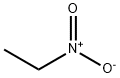
Nitroethane
- CAS No.
- 79-24-3
- Chemical Name:
- Nitroethane
- Synonyms
- C2H5NO2;1-Nitroethane;Nitroparaffin;nitro-ethan;2-Nitroethane;Ethane,nitro-;Nitroethane,99%;nitroetan(polish);NITROETHANE,REAGENT;Nitroetan
- CBNumber:
- CB9854402
- Molecular Formula:
- C2H5NO2
- Molecular Weight:
- 75.07
- MOL File:
- 79-24-3.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2025/2/27 17:16:38
| Melting point | -90 °C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 114-115 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.045 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 2.58 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 15.6 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index |
n |
| Flash point | 87 °F |
| storage temp. | Flammables area |
| solubility | acetone: soluble(lit.) |
| pka | 8.5(at 25℃) |
| form | Colorless, oily liquid |
| PH | 6 (1g/l, H2O, 25℃) |
| explosive limit | 3.4%(V) |
| Water Solubility | 4.6 g/100 mL (20 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,6596 |
| BRN | 1209324 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 3.50 at 20.00 °C, 5.86 at 30.00 °C, 9.38 at 40.00 °C, 15.7 at 50.00 °C (inert gas stripping, Bene? and Dohnal, 1999) |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH REL: TWA 100 ppm (310 mg/m3), IDLH 1,000 ppm; OSHA PEL: TWA 100 ppm; ACGIH TLV: TWA 100 ppm (adopted). |
| Dielectric constant | 19.7(20℃) |
| Stability | Stability Contact with a variety of materials may cause fire or explosion, especially if heated. Incompatible with amines, strong acids, strong oxidizing agents, combustible materials, metal oxides, strong bases, alkalies. |
| LogP | 0.162 at 22.4℃ |
| Surface tension | 31.9mN/m at 20°C |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 79-24-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Ethane, nitro-(79-24-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Nitroethane (79-24-3) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |     GHS02,GHS06,GHS08,GHS07 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H332-H226-H302-H331-H412-H341-H350 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P210-P261-P301+P312+P330-P304+P340+P312-P370+P378-P403+P233-P201-P280-P308+P313-P280a-P303+P361+P353-P304+P340-P501a | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | T,Xn | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 45-10-20/22-68 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 9-23-41-25-45-36/37-53 | |||||||||
| OEB | A | |||||||||
| OEL | TWA: 100 ppm (310 mg/m3) | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 2842 3/PG 3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 2 | |||||||||
| RTECS | KI5600000 | |||||||||
| Autoignition Temperature | 778 °F | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 3 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29042090 | |||||||||
| Hazardous Substances Data | 79-24-3(Hazardous Substances Data) | |||||||||
| Toxicity | Acute oral LD50 for mice 860 mg/kg, rats 1,100 mg/kg (quoted, RTECS, 1985). | |||||||||
| IDLA | 1,000 ppm | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Nitroethane Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
Nitroethane is a colorless, oily liquid with a mild, fruity odor. The Odor Threshold is 163 ppm.
Physical properties
Colorless, very flammable liquid with a fruity odor. Odor threshold concentration is 2.1 ppm (quoted, Amoore and Hautala, 1983). Concentrated mixtures usually contain 98 wt % nitroethane and 2 wt % moisture.
Uses
Solvent, artificial fingernail glue remover; in organic syntheses. Experimentally as liquid propellant.
Production Methods
Industrial production of nitroethane is by vapor-phase nitration of propane with nitric acid, followed by fractional distillation (Baker and Bollmeier 1978). U.S. production was greater than 454 kg in 1975 (HSDB 1988).
Definition
ChEBI: A nitroalkane that is ethane substituted by a nitro group.
General Description
A colorless oily liquid with a pleasant odor. Flash point of 82°F. Decomposes above 350°F. Density 1.052 g / cm3. Vapors much heavier than air. and insoluble in water. Vapors may irritate skin, eyes and mucous membranes. Produces toxic oxides of nitrogen during combustion. Used as a propellant and as a solvent.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
The nitroparaffins, nitromethane, nitropropane, etc. form salts with inorganic bases such as calcium hydroxide. The dry salts are explosive [Chem. Eng. News 30:2344. 1952]. Nitroethane and other nitro compounds are mild oxidizers and should not be heated with easily oxidizable hydrocarbons under confinement [Chem. Eng. News 30:2344. 1940].
Hazard
Moderate fire risk.Upper respiratory tract irritant, central nervous system impairment, and liver damage.
Health Hazard
Nitroethane is irritating to the eyes and mucous membranes (HSDB 1988), however, there have been no reports of serious toxic effects of the chemical in humans.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Toxic oxides of nitrogen may form in fire.
Industrial uses
Nitroethane is used as a solvent for cellulose esters, vinyl and other resins and waxes and as a solvent in batteries (Baker and Bollmeier 1978).
Safety Profile
Poison by intraperitoneal route. Moderately toxic by ingestion. Mildly toxic by inhalation. Causes injury to liver and hdneys. An eye and mucous membrane irritant. Flammable liquid when exposed to heat, sparks, flame, or oxidizers. To fight fire, use alcohol foam, CO2, dry chemical; water can blanket fire. Incompatible with Ca(OH)2, hydrocarbons, hydroxides, inorganic bases, KOH, NaOH, metal oxides, Explodes when heated. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx. See also NITRO COMPOUNDS.
Potential Exposure
Nitroethane is used as solvent for polymers, cellulose esters; vinyl, waxes, fats, dyestuffs, and alkyd resins; as a stabilizer. It has been used as a rocket propellant. It is used as an intermediate in pharmaceutical manufacture and in pesticide manufacture.
Environmental Fate
Chemical/Physical. 2-Nitroethane will not hydrolyze because it does not contain a hydrolyzable functional group.
Shipping
UN2842 Nitroethane, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3-Flammable liquid.
Purification Methods
Purify it as described for nitromethane below. A spectroscopic impurity can be removed by shaking it with activated alumina, decanting and distilling it rapidly. [Beilstein 1 IV 170.]
Incompatibilities
A nitroparaffin, nitroethane forms explosive mixture with air. Explodes when heated or when shocked; in confined area, with elevated temperatures. A strong reducing agent. Violent reaction with oxidizers, hydrocarbons, other combustibles; amines, metal oxides. Forms shock-sensitive compounds with strong acids; strong alkalis. Attacks some plastics and coatings.
Waste Disposal
Incineration: large quantities of material may require nitrogen oxide removal by catalytic or scrubbing processes.
Nitroethane Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
1of4
chevron_right79-24-3(Nitroethane)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




