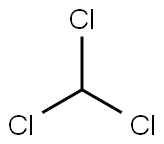
Chloroform
- CAS No.
- 67-66-3
- Chemical Name:
- Chloroform
- Synonyms
- CHCl3;TRICHLOROMETHANE;TCM;Fisher Chemical;Chloroform 5g [67-66-3];r20;Chloroforme;Trichlormethan;METHYLIDYNE TRICHLORIDE;Residual Solvent Class 2 - Chloroform
- CBNumber:
- CB5413313
- Molecular Formula:
- CHCl3
- Molecular Weight:
- 119.38
- MOL File:
- 67-66-3.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2024/3/14 15:18:26
| Melting point | -63 °C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 61 °C |
| Density | 1.492 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 4.1 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 160 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index |
n |
| Flash point | 60.5-61.5°C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Miscible with diethyl ether, oils, ligroin, alcohol, carbon tetrachloride and carbon disulfide. |
| pka | 15,5(at 25℃) |
| form | Liquid |
| color | ≤10(APHA) |
| Odor | Ethereal, sweet odor detectable at 133 to 276 ppm (mean = 192 ppm) |
| Relative polarity | 0.259 |
| Odor Threshold | 3.8ppm |
| Water Solubility | 8 g/L (20 ºC) |
| λmax |
λ: 245 nm Amax: 1.00 λ: 255 nm Amax: 0.15 λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.15 λ: 270 nm Amax: 0.02 λ: 290-400 nm Amax: 0.01 |
| Merck | 14,2141 |
| BRN | 1731042 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 1.07 at 2 °C, 1.49 at 6 °C, 1.79 at 10 °C, 3.02 at 18 °C, 4.02 at 25 °C, 5.20 at 30 °C, 7.60 at 40 °C, 11.1 at 50 °C, 14.8 at 60 °C (EPICS-SPME-GC, G?rgényi et al., 2002)) |
| Exposure limits | Potential occupational carcinogen. NIOSH REL: STEL (1 h) 2 ppm (9.78 mg/m3), IDLH 500 ppm; OSHA PEL: ceiling 50 ppm (240 mg/m3); ACGIH TLV: TWA 10 ppm (adopted). |
| Dielectric constant | 5.5(0℃) |
| Stability | Volatile |
| LogP | 1.970 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 67-66-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. Sup 7, 73) 1999 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Chloroform(67-66-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Chloroform (67-66-3) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS02,GHS07,GHS08 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H225-H319-H336-H351-H361d-H373 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P202-P210-P233-P240-P305+P351+P338-P308+P313 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xn,F,T,Xi | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 45-46-11-23/24/25-36/37/38-48/20/22-40-38-22-67-66-36/38-41-37/38-39/23/24/25-20-63-20/22-36-48/20 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 9-16-26-36-36/37-45-36/37/39-25-23-53-33-7 | |||||||||
| OEL | STEL: 2 ppm (9.78 mg/m3) [60-minute] | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 1888 6.1/PG 3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | FS9100000 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 6.1 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29031300 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 (14 day) orally in rats: 2.18 ml/kg (Smyth); 0.9 ml/kg (Kimura) | |||||||||
| IDLA | 500 ppm | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Chloroform price More Price(80)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | C2432 | Chloroform contains 100-200?ppm amylenes as stabilizer, ≥99.5% | 67-66-3 | 25ML | ₹2219.13 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | C2432 | Chloroform contains 100-200?ppm amylenes as stabilizer, ≥99.5% | 67-66-3 | 4X25ML | ₹6581.6 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | C2432 | Chloroform contains 100-200?ppm amylenes as stabilizer, ≥99.5% | 67-66-3 | 500ML | ₹7166.15 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | C2432 | Chloroform contains 100-200?ppm amylenes as stabilizer, ≥99.5% | 67-66-3 | 1L | ₹9569.3 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | C2432 | Chloroform contains 100-200?ppm amylenes as stabilizer, ≥99.5% | 67-66-3 | 2.5L | ₹16475.65 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Chloroform Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Chloroform is a trichlorinated organic substance with the chemical formula of CHCl3. It is a clear liquid at room temperature and has a pleasant, sweet odor. Chloroform is only slightly soluble in water and evaporates quickly into surrounding air, increasing the risk of inhalation exposure. In addition, chloroform persists for a long time in both water and air. There are no natural sources of chloroform, but this contaminant enters the environment through a variety of industrial operations, including the chlorination of water. Humans can be exposed to chloroform through inhalation, ingestion, and dermal contact.
