Azithromycin
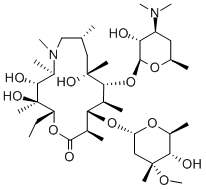
- CAS No.
- 83905-01-5
- Chemical Name:
- Azithromycin
- Synonyms
- Zithromax;AZITHROMYCINE;Zeto;Azitromvcin;Azenil;Setron;AZYTHROMYCIN;Azithromycin 98%;Tobil;Zifin
- CBNumber:
- CB1442887
- Molecular Formula:
- C38H72N2O12
- Molecular Weight:
- 748.98
- MOL File:
- 83905-01-5.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2025/4/22 12:35:22
| Melting point | 113-115°C |
|---|---|
| alpha | D20 -37° (c = 1 in CHCl3) |
| Boiling point | 822.1±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.18±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in anhydrous ethanol and in methylene chloride. |
| form | Solid |
| pka | pKa 8.74 (H2O t=25 I=0.167) (Uncertain);9.45(H2O t=25 I=0.167) (Uncertain) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| optical activity | [α]/D 45±2°, c = 1% in ethanol |
| BCS Class | 4 |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 83905-01-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Azithromycin (83905-01-5) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H317-H334 |
| Precautionary statements | P261-P280-P342+P311 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi,Xn |
| Risk Statements | 42/43 |
| Safety Statements | 22-36/37-45 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | RN6960000 |
| HS Code | 29419090 |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 83905-01-5(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| Toxicity | LD50 oral in rat: > 2gm/kg |
Azithromycin Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
White Crystalline Powder
Indications
Azithromycin in a 500-mg dose three times a week has been shown to yield a 60% reduction in inflammatory papules in 83% of patients enrolled in a 12- week study. There is no associated pseudotumor cerebri and, therefore, it can be used for an acne flare during early Accutane therapy.
Definition
ChEBI: Azithromycin is a macrolide antibiotic useful for the treatment of bacterial infections. It is an azalide, derived from erythromycin, and a member of a subclass of macrolide antibiotics with bacteriocidal and bacteriostatic activities.
Antimicrobial activity
It is less potent than erythromycin A against Gram-positive isolates, but is more active against Gram-negative bacteria. It is four times more potent than erythromycin A against H. influenzae, N. gonorrhoeae and Campylobacter spp., and twice as active against Mor. catarrhalis. It also exhibits superior potency against Enterobacteriaceae, notably Esch. coli, Salmonella enterica serotypes, and Shigella spp. It is active against Mycobacteria, notably the M. avium complex and against intracellular micro-organisms such as Legionella and Chlamydia spp.
Chemical modification at the 9 position of the erythronolide A ring of erythromycin A blocks the internal ketalization and markedly improves acid stability. At pH 2, loss of 10% activity occurred in less than 4 s with erythromycin A, but took 20 min with azithromycin. The AUC at 0–24 h is 4.5 mg.h/L. The level is only slightly increased on repeated dosing.
Binding to plasma protein varies with the concentration, from around 50% at 0.05 mg/L to 7.1% at 1 mg/L. The apparent elimination half-life is dependent upon sampling interval: between 8 and 24 h it ranged from 11 to 14 h; between 24 and 72 h it was 35–40 h.
It rapidly penetrates the tissues, reaching levels that approach or, in some cases, exceed the simultaneous plasma levels and persist for 2–3 days. Only about 6% of the dose is found in urine in the first 24 h.
General Description
The spectrum of antimicrobial activity of azithromycin issimilar to that observed for erythromycin and clarithromycinbut with some interesting differences. In general,it is more active against Gram-negative bacteria and less activeagainst Gram-positive bacteria than its close relatives.The greater activity of azithromycin against H. influenzae,M. catarrhalis, and M. pneumoniae coupled with its extendedhalf-life permits a 5-day dosing schedule for thetreatment of respiratory tract infections caused by thesepathogens. The clinical efficacy of azithromycin in the treatmentof urogenital and other sexually transmitted infectionscaused by Chlamydia trachomatis, N. gonorrhoeae, H.ducreyi, and Ureaplasma urealyticum suggests that singledosetherapy with it for uncomplicated urethritis or cervicitismay have advantages over use of other antibiotics.
