 30.3 years) are produced in nuclear reactors and are potentially dangerous atmospheric pollutants.
General Description
A soft metallic solid. Melts at 85°F. Causes burns to skin and eyes.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Cesium is spontaneously flammable in air at room temperature, if the surface is clean [Merck 11th ed. 1989]. Reacts with water to generate enough heat to ignite the hydrogen produced during the reaction, and to generate caustic Cesium hydroxide [Mellor 2 419 1946-47].
Reactivity Profile
Cesium METAL reacts violently with oxidizing agents, even weaker ones. Reacts with boron trifluoride with incandescence when heated [Merck 11th ed. 1989]. Reacts explosively with maleic anhydride [Chem Safety Data Sheet SD-88 1962; Chem. Haz. Info. Series C-71 1960]. Burns in chlorine with a luminous flame [Mellor 2 Supp. 1:380 1956]. Reacts violently with most acids. Reacts violently with fluorine, chlorine, bromine and iodine. Reacts with incandescence with sulfur and phosphorus. Burns vigorously in air.
Hazard
Although cesium has many of the properties and characteristics of the other alkali metals,because of the large size of its atoms, cesium metal is much more reactive and dangerousto handle. Special precautions need to be taken to keep it away from air, water, and organicsubstances with which it can vigorously react. Its use should be restricted to laboratories andindustries capable of using it safely.
Cesium-137, with a half-life of about 30 years, produces dangerous radiation and can causeradiation poisoning if mishandled. It is used to sterilize wheat, potatoes, and other foods toprotect them from insect damage and rotting. It is also used to kill bacteria in the treatmentof sewage sludge.
Health Hazard
Inhalation or contact with vapors, substance or decomposition products may cause severe injury or death. May produce corrosive solutions on contact with water. Fire will produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control may cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
Produce flammable gases on contact with water. May ignite on contact with water or moist air. Some react vigorously or explosively on contact with water. May be ignited by heat, sparks or flames. May re-ignite after fire is extinguished. Some are transported in highly flammable liquids. Runoff may create fire or explosion hazard.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by intraperitoneal route. Cesium is quite similar to potassium in its elemental state. It has been shown, however, to have pronounced physiological action in experimentation with animals. Hyper-irritability, including marked spasms, has been shown to follow the administration of cesium in amounts equal to the potassium content of the diet. It has been found that replacing the potassium in the diet of rats with cesium caused death after 10-17 days. Ignites spontaneously in air. Violent reaction with water, moisture, or steam releases hydrogen gas whch explodes. Violent reaction with acids, halogens, and other oxidizing materials. Incandescent reaction with nonmetals (e.g., sulfur, phosphorus). See also SODIUM.
Environmental Fate
Stable cesium was shown to affect various central nervous
system functions, mainly involving displacing potassium, with
which it competes for transport through the potassium
channel, and it can also activate sodium pump and subsequent
transport into the cell across membranes. Thus, this resulted in
potassium deficiency.
Radioactive isotopes of cesium, such as 134Cs and 137Cs, are
a greater health concern than stable cesium. These radioactive
isotopes of cesium are formed during nuclear fission. Both
134Cs and 137Cs emit beta and gamma radiations. Beta radiation
travels short distances and can penetrate the skin and
superficial body tissues, whereas gamma radiation can travel
great distances and penetrate the entire body. Both beta and
gamma radiations may induce tissue damage and disruption of
cellular function.
Cesium Preparation Products And Raw materials
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alfa Aesar | 1 800 209 7001 | Maharashtra, India | 6905 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Hebei Mujin Biotechnology Co.,Ltd | +86 13288715578 +8613288715578 | China | 12809 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Neostar United (Changzhou) Industrial Co., Ltd. | +86-0519-85551759 +8613506123987 | China | 8831 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co.,Ltd. | +86-0551-65418671 +8618949823763 | China | 34563 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Shaanxi Dideu Medichem Co. Ltd | +86-029-89586680 +86-18192503167 | China | 7859 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Zhuoer Chemical Co., Ltd | 02120970332; +8613524231522 | China | 2904 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Nacalai Tesque Inc | +81-810752511730 +81-810752511730 | Japan | 4 | 58 | Inquiry |
| SUZHOU SENFEIDA CHEMICAL CO.,LTD | +86-0512-83500002 +8615195660023 | China | 26362 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Aladdin Scientific | United States | 57505 | 58 | Inquiry | |
| XIAMEN AMITY INDUSTRY AND TRADE CO., LTD. | +8618950047208 | China | 43416 | 58 | Inquiry |
Related articles
- Cesium:Discovery,Minerals,Chemistry,Uses,Hazards
- Cesium is a relatively rare element, about 3 ppm in the Earth’s crust. It is the 45th most abundant element and the 36th among....
- May 31,2024
- Mechanism of Cesium
- Cesium was discovered in 1860 by Robert Bunsen and Gustav Kirchoff. It is used in the most accurate atomic clocks. Cesium melt....
- Dec 30,2021
- The applications and Preparation of Cesium
- Cesium, or Caesium, chemical symbol Cs, atomic number 55, and relative atomic mass (i.e., atomic weight) 132.90545, is the fif....
- Sep 27,2019
7440-46-2(Cesium)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