Chloroform has a relatively narrow margin of safety and has been replaced by better inhalation anesthetics. In addition, it is believed to be toxic to the liver and kidneys and may cause liver cancer. Chloroform was once widely used as a solvent, but safety and environmental concerns have reduced this use as well. Nevertheless, chloroform has remained an important industrial chemical.
Chemical Properties
Chloroform is a noncombustible, clear, colorless liquid with a pleasant, sweet odor. The Odor Threshold is 12 ppm.
Physical properties
Chloroform is a clear, colorless liquid with a pleasant odor and sweet burning taste. It is used to make hydrochloroflurocarbons (HCFCs), as a solvent for organic chemicals, and in chemical synthesis. Its use in many commercial products has been eliminated in recent decades because of its toxic and carcinogenic properties. It was once used extensively as an anesthetic, in medicines, in dry cleaning, and in refrigerants.
History
Chloroform (CHCl3) was first discovered in 1831 by American physician Samuel Guthrie; and independently a few months later by Frenchman Eugène Soubeiran and Justus von Liebig in Germany. Chloroform was named and chemically characterised in 1834 by Jean-Baptiste Dumas. Its anaesthetic properties were noted early in 1847 by Marie-Jean-Pierre Flourens. Unlike ether, chloroform's characteristically sweet odour isn't irritating, although inhalation of concentrated chloroform vapour may cause irritation of exposed mucous surfaces. Chloroform is a more effective anaesthetic than nitrous oxide.
In 1864, the Report of Chloroform Committee of Royal Medical and Chirurgical Society endorsed chloroform as Britain's favourite anaesthetic. But ether was safer for patients.
In 1871, leading anaesthetic manufacturer Edward E. Squibb of Brooklyn estimated [New York Medical Journal (April 1871) 13;389] that of 400,000 administrations of anaesthesia in the USA in 1870, chloroform was the agent used in some 50%, ether for 40%, and other gases and mixtures accounted for the rest.
Uses
Chloroform is a widely used industrial and laboratory solvent. It is a volatile chlorinated organic solvent whose vapors have a narcotic effect.Due to its light sensitivity, it may undergo degradation with time. This can be suppressed by adding ethanol as a stabilizer. The addition will increase the polarity of the solvent and potentially impact certain applications.
- Chloroform has been used as a solvent for dissolving lipids and also as a cleansing agent.
- It may also be used in solvent extraction process and also for recrystallization.
- Suitable for HPLC, spectrophotometry, environmental testing
- Facilitates recovery of the aqueous phase of PCRs which have been overlaid with mineral oil.
- Meets ACS specifications.
Production Methods
Chloroform was first synthesized by treating acetone or ethanol with calcium hypochlorite or sodium hypochlorite bleaching powder. Chlorination of ethanol produces acetaldehyde and then trichloroacetaldehyde. Acetaldehyde yields chloroform and the formate ion by action of hydroxide ion. Acetone is chlorinated to trichloroacetone, which then splits into chloroform and the acetateion. The modern industrial preparation of chloroform involves the chlorination of methane or methyl chloride, CH3Cl, using heat to substitute the chlorine atoms for hydrogen. The reaction is carried out at approximately 500°C. Hydrochlorination by reacting methanol and hydrogen chloride can also be used to produce chloroform.
Definition
ChEBI: A one-carbon compound that is methane in which three of the hydrogens are replaced by chlorines.
World Health Organization (WHO)
Chloroform was formerly widely used in pharmaceutical preparations as a solvent and preservative as well as for its anaesthetic and flavouring properties. By the late 1970s reservations concerning its safety, including positive results in a carcinogenicity screening programme sponsored by the National Cancer Institute in the USA, had led to considerable restrictions in its use in pharmaceutical preparations. While many pharmaceutical products containing chloroform have been withdrawn or reformulated to exclude this substance, it may still be incorporated in toothpastes and other specified products in some countries, subject to statutorily-imposed concentration limits. (Reference: (IARCCD) Chloroform: IARC Monograph, 20(20), 401-427, 1979)
General Description
A clear colorless liquid with a characteristic odor. Denser (12.3 lb / gal) than water and slightly soluble in water. Hence sinks in water. Nonflammable under most conditions, but burns under extreme conditions. May cause illness by inhalation, skin absorption or ingestion. Used as a solvent, to make other chemicals, as a fumigant.
Air & Water Reactions
Slightly soluble in water. Dissolves in water to form a corrosive solution of hypochlorous acid which decomposes on standing to chlorine, oxygen, and chloric acid.
