Hexane
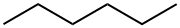
- CAS No.
- 110-54-3
- Chemical Name:
- Hexane
- Synonyms
- n-Hexane;HEXANES;1-HEXANE;n-Hexan;dipropyl;NAPHTHA SOLVENT;ISOHEXANES;n-Hexane, HPLC, 95.0% min.;OXFORD;HEXANES HPLC
- CBNumber:
- CB1852811
- Molecular Formula:
- C6H14
- Molecular Weight:
- 86.18
- MOL File:
- 110-54-3.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/7/2 14:09:54
| Melting point | -95 °C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 68.95 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.659 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 3.5 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 40 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index |
n |
| Flash point | 30 °F |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | Very soluble in ethanol, ethyl ether and chloroform. |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | >14 (Schwarzenbach et al., 1993) |
| color | Colorless |
| Specific Gravity | 0.660 (20/4℃) |
| Odor | Mild gasoline-like odor detectable at 65 to 248 ppm |
| Relative polarity | 0.009 |
| explosive limit | 1.0-8.1%(V) |
| Odor Threshold | 1.5ppm |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
| λmax |
λ: 200 nm Amax: ≤0.70 λ: 225 nm Amax: ≤0.10 λ: 250 nm Amax: ≤0.01 |
| Merck | 14,4694 |
| BRN | 1730733 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 0.238, 0.413, 0.883, 0.768, and 1.56 at 10, 15, 20, 25, and 30 °C, respectively (EPICS, Ashworth et al., 1988) |
| Dielectric constant | 2.0(-90℃) |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 50 ppm (~175 mg/m3) (ACGIH), 500 ppm (~1750 mg/m3) (OSHA); IDLH 5000 ppm (NIOSH). |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with oxidizing agents, chlorine, fluorine, magnesium perchlorate. Highly flammable. Readily forms explosive mixtures with air. Note low flash point. |
| InChIKey | VLKZOEOYAKHREP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | 4 at 20℃ and pH7 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 110-54-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Hexane(110-54-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Hexane (110-54-3) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |     GHS02,GHS07,GHS08,GHS09 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H225-H304-H315-H336-H361f-H373-H411 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P201-P210-P273-P301+P310-P303+P361+P353-P331 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | F,Xn,N | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 11-38-50/53-65-67-62-51/53-48/20-36/37/38 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 9-16-29-33-60-61-62-36/37-45-36/37/39-53-26 | |||||||||
| OEB | A | |||||||||
| OEL | TWA: 50 ppm (180 mg/m3) | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 3295 3/PG 2 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | MN9275000 | |||||||||
| F | 3-10 | |||||||||
| Autoignition Temperature | 225 °C | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 3 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | II | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29011000 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LC50 (4 hr) in mice by inhalation: 48000 ppm; LD50 orally in rats: 32.0 g/kg (Couri, Milks) | |||||||||
| IDLA | 1,100 ppm [10% LEL] | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Hexane price More Price(81)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | RTC000084 | Hexane Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material | 110-54-3 | 20ML | ₹11723.78 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | PHR1555 | Hexane Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material | 110-54-3 | 3X1.2ML | ₹8661.83 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 650552 | Hexane HPLC Plus, for HPLC, GC, and residue analysis, ≥95% | 110-54-3 | 1L | ₹9668.78 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 52750 | Hexane analytical standard | 110-54-3 | 10ML | ₹20385.6 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 52750 | Hexane analytical standard | 110-54-3 | 50ML | ₹38695.65 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Hexane Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
n-Hexane is a highly flammable liquid, usually isolated from crude oil, and has extensive industrial applications as a solvent in adhesive bandage factories and other industries.

It is highly toxic, triggering several adverse health effects, i.e., nausea, skin irritation, dizziness, numbness of limbs, CNS depression, vertigo, and respiratory tract irritation to animals and humans. Occupational exposure of industrial workers has demonstrated motor polyneuropathy. Workers associated with long-term glue sniffi ng showed adverse effects in the form of degeneration of axons and nerve terminals.
Physical properties
Clear, colorless, very flammable liquid with a faint, gasoline-like odor. An odor threshold concentration of 1.5 ppmv was reported by Nagata and Takeuchi (1990).
