Telithromycin
- CAS No.
- 191114-48-4
- Chemical Name:
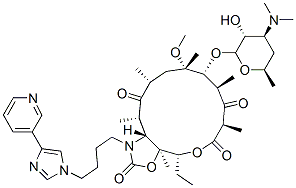
- Telithromycin
- Synonyms
- KETEK;RU 66647;HMR 3647;TELITHROMYCIN;TelithroMycin 90%;Telithromycin (90%);Telithromycin USP/EP/BP;Telithromycin 90% (10mM in DMSO);(1R,2R,4R,6S,7R,8R,10R,13R,14S)-7-[(2S,3R,4S,6R)-4-Dimethylamino-3-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-13-ethyl-6-methoxy-2,4,6,8,10,14-hexamethyl-17-[4-(4-pyridin-3-ylimidazol-1-yl)butyl]-12,15-dioxa-17-azabicyclo[12.3.0]heptadecane-3,9,11,16-tetrone;2H-Oxacyclotetradecino[4,3-d]oxazole-2,6,8,14(1H,7H,9H)-tetrone,4-ethyloctahydro-11-Methoxy-3a,7,9,11,13,15-hexaMethyl-1-[4-[4-(3-pyridinyl)-1H-iMidazol-1-yl]butyl]-10-[[3,4,6-trideoxy-3-(diMethylaMino)-b-D-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-,(3aS,4R,7R,9R,10R,11R,1
- CBNumber:
- CB1482102
- Molecular Formula:
- C43H65N5O10
- Molecular Weight:
- 812
- MOL File:
- 191114-48-4.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2023/5/18 11:31:03
| Melting point | 176-188 C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 966℃ |
| Density | 1.26±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| RTECS | KF4674500 |
| Flash point | >110°(230°F) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 10.85±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | White to Light Beige |
| Water Solubility | Sparingly soluble in water |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 191114-48-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS07,GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H315-H319-H335-H400-H410 |
| Precautionary statements | P261-P280a-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P405-P501a |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Statements | 36/37/38 |
| Safety Statements | 26-36 |
| HazardClass | 9 |
Telithromycin Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Telithromycin was first launched in Germany as a once-daily oral treatment for respiratory infections including community-acquired pneumonia, acute bacterial exacerbations of chronic bronchitis, acute sinusitis and tonsillitis/pharyngitis. This semisynthetic derivative of the natural macrolide erythromycin is the first marketed ketolide, a new class of antibiotics featuring a C3-ketone instead of the L-cladinose group. The 14-membered ring antibacterial agent prevents bacterial protein synthesis by binding to two domains of the 50S subunit of bacterial ribosomes. It shows potent in vitro activity against common respiratory pathogens including Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis and Streptococcus pyogenes as well as other atypical pathogens. The 3-keto group confers increased acidic stability and reduced induction of macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B resistance that is frequently observed with macrolides. The substituted C11-C12 carbamate residue appears not only to increase affinity for the ribosomal binding site but also to stabilize the compound against esterase hydrolysis and avoid resistance due to elimination of macrolides from the cell by an efflux pump encoded by the mef gene in certain pathogens. Telithromycin is both a competitive inhibitor and a substrate of CYP3A4. However, unlike several macrolides such as troleandomycin, it does not form a stable inhibitory CYP P-450 Fe2+-nitrosoalkane metabolite complex which is potentially hepatotoxic. The drug is well tolerated and well distributed into pulmonary tissues, bronchial secretions, tonsils and saliva. It turns out to be highly concentrated in azurophil granules of polymorphonuclear neutrophils thereby facilitating its delivery to the phagocytosed bacteria.
Chemical Properties
Pale Beige Solid
Uses
Telithromycin represents the first member of the current generation of erythromycin descendants, belonging to the ketolide class. The ketolides are characterised by the hydrolysis of the cladinose sugar and subsequent oxidation of the alcohol to a ketone. Telithromycin is acid stabile and has good activity against erythromycin-resistant S. aureus, and improved pharmacokinetics.
Antimicrobial activity
The spectrum covers Gram-positive and Gramnegative cocci, Gram-positive bacilli, fastidious Gram-negative bacilli, atypical mycobacteria, M. leprae, H. pylori, anaerobes, T. pallidum, intracellular pathogens and atypical organisms.
