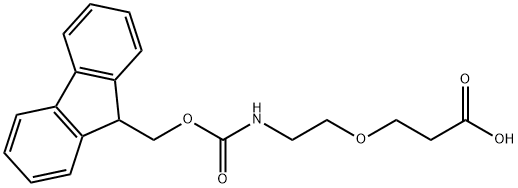
Fmoc-N-amido-PEG1-acid
|
- ₹0
- Product name: Fmoc-N-amido-PEG1-acid
- CAS: 1654740-73-4
- MF: C20H21NO5
- MW: 355.38
- EINECS:
- MDL Number:MFCD16294357
- Synonyms:Fmoc-N-amido-PEG1-acid;Fmoc-PEG1-propionic acid;Fmoc-AEP;3-[2-(Fmoc-amino)ethoxy]propanoic acid;6-(Fmoc-amino)-4-oxahexanoic Acid;Fmoc-PEG1- CH2CH2COOH;Fmoc-NH-PEG1-C2-acid;Propanoic acid, 3-[2-[[(9H-fluoren-9-ylmethoxy)carbonyl]amino]ethoxy]-
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|
Properties
Boiling point :589.9±40.0 °C(Predicted)
Density :1.261±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
storage temp. :2-8°C
pka :4.29±0.10(Predicted)
form :Solid
color :White to off-white
Density :1.261±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
storage temp. :2-8°C
pka :4.29±0.10(Predicted)
form :Solid
color :White to off-white
Safety Information
| Symbol(GHS): |

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word: | Warning | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard statements: |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary statements: |
|
Description
Fmoc-N-amido-PEG1-acid is a PEG linker containing an Fmoc-protected amine and a terminal carboxylic acid. The hydrophilic PEG spacer increases solubility in aqueous media. The Fmoc group can be deprotected under basic condition to obtain the free amine which can be used for further conjugations. The terminal carboxylic acid can react with primary amine groups in the presence of activators (e.g. EDC, or HATU) to form a stable amide bond.More related product prices
FMOC-12-AMINO-4,7,10-TRIOXADODECANOIC ACID FMoc-NH-PEG7-CH2CH2COOH Fmoc-AEEA-AEEA FMoc-NH-PEG12-CH2CH2COOH FMoc-NH-PEG9-CH2CH2COOH 560088-79-1 FMOC-18-AMINO-4,7,10,13,16-PENTAOXAOCTADECANOIC ACID 5,8,11,14,17,20,23,26-Octaoxa-2-azanonacosanedioic acid,1-(9-fluren-9-ylmethyl)ester 2,2-DIMETHYL-4-OXO-3,8,11,14-TETRAOXA-5-AZAHEXADECAN-16-OIC ACID 872679-70-4 5-(9-FLUORENYLMETHYLOXYCARBONYL-AMINO)-3-OXAPENTANOIC ACID Fmoc-9-amino-4,7-dioxanonanoic acid FMOC-15-AMINO-4,7,10,13-TETRAOXAPENTADECANOIC ACID 5,8,11,14-Tetraoxa-2-azahexadecanedioic acid 882847-34-9 Fmoc-PEG4-NHS ester FMoc-Val-Cit-PAB-PNP