Biological Activity
Azithromycin is a macrolide antibiotic. It is active against S. pneumoniae, S. aureus, N. gonorrhoeae, M. pneumoniae, H. pylori, C. trachomatis, and H. influenzae in vitro (MIC90s = <0.01-2 mg/L). Azithromycin increases survival in mouse models of intraperitoneal S. pyogenes, S. pneumoniae, E. faecalis, or H. influenzae infection (ED50s = 0.78, 8.7, 12.7, and 30.3 mg/kg, respectively). It inhibits replication of severe acute respiratory coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), but not Middle East respiratory syndrome CoV (MERS-CoV), when used at concentrations of 5 and 10 μM. Azithromycin also decreases plasma levels of IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-1β and increases survival in a mouse model of LPS-induced sepsis when administered at a dose of 100 mg/kg. Formulations containing azithromycin have been used in the treatment of a variety of bacterial infections.
Pharmacokinetics
Oral absorption:37%
Cmax 250 mg oral: 0.17 mg/L after 2.2 h
500 mg oral: 0.4 mg/L after2h
Plasma half-life (terminal): 11–40 h
Volume of distribution: 31 L/kg
Plasma protein binding :7–50%
Chemical modification at the 9 position of the erythronolide A ring of erythromycin A blocks the internal ketalization and markedly improves acid stability. At pH 2, loss of 10% activity occurred in less than 4 s with erythromycin A, but took 20 min with azithromycin. The AUC at 0–24 h is 4.5 mg.h/L. The level is only slightly increased on repeated dosing.
Binding to plasma protein varies with the concentration, from around 50% at 0.05 mg/L to 7.1% at 1 mg/L. The apparent elimination half-life is dependent upon sampling interval: between 8 and 24 h it ranged from 11 to 14 h: between 24 and 72 h it was 35–40 h.
It rapidly penetrates the tissues, reaching levels that approach or, in some cases, exceed the simultaneous plasma levels and persist for 2–3 days. Only about 6% of the dose is found in urine in the first 24 h.
Side effects
Azithromycin is well tolerated with little gastrointestinal disturbance.
Mode of action
Azithromycin reversibly binds to the 50S ribosomal subunit of the 70S ribosome of sensitive microorganisms, thereby inhibiting the translocation step of protein synthesis, wherein a newly synthesized peptidyl tRNA molecule moves from the acceptor site on the ribosome to the peptidyl (donor) site, and consequently inhibiting RNA-dependent protein synthesis leading to cell growth inhibition and cell death.
Azithromycin Preparation Products And Raw materials
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIMSON PHARMA LIMITED | +91-8291074273 | Shanghai, India | 228 | 58 | Inquiry |
| CHEMXTREE STANDARDS | +919872732255 | Punjab, India | 96 | 58 | Inquiry |
| ANWITA APIS | +919000311012 | Hyderabad, India | 195 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Anant Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd | +91-8550986868 +91-9485998001 | Haryana, India | 460 | 58 | Inquiry |
| S.V ENTERPRISES | +919322701159 | Mumbai, India | 150 | 58 | Inquiry |
| SNECOFRi Pvt Ltd | +91-9032850129 +91-9032850129 | Telangana, India | 403 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Frolic Pharmachem | +919711094561 | Himachal Pradesh, India | 94 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Shree HariKrishna Pharmaceuticals | +91-9925611910 +91-9925611910 | Gujarat, India | 16 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Varanous Labs Pvt Ltd | +91-7036248882 +91-7036248882 | Hyderabad, India | 1537 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Medi Pharma Drug House | +919930911911 | Mumbai, India | 143 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| SIMSON PHARMA LIMITED | 58 |
| CHEMXTREE STANDARDS | 58 |
| ANWITA APIS | 58 |
| Anant Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| S.V ENTERPRISES | 58 |
| SNECOFRi Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| Frolic Pharmachem | 58 |
| Shree HariKrishna Pharmaceuticals | 58 |
| Varanous Labs Pvt Ltd | 58 |
| Medi Pharma Drug House | 58 |
Related articles
- Which should be given orally or intravenously for the treatment of respiratory infections in children with Azithromycin?
- Azithromycin is a macrolide antibiotic that can be widely used to treat a variety of respiratory infections in children.
- Jan 13,2025
- Does azithromycin have to be refrigerated?
- Azithromycin is a macrolide-type antibiotic, it is used to treat a wide variety of bacterial infections.
- Mar 21,2024
- Azithromycin vs Amoxicillin
- Both Azithromycin and Amoxicillin are considered broad-spectrum antibiotics, which means they treat a wide range of infections....
- Nov 8,2023
Related Qustion
- Q:Can Azithromycin be used during pregnancy?
- A:Yes. Azithromycin is an azamide antibiotic with a wide range of indications. It is a pregnancy category B drug.
- Jun 5,2024
83905-01-5(Azithromycin)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