It exhibits bactericidal activity in vitro against isolates of Str. pneumoniae regardless of the underlying resistance to penicillin G, erythromycin A and other agents. It is 2–4 times more active than clarithromycin against erythromycin A-susceptible isolates of Str. pneumoniae and other streptococci. Against H. influenzae the MIC range is 1–4 mg/L. It also exhibits good in-vitro activity against Coxiella burnetii (MIC 1 mg/L) and various Gram-positive species, including viridans streptococci (MIC ≤0.015–0.25 mg/L), C. diphtheriae (MIC 0.004–0.008 mg/L) and Listeria spp. (MIC 0.03–0.25 mg/L).
Acquired resistance
It retains activity against isolates resistant to erythromycin A. Str. pneumoniae and Str. pyogenes isolates for which the MIC of telithromycin is above the resistance breakpoint of 2 mg/L are presently rare. It is not active against Staph. aureus isolates that owe their resistance to erythromycin to constitutive methylation of adenine 2058 on domain V of the peptidyl transferase loop.
General Description
Telithromycin (Ketek) is an orally bioavailable macrolide.The antibiotic is semisynthetic. Telithromycin is classifiedas a ketolide, and it differs chemically from the macrolidegroup of antibacterials by the lack of α-L-cladinose at 3-position of the erythronolide A ring, resulting in a 3-ketofunction. It is further characterized by imidazolyl andpyridyl rings inked to the macrolide nucleus through a butylchain. The mechanism of action of telithromycin is the sameas that of the macrolide class.
Telithromycin causes a blockade of protein synthesis bybinding to domains II and V of 23S rRNA of the 50S ribosomalsubunit. Because telithromycin binds at domain II,activity against Gram-positive cocci is retained in the presenceof resistance mediated by methylases that alter thedomain V binding site. The antibiotic is also believed to inhibitthe assembly of ribosomes. Resistance to telithromycinoccurs because of riboprotein mutations.
Pharmaceutical Applications
A 14-membered-ring ketolide, obtained by semisynthesis from erythromycin A. Formulated for oral administration.
Pharmacokinetics
Oral absorption :90%
Cmax 800 mg oral :1.9–2.27 mg/L (steady state after 2–3 days)
Plasma half-life: 10–12 h
Volume of distribution :210 L
Plasma protein binding:60–70%
After oral administration the absolute bioavailability is 57% in both young and elderly subjects. The rate and extent of absorption are not influenced by food. In a study of ascending doses administered to healthy volunteers, peak plasma concentration ranged from 0.8 mg/L (400 mg dose) to 6 mg/L (2400 mg dose). The peak plasma concentration was reached after 1–2 h. The apparent elimination half-lives ranged from 10 to 14 h, with an AUC of 2.6 mg.h/L (400 mg dose) to 43.3 mg.h/L (2400 mg dose). After repeated oral doses the ratios between day 1 and day 10 ranged from 1.3 to 1.5. After once-daily oral dosing with 800 mg, the AUC is 8.25 mg.h/L.
Side effects
It is generally well tolerated. The main adverse event is diarrhea.
Telithromycin Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neugen Labs | +91-8133254502 +91-8133254502 | Karnataka, India | 195 | 58 | Inquiry |
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | +91-22-45045900 | Hyderabad, India | 6351 | 58 | Inquiry |
| OCEAN TRADING CORPORATION | +91(22) 24921669 | New Delhi, India | 6211 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 | China | 21675 | 55 | Inquiry |
| career henan chemical co | +86-0371-86658258 +8613203830695 | China | 29900 | 58 | Inquiry |
| BOC Sciences | +1-631-485-4226 | United States | 19553 | 58 | Inquiry |
| CONIER CHEM AND PHARMA LIMITED | +8618523575427 | China | 49391 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Shaanxi Dideu Medichem Co. Ltd | +86-029-89586680 +86-18192503167 | China | 9030 | 58 | Inquiry |
| AFINE CHEMICALS LIMITED | +86-0571-85134551 | China | 15395 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Wuhan Fortuna Chemical Co., Ltd | +86-027-59207850 | China | 5999 | 58 | Inquiry |
Related articles
- Telithromycin---semisynthetic antibiotics
- Telithromycin (Keteks, Sanofi-Aventis) is the first marketed member of a new class of semisynthetic antibiotics, the ketolides....
- Mar 16,2022
191114-48-4(Telithromycin)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




