Ethambutol
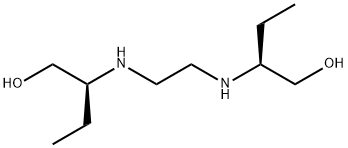
- CAS No.
- 74-55-5
- Chemical Name:
- Ethambutol
- Synonyms
- emb;C06984;tibutol;MGC71745;diambutol;Etambutol;ETHAMBUTOL;d-ethambutol;Ethambutolum;Aethambutolum
- CBNumber:
- CB3324345
- Molecular Formula:
- C10H24N2O2
- Molecular Weight:
- 204.31
- MOL File:
- 74-55-5.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/7/2 8:55:06
| Melting point | 199-204℃ |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 345℃ |
| alpha | D25 +13.7° (c = 2 in water) |
| Density | 1.0048 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4610 (estimate) |
| RTECS | EL3640000 |
| Flash point | >110°(230°F) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO |
| form | Powder |
| pka | pKa 6.6 (H2O) (Uncertain);9.5(H3O) (Uncertain) |
| color | White to off-white |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water. Also soluble in chloroform and methylene chloride |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H302 |
| Precautionary statements | P264-P270-P301+P312a-P330-P501a |
| Toxicity | LD50 oral in rat: 998mg/kg |
Ethambutol Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Uses
Ethambutol is an antitubercular antibiotic.
Indications
Ethambutol is a water-soluble, heat-stable compound that acts by inhibition of arabinosyl transferase enzymes that are involved in cell wall biosynthesis. Nearly all strains of M. tuberculosis and M. kansasii and most strains of Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare are sensitive to ethambutol. Drug resistance relates to point mutations in the gene (EmbB) that encodes the arabinosyl transferases that are involved in mycobacterial cell wall synthesis.
Definition
ChEBI: An ethylenediamine derivative that is ethane-1,2-diamine in which one hydrogen attached to each of the nitrogens is sutstituted by a 1-hydroxybutan-2-yl group (S,S-configuration). It is a bacteriostatic antimycobacterial d ug, effective against Mycobacterium tuberculosis and some other mycobacteria. It is used (as the dihydrochloride salt) in combination with other antituberculous drugs in the treatment of pulmonary and extrapulmonary tuberculosis; resistant str ins of M. tuberculosis are readily produced if ethambutol is used alone.
Antimicrobial activity
Ethambutol is active against several species of mycobacteria
and nocardiae. MICs on solid media are: M. tuberculosis
0.5–2 mg/L; M. kansasii 1–4 mg/L; other slowly growing
mycobacteria 2–8 mg/L; rapidly growing pathogens 2–16
mg/L; Nocardia spp. 8–32 mg/L.
Resistance is uncommon and is a multistep process due to
mutations in the embA, embB and embC gene cluster. A mutation
in codon 306 of the embB gene predisposes to the development
of resistance to a range of antituberculosis agents,
possibly by affecting cell-wall permeability.
Pharmaceutical Applications
A synthetic ethylenediamine derivative formulated as the dihydrochloride for oral administration. The dry powder is very soluble and stable.
Mechanism of action
The mechanism of action of EMB remains unknown, although mounting evidence suggests a specific site of action for EMB. It has been known for some time that EMB affects mycobacterial cell wall synthesis; however, the complicated nature of the mycobacterial cell wall has made pinpointing the site of action difficult. In addition to the peptidoglycan portion of the cell wall, the mycobacterium have a unique outer envelop consisting of arabinofuranose and galactose (AG), which is covalently attached to the peptidoglycan and an intercalated framework of lipoarabinomannan (LAM) . The AG portion of the cell wall is highly branched and contains distinct segments of galactan and distinct segments of arabinan. At various locations within the arabinan segments (terminal and penultimate), the mycolic acids are attached to the C-5′ position of arabinan. Initially, Takayama et al. reported that EMB inhibited the synthesis of the AG portion of the cell wall. More recently, it has been reported that EMB inhibits the enzymes arabinosyl transferase. One action of arabinosyl transferase is to catalyze the polymerization of D-arabinofuranose, leading to AG. Ethambutol mimics arabinan, resulting in a buildup of the arabinan precursor β-D-arabinofuranosyl- 1-monophosphoryldecaprenol and, as a result, a block of the synthesis of both AG and LAM. The mechanism of resistance to EMB involves a gene overexpression o
Pharmacology
Orally administered ethambutol is well absorbed (70–80%) from the gut, and peak serum concentrations are obtained within 2 to 4 hours of drug administration; it has a half-life of 3 to 4 hours. Ethambutol is widely distributed in all body fluids, including the cerebrospinal fluid, even in the absence of inflammation.A majority of the unchanged drug is excreted in the urine within 24 hours of ingestion. Up to 15% is excreted in the urine as an aldehyde and a dicarboxylic acid metabolite. Ethambutol doses may have to be modified in patients with renal failure.
Pharmacokinetics
Oral absorption: c. 80%, but some patients absorb it poorly
Cmax 25 mg/kg oral: 2–6 mg/L after 2–3 h
Plasma half-life: 10–15 h
Volume of distribution: >3 L/kg
Plasma protein binding: 20–30%
Absorption is impeded by aluminum hydroxide and alcohol.
It is concentrated in the phagolysosomes of alveolar macrophages.
It does not enter the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in
health but CSF levels of 25–40% of the plasma concentration,
with considerable variation between patients, are achieved in
cases of tuberculous meningitis.
Various metabolites are produced, including dialdehyde,
dicarboxylic acid and glucuronide derivatives. Around 50% is
excreted unchanged in the urine, with an additional 10–15%
as metabolites, and 20% is excreted unchanged in feces.
Clinical Use
Ethambutol has replaced aminosalicylic acid as a first-line antitubercular drug. It is commonly included as a fourth drug, along with isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and rifampin, in patients infected with MDR strains. It also is used in combination in the treatment of M. aviumintracellulare infection in AIDS patients.
Side effects
The major toxicity associated with ethambutol use is retrobulbar neuritis impairing visual acuity and redgreen color discrimination; this side effect is dose related and reverses slowly once the drug is discontinued. Mild GI intolerance, allergic reaction, fever, dizziness, and mental confusion are also possible. Hyperuricemia is associated with ethambutol use due to a decreased renal excretion of urates; gouty arthritis may result.
Ethambutol Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of2
chevron_rightPreparation Products
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | +91-22-45045900 | Hyderabad, India | 6351 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Triveni chemicals | 08048762458 | New Delhi, India | 6093 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Pharmaffiliates Analytics and Synthetics P. Ltd | +91-172-5066494 | Haryana, India | 6773 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Pharma Affiliates | 172-5066494 | Haryana, India | 6761 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Shaanxi TNJONE Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd | +8618740459177 | China | 1142 | 58 | Inquiry |
| .GZ HONESTCHEM CO.,LTD | +86-15013270415 | China | 246 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Xiamen AmoyChem Co., Ltd | +86-592-6051114 +8618959220845 | China | 6387 | 58 | Inquiry |
| career henan chemical co | +86-0371-86658258 +8613203830695 | China | 29826 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co.,Ltd. | 0551-65418671 | China | 34571 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Dideu Industries Group Limited | +86-29-89586680 +86-15129568250 | China | 26114 | 58 | Inquiry |
Related articles
- Side-effects of Ethambutol
- Ethambutol was discovered at Lederle Laboratories in 1961, when randomly selected synthetic compounds were being tested for an....
- Mar 25,2022
74-55-5(Ethambutol)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




