Lead azide
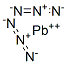
- CAS No.
- 13424-46-9
- Chemical Name:
- Lead azide
- Synonyms
- Lead azide;lead diazide;plumbous azide;Lead(II)diazide;Diazidolead(II);Lead(II) azide.;Lead azide (Pb(N3)2);lead diazide lead azide;Lead azide ISO 9001:2015 REACH
- CBNumber:
- CB0851554
- Molecular Formula:
- N6Pb
- Molecular Weight:
- 291.2402
- MOL File:
- 13424-46-9.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2023/10/17 17:11:55
| Density | 4.700 |
|---|---|
| solubility | very soluble in H2OAc |
| form | colorless orthorhombic needles |
| color | colorless orthorhombic needles; explodes, explosive |
| Water Solubility | 0.023% H2O (18°C), 0.09% (70°C) [MER06]; insoluble NH4OH; very soluble acetic acid [KIR78] |
| Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) | pKsp: 8.59 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 13424-46-9 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Lead(II) azide (13424-46-9) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |     GHS01,GHS08,GHS07,GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H201-H302-H332-H360Df-H373-H410 |
| Precautionary statements | P210-P230-P240-P250-P280-P370+P380-P372-P373-P401-P501-P264-P270-P301+P312-P330-P501-P261-P271-P304+P340-P312-P260-P314-P501-P273-P391-P501 |
| Hazard Codes | E,T,N |
| Risk Statements | 61-3-20/22-33-50/53-62 |
| Safety Statements | 53-45-60-61 |
| RIDADR | 0129 |
| HazardClass | 1.1A |
| PackingGroup | II |
Lead azide Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Lead azide is a severe explosion risk and should be handled under water; it is also a primary detonating compound.
Chemical Properties
needles or white powder(s); prepared by reaction of dilute solutions of lead nitrate and sodium azide; used as a primary detonating compound for high explosives; α-Pb(N3)2: orthorhombic, a=0.663nm, b=0.546 nm, c=1.625nm; β-Pb(N3)3: monoclinic, a=0.509 nm, b=0.884nm, c=1.751 nm; γ-Pb(N3)2: a=0.622nm, b=1.051 nm, c=1.217 nm [MER06] [CIC73] [KIR78]
Physical properties
Colorless needles or white powder; density ~4.0 g/cm3; explodes on heating at 350°C; slightly soluble in water, 230 mg/L at 18°C and 900 mg/L at 70°C; very soluble in acetic acid; insoluble in ammonia solution.
Uses
As primer in explosives. In the form of dextrinated lead azide.
Production Methods
Lead azide crystallizes as colorless needles. It is a sensitive detonating agent, exploding at 350 °C. Lead azide is commonly prepared by the reaction between dilute solutions of lead nitrate and sodium azide. For safety, it is stirred vigorously to prevent formation of large crystals, which may detonate. Lead azide is usually precipitated with a protective material, such as gelatin, and then granulated. Lead azide is also used to prepare electrophotographic layers and for information storage on styrene–butadiene resins.
Preparation
Lead azide is prepared by the reaction of sodium azide with lead nitrate:
2NaN3 + Pb(NO3)2 → Pb(N3)2 + 2NaNO3
.
General Description
Needles or white powder. Explodes at 350°C. Insoluble in water. May explode from shock, heat, flame or friction when dry. The primary hazard is the blast effect of an instantaneous explosion and not flying projectiles and fragments.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Lead azide is unstable. May, when dry, decompose explosively if shocked, heated or subjected to friction. Forms violently explosive products with carbon disulfide. Can be sensitized to explosive decomposition by metal salts (copper or zinc) or by traces of strong acids [Sax, 9th ed., 1996, p. 298]. An explosion occurred by mixing Lead azide with 0.5% of calcium stearate, [MCA Case History No. 949].
Hazard
Lead azide explodes on heating at 350°C or on percussion. Its detonation velocity is 5.1 km/sec (Meyer, E. 1989. Chemistry of Hazardous Materials, 2nd ed. Englewood Cliffs, N.J.: Prentice Hall). It undergoes violent explosive reaction with carbon disulfide and forms shock-sensitive copper and zinc azides when mixed with the solutions of copper and zinc salts (Patnaik, P. 1999. A Comprehensive Guide to the Hazardous Properties of Chemical Substances, 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley).
Health Hazard
Toxicity data for lead azide are not available.Its aqueous solution is toxic, exhibitingpoisoning effect of lead.
Fire Hazard
MAY EXPLODE AND THROW FRAGMENTS 1600 meters (1 MILE) OR MORE IF FIRE REACHES CARGO.
Carcinogenicity
Results in an early study were
deemed inconclusive because dose levels were not considered
high enough. Rats were fed diets containing 100 or
200 ppm (6 or 12 mg/kg/day) sodium azide for 18 months
followed by 6 months of observation. An increase in pituitary
adenomas in the low-dose females compared to concurrent
controls was found, but in this study the incidence in the
control rats was unusually low compared to historical controls.
A similar result occurred with mammary tumors.
No carcinogenicity studies were found for hydrogen azide
or lead azide but lead should be used as an analog for the latter
chemical.
Waste Disposal
Lead azide is decomposed by treatment withnitrous acid or ceric ammonium nitrate (Wear1981).
Lead azide Preparation Products And Raw materials
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triveni chemicals | 08048762458 | New Delhi, India | 6093 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 | China | 21669 | 55 | Inquiry |
| Shaanxi Didu New Materials Co. Ltd | +86-89586680 +86-13289823923 | China | 9003 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Shaanxi Dideu Newmaterial Co., Ltd. | 029-63373950 15353716720 | China | 10011 | 58 | Inquiry |
| HONEST JOY HOLDINGS LIMITED | +86-755-26404303 | United States | 6702 | 54 | Inquiry |
| Portail Substances Chimiques | 10 20 0000 | France | 6027 | 58 | Inquiry |
13424-46-9(Lead azide)Related Search:
1of3
chevron_right




