Potassium oxide
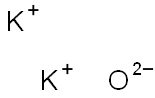
- CAS No.
- 12136-45-7
- Chemical Name:
- Potassium oxide
- Synonyms
- dipotassium oxide;Potassium monoxide;Kaliumoxid;POTASSIUM OXIDE;Oxybispotassium;Potassium oxide (K2O)
- CBNumber:
- CB1851546
- Molecular Formula:
- K2O
- Molecular Weight:
- 94.196
- MOL File:
- 12136-45-7.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2024/8/28 13:53:21
| Melting point | decomposes at 350℃ [HAW93] | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boiling point | 691.46℃[at 101 325 Pa] | ||||||||||||||
| Density | 2.350 | ||||||||||||||
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ | ||||||||||||||
| solubility | soluble in H2O, ethanol, ethyl ether | ||||||||||||||
| form | gray cubic crystals | ||||||||||||||
| color | gray cubic crystals, crystalline | ||||||||||||||
| Water Solubility | soluble H2O, forming KOH; soluble alcohol and ether [HAW93] | ||||||||||||||
| Crystal Structure | Reverse CaF2 type | ||||||||||||||
| crystal system | Cube | ||||||||||||||
| Space group | Fm3m | ||||||||||||||
| Lattice constant |
|
||||||||||||||
| LogP | -5.08 at 25℃ | ||||||||||||||
| CAS DataBase Reference | 12136-45-7 | ||||||||||||||
| EPA Substance Registry System | Potassium oxide (12136-45-7) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS05 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H314 |
| Precautionary statements | P260-P264-P280-P301+P330+P331-P303+P361+P353-P363-P304+P340-P310-P321-P305+P351+P338-P405-P501 |
| RIDADR | 2033 |
| HazardClass | 8 |
| PackingGroup | II |
Potassium oxide Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
gray crystal(s) mass; hygroscopic [CRC10] [HAW93]
Uses
Potassium oxide is a strong alkaline flux which is similar to sodium oxide but is slightly less strong and it begins its fluxing action earlier than does sodium oxide, at approximately 1382°F (750°C). It's a predictable, stable flux that produces bright glossy glazes, but it can't be used alone as a flux. Potassium produces slightly stronger glaze surfaces than does sodium oxide. Its low viscosity and surface tension create fluid glaze melts, but its high coefficient of expansion and contraction may cause crazing.
As mentioned above, potassium oxide is often found combined with sodium oxide, so it's often written as KNaO. lt's only slightly volatile at ceramic temperatures and is just slightly soluble.Usually used in its insoluble forms as feldspars or slightly soluble frits, potassium oxide can also be introduced to the glaze recipe as soluble pearl ash (potassium carbonate), which can cause some flashing like sodium carbonate.
Insoluble sources of potassium oxide are potash feldspars such as Custer, G-200, K-200, A-3, Kona F-4(Del Monte), Cornwall stone, Plastic Vitrox, volcanic ash, Kona A-1, Bell, Eureka, A-300, and mica. All soda feldspars have some potassium oxide; frits P-25, 3110, and 3124 contain minor amounts. Soluble forms of potassium oxide include pearl ash(K2CO3), potassium nitrate (saltpeter), and unwashed wood ash.
Definition
ChEBI: A metal oxide with formula K2O.
General Description
A white-colored crystalline solid. Denser than water. Contact may severely irritate skin, eyes and mucous membranes. May be toxic by ingestion, inhalation and skin absorption. Used to make other chemicals.
Air & Water Reactions
Soluble in water. The oxides of potassium react with water vigorously and with enough evolution of heat to cause boiling and spattering of hot caustic solution, [Chemical Safety Data Sheets SD-9, SD-10. 1947]. Reacts with warm water with violent explosion [Thorpe and Tlitton J. Chem. Soc. 59:1019: 1891].
Reactivity Profile
The higher oxides of potassium, formed in air, react explosively with pure potassium, sodium, sodium-potassium alloys, and organic matter [Mellor 2, Supp. 3:1559. 1963].
Health Hazard
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
Non-combustible, substance itself does not burn but may decompose upon heating to produce corrosive and/or toxic fumes. Some are oxidizers and may ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated.
Potassium oxide Preparation Products And Raw materials
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 | China | 21667 | 55 | Inquiry |
| Shaanxi Didu New Materials Co. Ltd | +86-89586680 +86-13289823923 | China | 8673 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Camida | +353-52-25455 | Europe | 3711 | 71 | Inquiry |
| Honeywell Specialty Chemicals Seelze GmbH | 973 455 2000 | United States | 639 | 87 | Inquiry |
| Chevron Phillips Chemicals, S.A. de C.V. | (832)813-4100 | United States | 145 | 81 | Inquiry |
| Hummel Croton Inc. | (908)754-1800 | Canada | 115 | 64 | Inquiry |
| Structure Probe, Inc. | 1-(800)-2424-SPI | United States | 269 | 82 | Inquiry |
| SKC Inc. | 724-941-9701 | United States | 1379 | 76 | Inquiry |
| Yixing Tianpeng Fine Chemical Co.,Ltd. | 0510-83128653 | China | 194 | 51 | Inquiry |
| HONEST JOY HOLDINGS LIMITED | +86-755-26404303 | United States | 6702 | 54 | Inquiry |
Related articles
- Is k2o ionic or covalent?
- Potassium oxide(K2O)also called Potassium Monoxide, Di-potassium Hydroxide, and Kalium Oxide, is an ionic compound formed by c....
- Mar 15,2024
12136-45-7(Potassium oxide)Related Search:
1of3
chevron_right




