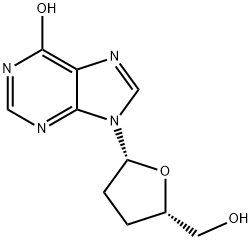
Dideoxyinosine
- CAS No.
- 69655-05-6
- Chemical Name:
- Dideoxyinosine
- Synonyms
- DIDANOSINE;DDI;VIDEX;ddino;DDLNO;Dinosin;bmy40900;Videx EC;nsc612049;Didansine
- CBNumber:
- CB0680765
- Molecular Formula:
- C10H12N4O3
- Molecular Weight:
- 236.23
- MOL File:
- 69655-05-6.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/6/4 15:29:52
| Melting point | 193-195 °C |
|---|---|
| alpha | D25 -26.3° (c = 10 in water) |
| Boiling point | 193-195 C |
| Density | 1.2917 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | -28 ° (C=0.34, H2O) |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO or methanol |
| form | Powder |
| pka | 9.12(at 25℃) |
| color | White to Off-white |
| Water Solubility | 1-5 g/100 mL at 21 ºC |
| Merck | 14,3098 |
| BRN | 3619529 |
| BCS Class | 3 |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 69655-05-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 76) 2000 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Inosine, 2',3'-dideoxy- (69655-05-6) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS08 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Warning | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H341-H373 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P201-P202-P260-P280-P308+P313-P405-P501 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | C | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 34-36/37 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 26-27-36/37/39-45-24/25 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 2 | |||||||||
| RTECS | NM7460700 | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29335990 | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Dideoxyinosine price More Price(7)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | D0162 | 2′,3′-Dideoxyinosine ≥98% (HPLC) | 69655-05-6 | 5MG | ₹12589.48 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | D0162 | 2′,3′-Dideoxyinosine ≥98% (HPLC) | 69655-05-6 | 25MG | ₹43256.7 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | D0162 | 2′,3′-Dideoxyinosine ≥98% (HPLC) | 69655-05-6 | 100MG | ₹152318.58 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| TCI Chemicals (India) | D3066 | 2',3'-Dideoxyinosine | 69655-05-6 | 100MG | ₹5400 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
| TCI Chemicals (India) | D3066 | 2',3'-Dideoxyinosine | 69655-05-6 | 500MG | ₹7100 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
Dideoxyinosine Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Didanosine is an orally active purine dideoxynucleoside analog indicated for adult and pediatric patients with advanced HIV infection who are either intolerant or significantly deteriorated on zidovudine. It appears to increase CD4 cell counts and decrease p24 antigen levels.Major adverse effects are pancreatitis, peripheral neuropathy and diarrhea.Unlike zidovudine, didanosine exhibits insignificant bone marrow suppression.
Chemical Properties
White Powder
Uses
2?,3?-Dideoxyinosine is a potent anti-retroviral agent. It is most effective in combination therapy for the treatment of HIV and related lymphoma.
Indications
Didanosine (ddI, Videx) is an adenosine analogue with activity against HIV-1, HIV-2, and HTLV-I. It is approved as part of a multidrug regimen for the therapy of HIV infection and is also used as postexposure HIV prophylaxis
Definition
ChEBI: A purine 2',3'-dideoxyribonucleoside that is inosine in which the hydroxy groups at both the 2' and the 3' positions on the sugar moiety have been replaced by hydrogen.
Antimicrobial activity
Didanosine is active against HIV-1, HIV-2 and HTLV-1.
Acquired resistance
Codon changes at positions 65 or 74 in HIV reverse transcriptase are associated with reduced susceptibility.
General Description
Didanosine (Videx, ddI) is 2',3'-dideoxyinosine (ddI), a synthetic purine nucleoside analog that is bioactivatedto 2',3'-dideoxy-ATP (ddATP) by host cellularenzymes.The metabolite, ddATP, accumulates intracellularly,where it inhibits RT and is incorporated intoviral DNA to cause chain termination in HIVinfectedcells. The potency of didanosine is 10-to 100-foldless than that of AZT with respect to antiviral activity andcytotoxicity, but the drug causes less myelosuppressionthan AZT causes.
Didanosine is recommended for the treatment of patientswith advanced HIV infection who have received prolongedtreatment with AZT but have become intolerant to, or experiencedimmunosuppression from, the drug. AZT and ddIact synergistically to inhibit HIV replication in vitro, andddI is effective against some AZT-resistant strains of HIV.Painful peripheral neuropathy (tingling, numbness, and painin the hands and feet) and pancreatitis (nausea, abdominalpain, elevated amylase) are the major dose-limiting toxicitiesof didanosine. Didanosine is given orally in the form ofbuffered chewable tablets or as a solution prepared from thepowder. Both oral dosage forms are buffered to preventacidic decomposition of ddI to hypoxanthine in the stomach.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Health Hazard
SYMPTOMS: Symptoms of exposure to a related compound include cutaneous eruptions, fever, mouth sores, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, reversible peripheral neuropathy, gastrointestinal distress, headache, nausea and vomiting.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Dideoxyinosine are not available; however, Dideoxyinosine is probably combustible.
Pharmaceutical Applications
An analog of deoxyadenosine, formulated for oral administration.
