Potassium superoxide
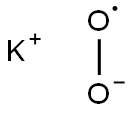
- CAS No.
- 12030-88-5
- Chemical Name:
- Potassium superoxide
- Synonyms
- POTASSIUM DIOXIDE;PotassiuM dioxide powder;K(O2);burntpotash;cacinedpotash;Kaliumperoxid;dipotassium peroxide;potassium hyperoxide;POTASSIUM SUPEROXIDE;Potassium oxide super
- CBNumber:
- CB7247558
- Molecular Formula:
- KO2*
- Molecular Weight:
- 71.1
- MOL File:
- 12030-88-5.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2025/1/27 9:38:02
| Melting point | 400 °C |
|---|---|
| Density | 2,14 g/cm3 |
| storage temp. | Store at +15°C to +25°C. |
| solubility | Soluble in ethanol and ether. |
| form | powder |
| color | Yellow-green |
| Specific Gravity | 2.14 |
| PH | >7 (H2O, 20℃) |
| Water Solubility | reacts |
| Sensitive | Air & Moisture Sensitive |
| Stability | Stable, but reacts violently with water. Incompatible with moisture, alcohols, strong reducing agents, strong acids, finely powdered metals. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 12030-88-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Potassium superoxide(12030-88-5) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Potassium superoxide (K(O2)) (12030-88-5) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS03,GHS05 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H271-H314 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P220-P280-P305+P351+P338-P310 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | O,C | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 8-14-34-35 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 17-27-36/37/39-8-45-26 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 2466 5.1/PG 1 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | TT6053000 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 5.1 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | I | |||||||||
| HS Code | 28259080 | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Potassium superoxide price More Price(2)
Potassium superoxide Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
light yellow powder or chunks
Uses
Reagent and intermediate.
One use of potassium superoxide,KO2, is for generating oxygen. It has the ability to absorb carbon dioxide, while giving out oxygen at the same time:
4KO2(s)+ 2CO2(g)--->2K2CO3(s)+ 3O2(g)
This property has been made use of in breathing equipment,e.g.for mountaineers, in submarines and in spacecraft.
General Description
A yellowish to white solid. Melting point 948°F. Mixtures with combustible material readily ignite by friction, heat, or contact with moisture. Prolonged exposure to fire or heat may cause vigorous decomposition of the material and rupturing of the container.
Air & Water Reactions
Reacts explosively with water [Mellor 2, Supp. 3: 1631. 1963].
Reactivity Profile
Potassium superoxide is a powerful oxidizer. Forms on the surface of potassium metal, solid or molten, that is exposed to the air. Attempts to extinguish burning potassium with powdered graphite has resulted in violent explosions [Chem. Abstr. 63:424. 1965]. Highly oxidized potassium metal was dropped into a dish of ethyl alcohol, an immediate explosion shattered the dish. Potassium superoxide was considered the cause of the reaction [Health and Safety Inf. 251. 1967]. Potassium superoxide should not be added to pure organic materials (hydrocarbons), as ignition and violent explosion may occur. Oxidation of arsenic, antimony, copper, potassium, tin, or zinc proceeds with incandescence, [Mellor, 1941, Vol. 2, 493]. Interaction between the superoxide and diselenium dichloride is violent, [Mellor, 1947, Vol. 10, 897].
Hazard
Corrosive to tissue.
Health Hazard
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or contact (skin, eyes) with vapors, dusts or substance may cause severe injury, burns or death. Fire may produce irritating and/or toxic gases. Toxic fumes or dust may accumulate in confined areas (basement, tanks, hopper/tank cars, etc.). Runoff from fire control or dilution water may cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
May explode from friction, heat or contamination. These substances will accelerate burning when involved in a fire. May ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). Some will react explosively with hydrocarbons (fuels). Containers may explode when heated. Runoff may create fire or explosion hazard.
Safety Profile
Explosive reaction when heated with carbon, 2-aminophenol + tetrahydrofuran (at 65°C). Forms a friction- sensitive explosive mixture with hydrocarbons. Violent reaction with lselenium dichloride, ethanol, potassium- sodium alloy. May ignite on contact with organic compounds. Incandescent reaction with metals (e.g., arsenic, antimony, copper, potassium, tin, and zinc). When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of K2O. See also PEROXIDES.
Potassium superoxide Preparation Products And Raw materials
12030-88-5(Potassium superoxide )Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




