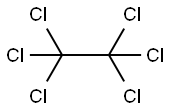
Hexachloroethane
- CAS No.
- 67-72-1
- Chemical Name:
- Hexachloroethane
- Synonyms
- C2Cl6;PERCHLOROETHANE;1,1,1,2,2,2-Hexachloroethane;CCl3CCl3;Hexachlorethane;Avlothane;Egitol;Fron110;NA 9037;Distopin
- CBNumber:
- CB5182855
- Molecular Formula:
- C2Cl6
- Molecular Weight:
- 236.74
- MOL File:
- 67-72-1.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/7/26 17:49:17
| Melting point | 183-185 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 186℃ |
| Density | 2.091 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 8.16 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 0.4 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.5282 (estimate) |
| Flash point | 9℃ |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Soluble in alcohol, benzene, chloroform, ether |
| form | Crystals or Crystalline Powder |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | 0.05 g/L (22 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,4679 |
| BRN | 1740341 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 1.43, 2.81, and 5.31 at 10, 20, and 30 °C, respectively (Munz and Roberts, 1987) |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 10 ppm (~100 mg/m3) (ACGIH), 1 ppm (MSHA and OSHA), Lowest Feasi ble Limit (NIOSH); carcinogenicity: Animal Limited Evidence (IARC). |
| Stability | Stable. Non-combustible. May react with hot metals, strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 67-72-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. 73) 1999 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Ethane, hexachloro-(67-72-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Hexachloroethane (67-72-1) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS07,GHS08,GHS09 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Warning | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H319-H351-H410 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P202-P264-P273-P280-P305+P351+P338-P308+P313 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xn,N,T,F | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 40-51/53-36/37/38-39/23/24/25-36/38-23/24/25-11-50/53-52/53 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 36/37-61-45-36/37/39-26-24-16-7-37/39 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 9037 | |||||||||
| OEB | B | |||||||||
| OEL | TWA: 1 ppm (10 mg/m3) [skin] (Chloroethanes) | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | KI4025000 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 9 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29031990 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | MLD i.v. in dogs: 325 mg/kg (Barsoum, Saad) | |||||||||
| IDLA | 300 ppm | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Hexachloroethane price More Price(12)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 185442 | Hexachloroethane 99% | 67-72-1 | 5G | ₹748 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 185442 | Hexachloroethane 99% | 67-72-1 | 100G | ₹1909.55 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 185442 | Hexachloroethane 99% | 67-72-1 | 500G | ₹5486 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| TCI Chemicals (India) | H0060 | Hexachloroethane min. 99.0 % | 67-72-1 | 25G | ₹1500 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
| TCI Chemicals (India) | H0060 | Hexachloroethane min. 99.0 % | 67-72-1 | 100G | ₹1900 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
Hexachloroethane Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
Hexachloroethane is a white solid with a camphor-like odor. It gradually evaporates when it is exposed to air.
Physical properties
Rhombic, triclinic or cubic, colorless crystals with a camphor-like odor. Odor threshold concentration is 0.15 ppm (quoted, Amoore and Hautala, 1983).
Uses
Hexachloroethane is used as a solvent, infireworks and smoke devices; in explosives,in celluloid, as an insecticide, and as a rubbervulcanizing accelerator. Earlier it was used asan anthelmintic for livestock. Hexachloroethane is a highly efficient chlorinating agent in the preparation of chlorosilanes from hydrosilanes.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of chloroethanes that is ethane in which all the hydrogens are replaced by chloro groups.
General Description
Hexachloroethane is a colorless, crystalline solid with a camphor-like odor. Hexachloroethane may cause illness from inhalation or ingestion and may irritate skin, eyes and mucous membranes. When heated to high temperatures Hexachloroethane may emit toxic fumes. The primary hazard is the threat to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit its spread to the environment. Hexachloroethane is used to make other chemicals.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Hexachloroethane can react with hot iron, zinc and aluminum. Dehalogenation of Hexachloroethane by reaction with alkalis and metals will produce unstable chloroacetylenes. Hexachloroethane can also react with strong oxidizing agents. .
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion and inhalation, strong irritant, absorbed by skin. Possible carcinogen.
Health Hazard
Vapors of hexachloroethane are an irritant tothe eyes and mucous membranes. Oral dosesof 1000 mg/kg produced weakness, stagger ing gait, and twitching muscles in dogs.Rabbits fed 1000 mg/kg for 12 days devel oped necrosis; a lower amount, 320 mg/kg,caused liver degeneration; no effects wereobserved at a dose level of 100 mg/kg(Weeks 1979).
Acute inhalation toxicity is of a loworder in animals. Subacute toxic effectsin dogs exposed to 260-ppm vapors ofhexachloroethane for 6 hours per day, 5days a week for 6 weeks were tremors,ataxia, hypersalivation, head bobbling, andfacial muscular fasciculations (Weeks 1979).The lethal concentration in rats is 5900 ppmfrom an 8-hour exposure.