Reactivity Profile
A mixture of acetone and Chloroform in a residue bottle exploded. Since addition of acetone to Chloroform in the presence of base will result in a highly exothermic reaction, Chloroform is thought that a base was in the bottle. [MCA Case History 1661(1970)]. Powdered aluminum and carbon tetrachloride(also methyl chloride and Chloroform or mixtures of these chemicals) exploded when heated(to 153°C.) and by impact, [Chem. Eng. News 32:258(1954); UL Bull. Research 34(1945), ASESB Pot. Incid. 39(1968)]. An inadequately cooled addition of sodium to a Chloroform-methanol mixture (sodium methoxide) caused a violent explosion, [MCA Case History No. 693]. Chloroform is incompatible with dinitrogen tetraoxide, fluorine, sodium metal and alcohols, nitromethane, and triisopropylphosphine.
Hazard
A possible carcinogen. Toxic by inhalation; anesthetic; prolonged inhalation or ingestion may be fatal. It has been prohibited by FDA from use in drugs, cosmetics, and food packaging, including cough medicines, toothpastes, etc. Nonflammable. Will burn on prolonged exposure to flame or high temperature. Liver and embryo/fetal damage, and central nervous system impairment.
Health Hazard
Chloroform is classified as moderately toxic. Probable oral lethal dose for humans is 0.5 to 5 g/kg (between 1 ounce and 1 pint) for a 150 lb. person. The mean lethal dose is probably near 1 fluid ounce (44 g). It is a human suspected carcinogen. Also, it is a central nervous system depressant and a gastrointestinal irritant. It has caused rapid death attributable to cardiac arrest and delayed death from liver and kidney damage.
Fire Hazard
Container may explode in the heat of fire. When heated Chloroform liberates phosgene, hydrogen chloride, chlorine and toxic and corrosive oxides of carbon and chlorine. Chloroform explodes when in contact with aluminum powder or magnesium powder or with alkali metals (e.g., lithium, sodium, and potassium) and dinitrogen tetroxide. Chloroform reacts vigorously with acetone in the presence of potassium hydroxide or calcium hydroxide. Chloroform is oxidized by strong oxidizers such as chromic acid forming phosgene and chlorine. Chloroform reacts vigorously with triisopropylphosphine. Chloroform develops acidity from prolonged exposure to air and light.
Flammability and Explosibility
Chloroform is noncombustible. Exposure to fire or high temperatures may lead to formation of phosgene, a highly toxic gas.
Chemical Reactivity
Reactivity with Water No reaction; Reactivity with Common Materials: No reactions; Stability During Transport: Stable; Neutralizing Agents for Acids and Caustics: Not pertinent; Polymerization: Not pertinent; Inhibitor of Polymerization: Not pertinent.
Potential Exposure
Chloroform was one of the earliest general anesthetics, but its use for this purpose has been abandoned because of toxic effects. Chloroform is widelyused as a solvent (especially in the lacquer industry); in the extraction and purification of penicillin and other pharmaceuticals; in the manufacture of artificial silk, propellents, plastics, floor polishes, and fluorocarbons (R-22); and in sterilization of catgut. Chemists and support workers as well as hospital workers are believed to be at a higher risk than the general population. Chloroform is widely distributed in the atmosphere and water (including municipal drinking water primarily as a consequence of chlorination). A survey of 80 American cities by EPA found chloroform in every water system in levels ranging from ,0.3 to 311 ppb.
Carcinogenicity
Chloroform is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in experimental animals.
storage
In the presence of light, chloroform undergoes autoxidation to generate phosgene; this can be minimized by storing this substance in the dark under nitrogen. Commercial samples of chloroform frequently contain 0.5 to 1% ethanol as a stabilizer.
Shipping
UN1888 Chloroform, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Incompatibilities
Though nonflammable, chloroform decomposes to form hydrogen chloride, phosgene, and chlorine upon contact with a flame. Chloroform decomposes slowly in air and light. Reacts violently with strong caustics (bases), strong oxidants, chemically active metals (especially powders), such as aluminum, lithium, magnesium, potassium, and sodium, causing fire and explosion hazard. Attacks plastic, rubber, and coatings. Corrodes iron and other metals in the presence of moisture.
Waste Disposal
Incineration, preferably after mixing with another combustible fuel. Care must be exercised to assure complete combustion to prevent the formation of phosgene. An acid scrubber is necessary to remove the halo acids produced. Where possible it should be recovered, purified by distillation, and returned to the supplier.
Chloroform Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of2
chevron_rightPreparation Products
1of8
chevron_right67-66-3(Chloroform)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