Uses
n-Hexane is a chief constituent of petroleumether, gasoline, and rubber solvent. It is usedas a solvent for adhesives, vegetable oils,and in organic analysis, and for denaturingalcohol.
Definition
ChEBI: An unbranched alkane containing six carbon atoms.
General Description
Clear colorless liquids with a petroleum-like odor. Flash points -9°F. Less dense than water and insoluble in water. Vapors heavier than air. Used as a solvent, paint thinner, and chemical reaction medium.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
HEXANE may be sensitive to light. Hexane may also be sensitive to prolonged exposure to heat. Hexane can react vigorously with oxidizing materials. This would include compounds such as liquid chlorine, concentrated O2, sodium hypochlorite and calcium hypochlorite. Hexane is also incompatible with dinitrogen tetraoxide. Hexane will attack some forms of plastics, rubber and coatings. .
Hazard
Flammable, dangerous fire risk.
Health Hazard
n-Hexane is a respiratory tract irritant andat high concentrations a narcotic. Its acutetoxicity is greater than that of n-pentane.Exposure to a concentration of 40,000 ppmfor an hour caused convulsions and death inmice. In humans a 10-minute exposure toabout 5000 ppm may produce hallucination,distorted vision, headache, dizziness, nausea,and irritation of eyes and throat. Chronicexposure to n-hexane may cause polyneuritis.
The metabolites of n-hexane injected inguinea pigs were reported as 2,5- hexanedioneand 5-hydroxy-2-hexanone, which arealso metabolites of methyl butyl ketone(DiVincenzo et al. 1976). Thus methyl butylketone and n- hexane should have similartoxicities. The neurotoxic metabolite, 2,5-hexanedione, however, is produced considerablyless in n-hexane. However, in the caseof hexane, the neurotoxic metabolite 2,5-hexanedione is produced to a much lesserextent. Continuous exposure to 250 ppmn-hexane produced neurotoxic effects in animals. Occupational exposure to 500 ppmmay cause polyneuropathy (ACGIH 1986).
Inhalation of n-hexane vapors have shownreproductive effects in rats and mice.
Flammability and Explosibility
Hexane is extremely flammable (NFPA rating = 3), and its vapor can travel a
considerable distance to an ignition source and "flash back." Hexane vapor forms
explosive mixtures with air at concentrations of 1.1 to 7.5 % (by volume).
Hydrocarbons of significantly higher molecular weight have correspondingly higher
vapor pressures and therefore present a reduced flammability hazard. Carbon
dioxide or dry chemical extinguishers should be used for hexane fires.
Chemical Reactivity
Reactivity with Water: No reaction; Reactivity with Common Materials: No reactions; Stability During Transport: Stable; Neutralizing Agents for Acids and Caustics: Not pertinent; Polymerization: Not pertinent; Inhibitor of Polymerization: Not pertinent.
Potential Exposure
n-Hexane is industrial chemical, emul sifier, in manufacture of plastics, resins; as a solvent, par ticularly in the extraction of edible fats and oils; as a laboratory reagent; and as the liquid in low temperature thermometers. Technical and commercial grades consist of 45 85% hexane, as well as cyclopentanes, isohexane, and 1% to 6% benzene.
Carcinogenicity
Male rabbits exposed to 3000 ppm hexane (8 h/day, 6 days/week for 24 weeks) developed papillary proliferation of nonciliated bronchiolar cells. No tumors were found in mice painted with hexane and croton oil as cocarcinogen, presumably for the lifetime of each animal. Hexane is inactive as a tumorpromoting agent.
Environmental Fate
Biological. Hexane may biodegrade in two ways. The first is the formation of hexyl hydroperoxide,
which decomposes to 1-hexanol followed by oxidation to hexanoic acid. The other
pathway involves dehydrogenation to 1-hexene, which may react with water giving 1-hexanol
(Dugan, 1972). Microorganisms can oxidize alkanes under aerobic conditions (Singer and
Finnerty, 1984). The most common degradative pathway involves the oxidation of the terminal
methyl group forming 1-hexanol. The alcohol may undergo a series of dehydrogenation steps
forming a hexanal followed by oxidation to form hexanoic acid. The fatty acid may then be
metabolized by β-oxidation to form the mineralization products, carbon dioxide and water (Singer
and Finnerty, 1984).