Mechanism of action
Didanosine (ddl) is a purine dideoxynucleoside, which is an analogue of inosine. Chemically, it is 2′,3′-dideoxyinosine, and it differs from inosine by having hydrogen atoms in place of the 2′- and 3′-hydroxyl groups on the ribose ring. Didanosine is a pro-drug that is bioactivated by metabolism to dideoxyadenosine triphosphate, which is a competitive inhibitor of viral RT and is incorporated into the developing viral DNA in place of deoxyladenosine triphosphate. As such, this agent causes chain termination because of the absence of a 3′-hydroxyl group. Didanosine inhibits HIV RT and exerts a virustatic effect on the retroviruses. Combined with ZDV, antiretroviral activity of ddI is increased.
Pharmacokinetics
Oral absorption: c. 40%
Cmax 400 mg once daily: 0.93 mg/L
Plasma half-life: c. 1.4 h
Volume of distribution: c. 1 L/kg
Plasma protein binding: <5%
Absorption
Bioavailability is reduced by about half when taken with food and the drug should be given at least 30 min before a meal. The peak plasma concentration achieved by enteric-coated tablets is less than half that of buffered tablets.
Distribution
Central nervous system (CNS) penetration is relatively poor. Median concentrations in semen (455 ng/mL; range < 50–2190 ng/mL) are greater than those in blood (<50 ng/mL; range <50–860 ng/mL). It is secreted in breast milk.
Metabolism
Based upon animal studies it is presumed that metabolism occurs by the pathways responsible for the elimination of endogenous purines by xanthine oxidase. Metabolism may be altered in patients with severe hepatic impairment; however, no specific dose adjustment is recommended.
Excretion
Renal clearance by glomerular filtration and active tubular secretion accounts for 50% of total body clearance. Urinary recovery accounts for about 20% of the oral dose in adults. The half-life increases three-fold in patients requiring dialysis. Patients with a creatinine clearance <60 mL/min may be at greater risk of toxicity.
Clinical Use
Treatment of HIV infection (in combination with other antiretroviral drugs)
Side effects
Most serious are pancreatitis (fatal and non-fatal), lactic
acidosis
and severe hepatomegaly with steatosis (fatal and nonfatal),
retinopathy, optic neuritis and dose-related peripheral
neuropathy. Patients with low body weight may require dose
modification. A strong association with non-cirrhotic
portal
hypertension has been described.
The combination with stavudine should be avoided in
pregnant women as fatal cases of lactic acidosis have been
reported. Caution should also be exercised in patients
with known risk factors for liver disease. Therapy should
be stopped in patients who develop clinical or laboratory
evidence of lactic acidosis or hepatotoxicity. Monitoring
lactate levels prospectively is not recommended as mild
hyperlactatemia occurs in asymptomatic patients and has a
poor positive predictive value for the development of lactic
acidosis.
Caution should be exercised in co-administering other
drugs with known neurotoxicity and in patients with a history
of neuropathy. Treatment should stop if symptoms and
signs of neuropathy are observed, but the condition is usually
reversible and patients with resolved neuropathy may be
retreated at a reduced dosage. Retinal depigmentation has
been observed in children and twice-yearly dilated retinal
examination is recommended.
Metabolism
Didanosine is less toxic than ZDV. The CSF fluid/plasma
ratio of ddI is 0.2. Didanosine is ultimately converted to hypoxanthine, xanthine, and uric acid through the
usual metabolic pathway for purines. The latter is a nontoxic metabolic product.
Didanosine is given in advanced HIV infection, ZDV intolerance, or significant clinical/immunologic
deterioration.
Precautions
Buffering agents that are compounded with didanosineto counteract its degradation by gastric acid mayinterfere with the absorption of other drugs that requireacidity (e.g., indinavir, delavirdine, ketoconazole, fluoroquinolones,tetracyclines, dapsone). An enteric-coatedformulation (Videx EC) that dissolves in the basic pH ofthe small intestine is not susceptible to these interactions.Ganciclovir and valganciclovir can increase bloodlevels of didanosine.The use of zalcitabine with didanosineis not recommended because that combination carriesan additive risk of peripheral neuropathy.The combinationof didanosine with stavudine increases the riskof pancreatitis, hepatotoxicity, and peripheral neuropa-thy. Stavudine should not be given with didanosine topregnant women because of the increased risk of metabolicacidosis.
Dideoxyinosine Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of3
chevron_rightPreparation Products
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hetero Drugs Limited | +91-4023704923 +91-4023704923 | Telangana, India | 296 | 58 | Inquiry |
| AUROBINDO PHARMA LTD | +91 (40) 6672 1200 | New Delhi, India | 209 | 58 | Inquiry |
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | +91-22-45045900 | Hyderabad, India | 6351 | 58 | Inquiry |
| A.J Chemicals | 91-9810153283 | New Delhi, India | 6124 | 58 | Inquiry |
| TCI Chemicals (India) Pvt. Ltd. | 1800 425 7889 | New Delhi, India | 6778 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Sisco Research Laboratories Pvt. Ltd. | +91-22-4268 5800 | Mumbai, India | 4317 | 58 | Inquiry |
| SynZeal Research Pvt Ltd | +1 226-802-2078 | Gujarat, India | 6522 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Pharmaffiliates Analytics and Synthetics P. Ltd | +91-172-5066494 | Haryana, India | 6773 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Triveni chemicals | 08048762458 | New Delhi, India | 6093 | 58 | Inquiry |
| MANGALAM DRUGS AND ORGANICS LIMITED | 08147509329 | Uttar Pradesh, India | 50 | 58 | Inquiry |
Related articles
- Treatment of HIV infection---Didanosine
- Didanosine (2u,3u-dideoxyinosine, ddI) is a synthetic purine nucleoside analog that is active against HIV-1 and HIV-2, includi....
- Apr 14,2022
69655-05-6(Dideoxyinosine)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