LD50 value, oral (rats): 4460 mg/kg
Tests for mutagenicity and teratogenic ity were negative. The carcinogenic poten tial of hexachloroethane was noted in testanimals only at extremely heavy dosagesgiven continuously for a long period of time(ACGIH 1986). It caused liver tumors inmice.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Irritating hydrogen chloride vapor may form in fire.
Potential Exposure
In the US, about half the HCE is used by the military for smoke-producing devices. It is also used to remove air bubbles in melted aluminum. It may be present as an ingredient in some fungicides, insecticides, lubricants, and plastics. It is no longer made in the United States, but it is formed as a by-product in the production of some chemicals. Can be formed by incinerators when mate rials containing chlorinated hydrocarbons are burned. Some HCE can also be formed when chlorine reacts with carbon compounds in drinking water. As a medicinal, HCE is used as an anthelmintic to treat fascioliasis in sheep and cattle. It is also added to the feed of ruminants, preventing metha nogenesis and increasing feed efficiency. HCE is used in metal and alloy production, mainly in refining aluminum alloys. It is also used for removing impurities from molten metals, recovering metals from ores or smelting products and improving the quality of various metals and alloys. HCE is contained in pyrotechnics. It inhibits the explosive ness of methane and the combustion of ammonium perchlo rate. Smoke containing HCE is used to extinguish fires. HCE has various applications as a polymer additive. It has flameproofing qualities, increases sensitivity to radiation crosslinking, and is used as a vulcanizing agent. Added to polymer fibers, HCE acts as a swelling agent and increases affinity for dyes.
Carcinogenicity
Hexachloroethane is reasonably anticipated to be ogen based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicit a human carciny from studies in experimental animals.
Environmental Fate
Biological. Under aerobic conditions or in experimental systems containing mixed cultures,
hexachloroethane was reported to degrade to tetrachloroethane (Vogel et al., 1987). In an
uninhibited anoxic-sediment water suspension, hexachloroethane degraded to tetrachloroethylene.
The reported half-life for this transformation was 19.7 min (Jafvert and Wolfe, 1987). When
hexachloroethane (5 and 10 mg/L) was statically incubated in the dark at 25 °C with yeast extract
and settled domestic wastewater inoculum for 7 d, 100% biodegradation with rapid adaptation was
observed (Tabak et al., 1981).
Photolytic. When an aqueous solution containing hexachloroethane was photooxidized by UV
light at 90–95 °C, 25, 50, and 75% degraded to carbon dioxide after 25.2, 93.7, and 172.0 h,
respectively (Knoevenagel and Himmelreich, 1976).
Chemical/Physical. The reported hydrolysis half-life at 25 °C and pH 7 is 1.8 x 109 yr (Jeffers et
al., 1989). No hydrolysis was observed after 13 d at 85 °C and pH values of 3, 7, and 11 (Ellington
et al., 1987). Similarly, no measureable hydrolysis was observed under neutral and alkaline
conditions (Jeffers and Wolfe, 1996).
Shipping
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required.
Purification Methods
Steam distil it, then crystallise it from 95% EtOH. Dry it in the dark under vacuum. [Beilstein 1 IV 148.]
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with strong acids, oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from strong bases.
Waste Disposal
Incineration after mixing with another combustible fuel. Care must be exercised to assure complete combustion to prevent the formation of phosgene. An acid scrubber is necessary to remove the halo acids pro duced. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must con form to EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal.
Hexachloroethane Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of3
chevron_rightPreparation Products
1of2
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scottish Chemical Industries | +91-2226056060 +91-2262396666 | Maharashtra, India | 1 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Teja Metallurgicals and Chemicals | +91-9444054586 +91-9444765502 | Tamil Nadu, India | 1 | 58 | Inquiry |
| S D Fine Chem Limited | +91-9323715856 +91-9323715856 | Maharashtra, India | 368 | 58 | Inquiry |
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | +91-22-45045900 | Hyderabad, India | 6351 | 58 | Inquiry |
| A.J Chemicals | 91-9810153283 | New Delhi, India | 6124 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Otto Chemie Pvt. Ltd. | +91 9820041841 | Mumbai, India | 5873 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Alfa Aesar | 1 800 209 7001 | Maharashtra, India | 6913 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Central Drug House(P) Ltd. | 91-11-49404040 | New Delhi, India | 6160 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Triveni chemicals | 08048762458 | New Delhi, India | 6093 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Anshul Specialty Molecules Pvt Ltd | 08048372472Ext 403 | Mumbai, India | 9 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Scottish Chemical Industries | 58 |
| Teja Metallurgicals and Chemicals | 58 |
| S D Fine Chem Limited | 58 |
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | 58 |
| A.J Chemicals | 58 |
| Otto Chemie Pvt. Ltd. | 58 |
| Alfa Aesar | 58 |
| Central Drug House(P) Ltd. | 58 |
| Triveni chemicals | 58 |
| Anshul Specialty Molecules Pvt Ltd | 58 |
Related articles
- What is Hexachloroethane?
- Hexachloroethane is a member of the class of chloroethanes, which is ethane, in which all the hydrogens are replaced by chloro....
- Jul 16,2024
67-72-1(Hexachloroethane)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




