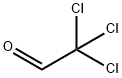
Chloral
- CAS No.
- 75-87-6
- Chemical Name:
- Chloral
- Synonyms
- 2,2,2-trichloroacetaldehyde;TRICHLOROACETALDEHYDE;Anhydrous chloral;CCl3CHO;Trichloroethanal;Grasex;CHLORAL;Cloralio;U.N. 2075;metachloral
- CBNumber:
- CB0437024
- Molecular Formula:
- C2HCl3O
- Molecular Weight:
- 147.39
- MOL File:
- 75-87-6.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2024/3/14 15:18:25
| Melting point | -57.5°C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 94-98 °C |
| Density | 1.51 g/mL at 20 °C(lit.) |
| refractive index |
n |
| Flash point | 75°C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Sparingly), DMSO (Sparingly), Ethyl Acetate (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 10.04(at 25℃) |
| color | Off-White |
| Water Solubility | Soluble |
| Merck | 13,9699 |
| Dielectric constant | 6.7(Ambient) |
| Stability | Stable. Flammable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 75-87-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 2A (Vol. 63, 84, 106) 2014 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Acetaldehyde, trichloro-(75-87-6) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Chloral (75-87-6) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H315-H319-H301-H335 |
| Precautionary statements | P264-P280-P305+P351+P338-P337+P313P-P264-P270-P301+P310-P321-P330-P405-P501-P264-P280-P302+P352-P321-P332+P313-P362 |
| Hazard Codes | T,Xn |
| Risk Statements | 23-36/37/38-22 |
| Safety Statements | 26-36/37-45-7/9-28 |
| RIDADR | UN 2075 6.1/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | FM7870000 |
| F | 1-8-9-13 |
| HazardClass | 6.1(a) |
| PackingGroup | II |
| HS Code | 29130000 |
Chloral Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
Chloral is a combustible, oily liquid with a pungent irritating odor.
Uses
manufacture of chloral hydrate, DDT.
Production Methods
Chloral can be prepared by action of Cl2 on ethanol, chlorination of acetaldehyde, oxidation of 1,1,2-trichloroethylene in the presence of a catalyst (FeCl3, AlCl3, TiCl4 or SbCl3, and by reaction of CCl4 with formaldehyde.
Definition
A colorless liquid aldehyde made by chlorinating ethanal. It was used to make the insecticide DDT. It can be hydrolyzed to give 2,2,2- trichloroethanediol (chloral hydrate, CCl3CH(OH)2). Most compounds with two –OH groups on the same carbon atom are unstable. However, in this case the effect of the three chlorine atoms stabilizes the compound. It is used as a sedative.
General Description
A colorless oily liquid with a penetrating odor. Reacts with water and denser than water. Contact may irritate skin, eyes and mucous membranes. Toxic by ingestion and inhalation. Used to make pesticides.
Air & Water Reactions
Chloral is sensitive to exposure to moisture and light. Soluble in water. Chloral reacts with water to form chloral hydrate.
Reactivity Profile
Chloral reacts with water to form chloral hydrate. Chloral polymerizes under the influence of light and in the presence of sulfuric acid forming a white solid trimer called metachloral.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion. Probable carcinogen.
Health Hazard
INHALATION: Sore throat, shortness of breath, drowsiness, irritation of respiratory tract, unconsciousness. EYES: Redness, pain and blurred vision. SKIN: Redness and pain. INGESTION: Dizziness, drowsiness, nausea, and unconsciousness. Acute hazard: Poison may be fatal if inhaled, swallowed, or absorbed through skin.
Safety Profile
A poison. Mutation E data reported.
Potential Exposure
Chloral is used as an intermediate in the manufacture of such pesticides as DDT, methoxychlor, DDVP, naled, trichlorfon, and TCA. Chloral is also used in the production of chloral hydrate; used as a therapeutic agent with hypnotic, sedative, and narcotic effects; used in a time prior to the introduction of barbiturates
Shipping
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Purification Methods
Distil chloral, then dry it by distilling through a heated column of CaSO4. [Beilstein 1 H 616, 1 I 328, 1 II 467, 1 III 2663, 1 IV 3142 for anhydr, 1 IV 3143 for hydrate.]
Incompatibilities
Chloral hydrate reacts with strong bases forming chloroform. Contact with acids, or exposure to light may cause polymerization. Reacts with water, forming chloral hydrate. Reacts with oxidizers, with a risk of fire or explosions.
Waste Disposal
Incineration after mixing with another combustible fuel; care must be taken to assure complete combustion to prevent phosgene formation; an acid scrubber is necessary to remove the halo acids produced.
Chloral Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of2
chevron_rightPreparation Products
1of8
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rivashaa Agrotech Biopharma Pvt. Ltd. | +91-26463395 +91-7926462688 | Gujarat, India | 1615 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Abhijeet Chemicals Pvt Ltd | +91-8888161067 +91-9822396123 | Maharashtra, India | 3 | 58 | Inquiry |
| OCEAN TRADING CORPORATION | +91(22) 24921669 | New Delhi, India | 6211 | 58 | Inquiry |
| A.J Chemicals | 91-9810153283 | New Delhi, India | 6124 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Bhagwati Industries | 08046042560 | Gujarat, India | 24 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Salasar Impex Limited | 09313992811 | Delhi, India | 2 | 58 | Inquiry |
| S P Chemical Industries | 08048371520Ext 248 | Mumbai, India | 14 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Akshay Industries | 08048372687Ext 420 | Maharashtra, India | 5 | 58 | Inquiry |
| RAMESH CHEMICALS INDUSTRIES | 08068442281Ext 517 | Gujarat, India | 2 | 58 | Inquiry |
| J. J. Enterprises | 08048372500Ext 575 | Madhya Pradesh, India | 3 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Rivashaa Agrotech Biopharma Pvt. Ltd. | 58 |
| Abhijeet Chemicals Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| OCEAN TRADING CORPORATION | 58 |
| A.J Chemicals | 58 |
| Bhagwati Industries | 58 |
| Salasar Impex Limited | 58 |
| S P Chemical Industries | 58 |
| Akshay Industries | 58 |
| RAMESH CHEMICALS INDUSTRIES | 58 |
| J. J. Enterprises | 58 |





