Lead(II) chloride
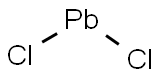
- CAS No.
- 7758-95-4
- Chemical Name:
- Lead(II) chloride
- Synonyms
- PbCl2;LEAD CHLORIDE;Leclo;PbCI2;NA 2291;Cotunnite;ead(II) chL;dichlorolead;Bleidichlorid;leaddichloride
- CBNumber:
- CB0385798
- Molecular Formula:
- Cl2Pb
- Molecular Weight:
- 278.11
- MOL File:
- 7758-95-4.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/6/29 22:56:24
| Melting point | 501 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 950 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 5.85 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 1 mm Hg ( 547 °C) |
| Flash point | 951°C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | aliphatic hydrocarbons: slightly soluble(lit.) |
| form | powder |
| color | White to off-white |
| Specific Gravity | 5.85 |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in hot water, alkali hydroxides and NH<sub>4</sub>Cl solution. Insoluble in cold water and alcohol. |
| Hydrolytic Sensitivity | 0: forms stable aqueous solutions |
| Merck | 14,5404 |
| Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) | pKsp: 4.77 |
| Exposure limits |
ACGIH: TWA 0.05 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 100 mg/m3; TWA 0.050 mg/m3 |
| Dielectric constant | 4.2(0.0℃) |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7758-95-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Lead dichloride(7758-95-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Lead(II) chloride (7758-95-4) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS07,GHS08,GHS09 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H302+H332-H351-H360Df-H372-H410 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P201-P273-P301+P312+P330-P304+P340+P312-P308+P313 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | T,N | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 61-20/22-33-50/53-62 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 53-45-60-61 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 2291 6.1/PG 3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | OF9450000 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 6.1 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| HS Code | 28273990 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | MLD in guinea pigs (mg/kg): 1500-2000 orally (Tartler) | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Lead(II) chloride price More Price(24)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 8.07383 | Lead(II) chloride anhydrous for synthesis | 7758-95-4 | 100G | ₹3610 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 8.07383 | Lead(II) chloride anhydrous for synthesis | 7758-95-4 | 500G | ₹17600 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 268690 | Lead(II) chloride powder, 98% | 7758-95-4 | 5G | ₹2219.13 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 268690 | Lead(II) chloride powder, 98% | 7758-95-4 | 250G | ₹2684.6 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 449865 | Lead(II) chloride AnhydroBeads?, ?10?mesh, 99.999% | 7758-95-4 | 5G | ₹6473.35 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Lead(II) chloride Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
Lead chloride is a white crystalline powder
Physical properties
White orthorhombic crystals; refractive index 2.199; density 5.85 g/cm3; melts at 501°C; vaporizes at 950°C; partially soluble in cold water (6.73 g/L at 0°C and 9.9 g/L at 20°C); KSP 1.17x10-5 at 25°C; moderately soluble in boiling water (33.4 g/L at 100°C); slightly soluble in dilute HCl and ammonia; insoluble in alcohol.
Occurrence
Lead dichloride occurs in nature as the mineral cotunnite. The compound is used in making many basic chlorides, such as Pattison’s lead white, Turner’s Patent Yellow, and Verona Yellow, used as pigments. Also, it is used as a flux for galvanizing steel; as a flame retardant in nylon wire coatings; as a cathode for seawater batteries; to remove H2S and ozone from effluent gases; as a sterilization indicator; as a polymerization catalyst for alphaolefins; and as a co-catalyst in manufacturing acrylonitrile.
Uses
Lead(II) chloride is used in the synthesis of lead titanate and barium lead titanate ceramics; employed in the production of infrared transmitting glass and ornamental glass (aurene glass); useful as an electrode in geophysical applications and in solar cells. Analytical reagent, preparation of lead salts, as solder and flux. Pattinson's white lead, pigment in white paint, is the basic lead chloride.
