MERCURIC NITRATE
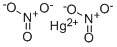
- CAS No.
- 10045-94-0
- Chemical Name:
- MERCURIC NITRATE
- Synonyms
- HG(NO3)2;mercuric;mercurynitrate;citrineointment;MERCURIC NITRATE;mercurydinitrate;nitratemercurique;mercury(2+)nitrate;MERCURIC(II)NITRATE;MERCURY(II) NITRATE
- CBNumber:
- CB3315107
- Molecular Formula:
- HgN2O6
- Molecular Weight:
- 324.6
- MOL File:
- 10045-94-0.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2024/3/14 15:18:26
| Melting point | 79°C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | decomposes [CRC10] |
| Density | 1.025 g/mL at 25 °C |
| solubility | soluble in H2O; insoluble in ethanol |
| form | colorless hygroscopic crystals |
| color | colorless hygroscopic crystals, crystalline |
| Water Solubility | soluble H2O; insoluble EtOH [CRC10] |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong reducing agents, combustible materials, most common metals. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 10045-94-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Mercuric nitrate (10045-94-0) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |     GHS03,GHS08,GHS09,GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H410-H272-H373-H300+H310+H330 |
| Precautionary statements | P210-P220-P221P280-P370+P378-P501-P260-P314-P501-P273-P391-P501 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Statements | 8-23/24/25-33-34 |
| Safety Statements | 36/37 |
| RIDADR | UN 3264 8/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HazardClass | 6.1(a) |
| PackingGroup | II |
MERCURIC NITRATE Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
Mercuric nitrate is a white to yellowish crystalline solid with an odor like nitric acid. Normally exists as the hemihydrate or the dihydrate
Uses
Nitration of aromatic organic compounds, felt manufacture, mercury fulminate manufacturing.
General Description
A white crystalline solid. Toxic by inhalation, ingestion and/or skin contact. Prolonged exposure to fire or heat may result in an explosion. Produces toxic oxides of nitrogen when heated to decomposition. Used to make other chemicals and in medicine.
Air & Water Reactions
Deliquescent. Soluble in a small amount of water. With much water or on boiling with water, an insoluble basic salt is formed.
Reactivity Profile
MERCURIC NITRATE is noncombustible, but, as an oxidizing agent, will accelerate the burning of combustible materials. If large quantities are involved in a fire or the combustible material is finely divided, an explosion may result. Light sensitive. Mixtures with alkyl esters may explode, owing to the formation of alkyl nitrates. Mixtures with phosphorus, tin(II) chloride, or other reducing agents may react explosively [Bretherick 1979. p. 108-109]. Acetylene forms a sensitive acetylide when passed into an aqueous solution of MERCURIC NITRATE [Mellor 4:933. 1946-47]. Should not be mixed with alcohols as explosive mercury fulminates may be formed [Bahme 1961. p. 9]. Is violently reduced by hypophosphoric acid [Mellor 4:993. 1946-47]. Reacts with phosphine to give a yellow precipitate that explodes when heated or subjected to shock [Mellor 4:993. 1946-47].
Hazard
Dangerous fire risk in contact with organic materials. Very toxic.
Health Hazard
Acute systemic poisoning may be fatal within a few minutes; death by uremic poisoning is usually delayed 5-12 days. Acute poisoning has resulted from inhaling dust concentrations of 1.2-8.5 mg/m 3 of air; symptoms inc lude tightness and pain in chest, coughing, and difficulty in breathing. Ingestion causes necrosis, pain, vomiting, and severe purging. Contact with eyes causes ulceration of conjunctiva and cornea. Contact with skin causes irritation and po ssible dermatitis; systemic poisoning can occur by absorption through skin.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, skin contact, intraperitoneal, and subcutaneous routes. A powerful oxidizer. Probably an eye, skin, and mucous membrane irritant. Reacts with acetylene to form the explosive mercury acetylide whch is sensitive to heat, friction, or contact with sulfuric acid. Reaction with ethanol forms the explosive mercury fulrmnate. Reaction with isobutene forms an unstable explosive product. Forms explosive mixtures with phosphine (heatand impact-sensitive), potassium cyanide (heat-sensitive), and sulfur. Violent reaction with phosphinic acid, hypophosphoric acid, unsaturated hydrocarbons, aromatics. Vigorous reaction with petroleum hydrocarbons. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of Hg and NOx. See also MERCURY COMPOUNDS, INORGANIC; and NITRATES.
Potential Exposure
Mercuric nitrate is used in making other chemicals; in felt manufacture and in making mercury fulminate
Shipping
UN1625 Mercuric nitrate, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Incompatibilities
A strong oxidizer. Reacts violently with combustibles, petroleum hydrocarbons; reducing agents; aldehydes, ammonia, ketones, phosphorus. Reacts with acetylene, alcohol, phosphine, and sulfur to form shocksensitive compounds. Aqueous solution attacks most metals. Vigorous and dangerous reaction with petroleum hydrocarbons. Incompatible with organic materials; acetylene, ethanol, phosphine, sulfur, hypophosphoric acid. Inorganic mercury compounds are incompatible with acetylene, ammonia, chlorine dioxide; azides, calcium (amalgam formation), sodium carbide; lithium, rubidium, copper. Decomposes in heat or on exposure to light, producing toxic fumes (mercury, nitrogen oxides)
MERCURIC NITRATE Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
10045-94-0(MERCURIC NITRATE)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