Photolytic. An aqueous solution irradiated by UV light at 50 °C for 1 d resulted in a 50.51%
yield of carbon dioxide (Knoevenagel and Himmelreich, 1976). Synthetic air containing gaseous
nitrous acid and exposed to artificial sunlight (λ = 300–450 nm) photooxidized hexane into two
isomers of hexyl nitrate and peroxyacetal nitrate (Cox et al., 1980).
Chemical/Physical. Complete combustion in air yields carbon dioxide and water vapor.
storage
hexane should be used only in areas free of ignition sources, and quantities greater than 1 liter should be stored in tightly sealed metal containers in areas separate from oxidizers.
Shipping
UN1208 Hexanes, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3-Flammable liquid.
Purification Methods
Purify as for n-heptane. Modifications include the use of chlorosulfonic acid or 35% fuming H2SO4 instead of conc H2SO4 in washing the alkane, and final drying and distilling from sodium hydride. Unsaturated impurities can be removed by shaking the hexane with nitrating acid (58% H2SO4, 25% conc HNO3, 17% water, or 50% HNO3, 50% H2SO4), then washing the hydrocarbon layer with conc H2SO4, followed by H2O, drying, and distilling over sodium or n-butyl lithium. It can also be purified by distillation under nitrogen from sodium benzophenone ketyl solubilised with tetraglyme. Also purify it by passage through a silica gel column followed by distillation [Kajii et al. J Phys Chem 91 2791 1987]. It is a FLAMMABLE liquid and a possible nerve toxin. [Beilstein 1 IV 338.] Rapid purification: Distil, discarding the first forerun and stored over 4A molecular sieves.
Incompatibilities
May form explosive mixture with air. Contact with strong oxidizers may cause fire and explo sions. Contact with dinitrogen tetraoxide may explode @ 28℃.Attacks some plastics, rubber and coatings. May accumulate static electrical charges, and may cause ignition of its vapors.
Waste Disposal
Dissolve or mix the material with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinera tor equipped with an afterburner and scrubber. All federal, state, and local environmental regulations must be observed.
Hexane Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
1of8
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLR Innovations | +91 9891111994 | New Delhi, India | 4542 | 58 | Inquiry |
| ANJI BIOSCIENCES | +91-9000100077 +91-9000100077 | Hyderabad, India | 430 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Choice Chemicals | +91-9895031268 +91-9895031268 | Kerela, India | 118 | 58 | Inquiry |
| JSK Chemicals | +919879767970 | Gujarat, India | 3756 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Chemino Pharma Ltd | +91-8689897373 +91-8689897373 | Maharashtra, India | 31 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Merck Ltd | +91-2262109800 +91-2262109000 | Maharashtra, India | 272 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Bharat Petroleum Corporation Limited | +91-22714000 +91-2222713000 | Maharashtra, India | 17 | 58 | Inquiry |
| DeFINE CHEMICALS | +91-8010769889 +91-9320057099 | Maharashtra, India | 120 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Ridhdhi Sidhdhi Chemicals | +91 9909006960 +91 9909006962 | Gujarat, India | 13 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Expresolv Limited | +91-787495635 +91-7069552255 | Gujarat, India | 49 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| GLR Innovations | 58 |
| ANJI BIOSCIENCES | 58 |
| Choice Chemicals | 58 |
| JSK Chemicals | 58 |
| Chemino Pharma Ltd | 58 |
| Merck Ltd | 58 |
| Bharat Petroleum Corporation Limited | 58 |
| DeFINE CHEMICALS | 58 |
| Ridhdhi Sidhdhi Chemicals | 58 |
| Expresolv Limited | 58 |
Related articles
- Applications of hexane as a non-polar solvent
- Hexane is undoubtedly the most widely used among the solvents used industrially for extracting non-polar edible natural produc....
- Dec 20,2023
- Hexane: Preparation, Uses and Toxicities
- Hexane is an organic compound, a straight-chain alkane with six carbon atoms with the molecular formula C6H14.
- Apr 13,2023
- Hexane-Hazard and Toxicity
- n-Hexane is a highly flammable liquid, usually isolated from crude oil, and has extensive industrial applications as a solvent....
- Sep 6,2019
110-54-3(Hexane)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