Preparation
Lead dichloride is precipitated by adding hydrochloric acid or any chloride salt solution to a cold solution of lead nitrate or other lead(II) salt:
Pb2+ + 2Clˉ → PbCl2
Alternatively, it is prepared by treating lead monoxide or basic lead carbonate with hydrochloric acid and allowing the precipitate to settle.
.
Definition
ChEBI: An inorganic chloride consisting of two chlorine atoms covalently bound to a central lead atom.
General Description
Prepared by reacting lead(II) oxide /acetate or carbonate with HCl. In crystalline PbCl2, each atom is coordinated by nine Cl atoms, six of which lie at the apices of a trigonal prism and the remaining three beyond the centers of the three prism faces. Each Cl is coordinated by four or five Pb atoms. Upon exposure to air it form basic chlorides such as PbCl2.Pb(OH)2.
Reactivity Profile
Lead dichloride is a weak reducing agent. Interaction of Lead dichloride and calcium is explosive on warming, [Mellor, 1941, Vol. 3, 369].
Hazard
Toxic effects from ingestion may vary from low to moderate. The oral lethal dose in guinea pigs is documented as 1,500 mg/kg. (Lewis (Sr.), R. J. 1996. Sax’s Dangerous Properties of Industrial Materials, 9th ed. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold).
Health Hazard
DUST AND FUMES. POISONOUS IF INHALED. SOLID: If swallowed, may cause metallic taste, abdominal pain, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Fire Hazard
Not flammable. POISONOUS METAL FUMES MAY BE PRODUCED IN FIRE. Toxic metal fumes. Can emit toxic metal fumes.
Potential Exposure
Used to make lead salts; lead chromate pigments; as an analytical reagent for making other chemicals; making printed circuit boards; as a solder and flux.
Shipping
UN2291 Lead compounds, soluble n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from distilled water at 100o (33mL/g) after filtering through sintered-glass and adding a few drops of HCl, by cooling. After three crystallisations the solid is dried under vacuum or under anhydrous HCl vapour by heating slowly to 400o. The solubility in H2O is 0.07% at ~10o, and 0.43% at ~ 100o.
Incompatibilities
A reducing agent. Violent reaction with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides, and chemically active metals. Explosive with calcium 1 warming
Lead(II) chloride Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of2
chevron_rightPreparation Products
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QUALIKEMS FINE CHEM PVT LTD | +911123618475 | New Delhi, India | 51 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Yogi Dye Chem Industries | +91-9821098577 +91-9821098577 | Mumbai, India | 124 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Nithyasri Chemicals (APURVA CHEMICALS) | +91-2512692130 +91-9323652199 | Maharashtra, India | 75 | 58 | Inquiry |
| CHEMSWORTH | +91-261-2397244 | New Delhi, India | 6707 | 30 | Inquiry |
| ALPHA CHEMIKA | +91-22-22061123 +91-22-66382501 | Mumbai, India | 1681 | 43 | Inquiry |
| Scientific OEM | +91-22- 2343 7546 / 2341 3094 | New Delhi, India | 1996 | 38 | Inquiry |
| TCI Chemicals (India) Pvt. Ltd. | 1800 425 7889 | New Delhi, India | 6778 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Otto Chemie Pvt. Ltd. | +91 9820041841 | Mumbai, India | 5873 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Alfa Aesar | 1 800 209 7001 | Maharashtra, India | 6913 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Sisco Research Laboratories Pvt. Ltd. | +91-22-4268 5800 | Mumbai, India | 4317 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| QUALIKEMS FINE CHEM PVT LTD | 58 |
| Yogi Dye Chem Industries | 58 |
| Nithyasri Chemicals (APURVA CHEMICALS) | 58 |
| CHEMSWORTH | 30 |
| ALPHA CHEMIKA | 43 |
| Scientific OEM | 38 |
| TCI Chemicals (India) Pvt. Ltd. | 58 |
| Otto Chemie Pvt. Ltd. | 58 |
| Alfa Aesar | 58 |
| Sisco Research Laboratories Pvt. Ltd. | 58 |
7758-95-4(Lead(II) chloride)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




